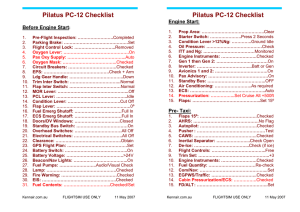
speed - Westminster College
advertisement
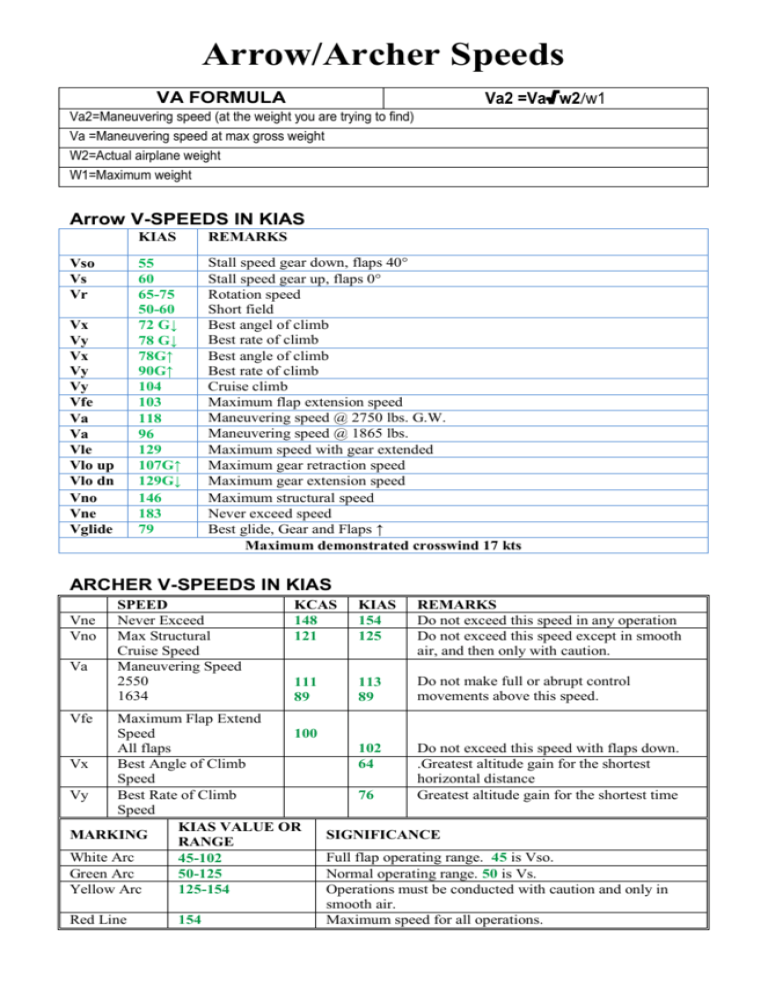
Arrow/Archer Speeds Va2 =Va√w2/w1 VA FORMULA Va2=Maneuvering speed (at the weight you are trying to find) Va =Maneuvering speed at max gross weight W2=Actual airplane weight W1=Maximum weight Arrow V-SPEEDS IN KIAS Vso Vs Vr Vx Vy Vx Vy Vy Vfe Va Va Vle Vlo up Vlo dn Vno Vne Vglide KIAS REMARKS 55 60 65-75 50-60 72 G↓ 78 G↓ 78G↑ 90G↑ 104 103 118 96 129 107G↑ 129G↓ 146 183 79 Stall speed gear down, flaps 40° Stall speed gear up, flaps 0° Rotation speed Short field Best angel of climb Best rate of climb Best angle of climb Best rate of climb Cruise climb Maximum flap extension speed Maneuvering speed @ 2750 lbs. G.W. Maneuvering speed @ 1865 lbs. Maximum speed with gear extended Maximum gear retraction speed Maximum gear extension speed Maximum structural speed Never exceed speed Best glide, Gear and Flaps ↑ Maximum demonstrated crosswind 17 kts ARCHER V-SPEEDS IN KIAS Vne Vno Va SPEED Never Exceed Max Structural Cruise Speed Maneuvering Speed 2550 1634 KCAS 148 121 KIAS 154 125 REMARKS Do not exceed this speed in any operation Do not exceed this speed except in smooth air, and then only with caution. 111 89 113 89 Do not make full or abrupt control movements above this speed. 102 64 Do not exceed this speed with flaps down. .Greatest altitude gain for the shortest horizontal distance Greatest altitude gain for the shortest time Vfe Maximum Flap Extend Speed 100 All flaps Vx Best Angle of Climb Speed Vy Best Rate of Climb Speed KIAS VALUE OR MARKING RANGE White Arc 45-102 Green Arc 50-125 Yellow Arc 125-154 Red Line 154 76 SIGNIFICANCE Full flap operating range. 45 is Vso. Normal operating range. 50 is Vs. Operations must be conducted with caution and only in smooth air. Maximum speed for all operations. HIGHER ARCHIE OF AIRSPEEDS A Indicated Airspeed (IAS) B Calibrated Airspeed (CAS) C True Airspeed (TAS) D Groundspeed (GS) Reading off of airspeed indicator. IAS does not reflect variations in air density as you climb to higher altitudes. IAS is also uncorrected for installation (position) and instrument errors. IAS corrected for installation and instrument errors. To determine calibrated airspeed, read indicated airspeed and then correct it by using the chart or table in the POH. True speed your plane travels through the air. Calibrated airspeed corrected for altitude and nonstandard temperature. For a given IAS, TAS increases with altitude. Actual speed of your airplane over the ground. True airspeed adjusted for wind. GS increases with tailwind, decreases with headwind. The pitot-static system provides impact, or ram, air pressure to the airspeed indictor. The speed of your airplane through the air is determined by comparing ram air pressure with static air pressure – the greater the differential, the greater the speed. If the pitot-tube becomes block and the drain hole remains clear, ram air no longer is able to enter the pitot system. Air already in the system will bent through the drain hole, and the remaining pressure will drop to ambient (outside) air pressure. Under these circumstances, the airspeed indicator reading decreases to zero, because the airspeed indicator senses no difference between ram and static air pressure. If the drain hole becomes blocked as well than the airspeed indicator acts like an altimeter. If the pitot tube, drain hole, and static system all become blocked in flight, changes in airspeed will not be indicated, due to the trapped pressures.