Cell Reproduction Unit
advertisement
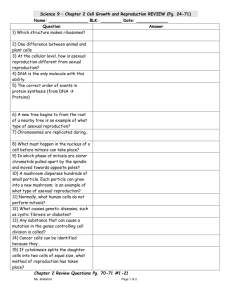
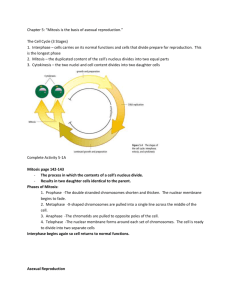
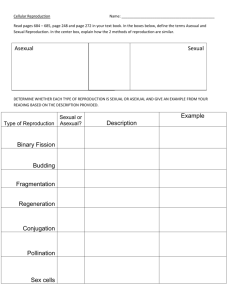
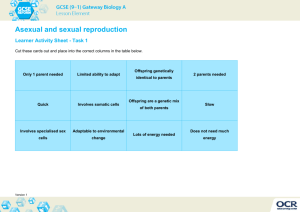
Cell Reproduction Unit Chromosome Structure - chromosome = a long continuous thread of DNA that consists of numerous genes with regulatory information coiled around proteins in compact structures - DNA wraps around proteins (called histones) to become compact Cell Cycle = the regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and cell division that occurs in cells - results in two cells (daughter cells) identical to one another - made up of 5 Phases 1) G1 Phase - cell grows in size (cell growth) Interphase 2) S Phase - makes a copy of its DNA (DNA is copied) 3) G2 Phase - cell prepares for cell division **G1, S, and G2 Phase collectively are called Interphase** 4) M Phase (Mitosis) - nucleus divides 5) C Phase (Cytokinesis) - cytoplasm divides Phases of Mitosis - discovered by Walther Flemming in 1882 - makes body cells (skin, blood, organs, etc) 1) Prophase - DNA coils to become chromosomes - nuclear membrane disappears - microtubules called spindle fibers grow from centrioles to center of cell 2) Metaphase - chromosomes line up in the center 3) Anaphase - chromosomes pull apart and move to opposite ends of cell 4) Telophase - chromosomes uncoil - nuclear membrane reforms Cytokinesis - cell membrane forms a cleavage furrow and cytoplasm divides - in plants, a cell plate forms between each cell Regulation of Cell Division - controlled by external and internal factors - External Factors 1) cell to cell contact 2) growth factors = group of proteins that stimulate cell division - most cells controlled by a combination of growth factors - Internal Factors - enzymes and proteins released by the cell ex) 1) kinases = enzymes that increase the energy to a cell 2) cyclins = proteins that control the cell cycle - apoptosis = programmed cell death Cancer = common name for a class of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell division - benign tumor = cancer cells typically remain clustered together - malignant tumor = some of the cancer cells can break away (metastasize) from the tumor - can form tumors in other parts of the body - why are tumors harmful? - use energy from the body but do nothing for the body - exert pressure on surrounding organs - carcinogens = substances known to produce or promote the development of cancer - treatment includes radiation and chemotherapy Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction - Asexual reproduction = reproduction of offspring from one parent - offspring are genetically identical to the parent….this is a BAD thing - Sexual reproduction = reproduction of offspring from two parents (egg and sperm = gametes) - offspring are genetically different from the parents ….this is a GOOD thing - Asexual reproduction is more efficient that sexual reproduction - Some eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis: plant cuttings, budding yeast, flatworms and sea stars can grow from pieces of original - some organisms can reproduce by asexual or sexual reproduction (depends on conditions)