Midterm review
advertisement

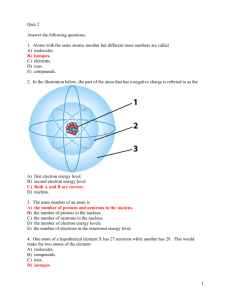
Earth Science Mid-Term Review The information below is a brief summary of the material covered by mid-term examination. Use this in combination with your notes, assignments and labs to ensure the best possible grade. For each chapter listed below, don’t forget to read the “Summaries” at the end of each chapter. Chapter 1 -- Studying Earth Science Independent variable Mass Dependant variable Density Control Hypothesis Volume Scientific method Know the steps to using the Scientific Method Know the 4 branches of Earth Science Be able to tell the SI (International Standard Unit) for mass, volume, and length Know how to use the formula for density Identify and use science skills Chapter 4 Earth Chemistry Matter Isotope Atom Molecule Ion Compound Element Mixture Understand the make-up of an atom (protons, electrons, & neutrons) Understand the relationship in isotopes and ions, and elements Chapter 5 -- Minerals Mineral Hardness Streak Color Luster Ore Cleavage Gem Fracture Crystal Know how to determine each of the mineral properties in a laboratory environment Be able to list the seven mineral groups, and identify which is the largest and smallest Memorize Moh’s Hardness Scale, and the hardness of everyday items like the ones we used in the mineral project Chapter 6 -- Rocks & the Rock Cycle Chemical Sedimentary rocks Extrusive (volcanic) Igneous rocks Clastic Sedimentary rocks Felsic / granitic Organic Sedimentary rocks Mafic / basaltic Contact Metamorphism Magma Regional Metamorphism Lava Intrusive (plutonic) Igneous rocks Be able to explain how chemical, organic, and clastic sedimentary rocks are made Understand the difference between foliated and nonfoliated metamorphic rocks Know what properties are visible in intrusive vs. extrusive igneous rocks Know the processes involved in the Rock Cycle Chapter 3 – Maps and Geography Landforms & Coastal Features Equator Hemisphere Map Projections Latitude (parallels) Scale Longitude (meridians) Topography Prime Meridian Contour line International Date Line Contour interval Know the 5 landforms and 6 coastal features Explain how latitude and longitude are used on maps Understand Mercator, Robinson and conic map projections and what each is used for Know how to determine the contour interval Chapter 16 – Ground Water Universal Solvent Porosity Evaporation Water table Condensation Aquifer Precipitation Zone of Saturation Groundwater Hot Spring Runoff Cave Tributary Know the processes involved in the Water Cycle Understand the differences between; permeable & impermeable artesian wells & natural wells springs & geysers Chapter 15 – Running Water Abrasion Erosion Discharge Oxbow lake Flash flood Levee Flood plain Meander Stream piracy Divide Hydrosphere Pot holes Water Cycle Understand how carrying power affects sediments being in solution, or suspension, or bed load (and percentages) Be able to explain the features found in a young, mature, or old stream Know the differences between deltas and alluvial fans Know how to conserve water