Calcium Chloride Lab Instructions
advertisement

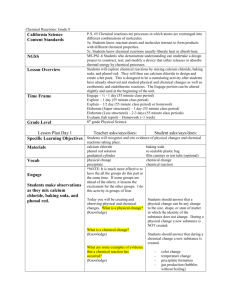
Adapted from April Aldott’s: Reaction in a Plastic Baggie http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/demos/reactioninbag2.htm Reaction in a Plastic Baggie Science Concept: This chemical reaction between two solids creates a new substance in the form of a gas that is observable by dramatically inflating the plastic baggie. Because 3rd grade students often miss observing the heat, they will do this reaction in two steps: First Ss mix the CaCl2 with water in order to observe the heat, then they add the baking soda and phenol red to make further observations. Safety Precautions: When handling the phenol red, use caution. If it contacts skin or clothing, it may stain. Additionally, be careful in letting the bag fill up with gas. If it gets too full, the bag might pop. Waste Disposal: Dispose of the plastic bag and its contents in the trash. Introduction & Commentary: How many of you like balloons? Do you like blowing them up? Sometimes that can make you kind of tired, though. I'm going to show you a way in which this plastic bag will fill up like a balloon, without having to blow air into it. Materials & Pre-Demo Preparation:Note to Teacher: It is highly recommended that teacher try out the chemical reaction before doing it in the classroom. Preparation: Prepare a tray with the following supplies for each group-Be sure everything is labeled! One quart-size ziplock baggie, goggles, plastic gloves, paper towels for clean up, one plastic medicine or small salsa cup, container for waste, plastic tablespoon labeled Calcium chloride and 3 plastic teaspoons (labeled “water”, “baking soda”, “ phenol red solution” In addition, the following supplies will be needed for each group for each investigation: Investigation 1: Calcium chloride -1 tablespoon Water bottle-students will need about 2 teaspoons Investigation 2: Baking soda- 2 teaspoons Phenol red solution-1 teaspoon or 5 ml (If only phenol red is available, a phenol red solution is made by adding four drops of phenol red to 10 ml of distilled water.) Directions for Investigation 1 (Produces Heat) 1. In the ziplock bag, place 1 tablespoon of calcium chloride into the baggie. Add 2 teaspoons of water into the baggie and seal. 2. Record your all your observations. Utilize all your senses to make your observations. (Teacher: Guide Ss to feel the bottom of the baggie if they are not doing so.) Directions for Investigation 2 (Produces Carbon Dioxide gas and a Color Change) 1. Measure 1 tsp of phenol red solution and pour into medicine cup. Carefully stand the medicine cup inside the baggie. Do not let the cup tip over. 2. Add 2 teaspoons of baking soda to the baggie and quickly seal the baggie (to prevent gas from escaping). 3. Now tip over the cup so that all substances mix. 4. Record your all your observations. Utilize all your senses to make your observations. (Teacher: Again, guide Ss to feel the bottom of the baggie! If baggie gets very big, teacher may open it or face it away from students.) Explanation and Background for Teacher Calcium chloride and baking soda (bicarbonate) react to form calcium carbonate, sodium chloride (salt), water, and carbon dioxide. To produce this reaction, calcium chloride and baking soda, which are both solid, are mixed together in water, which provides a solvent for the chemical reaction to occur. The two solids switch partners and form a new substance--the precipitate calcium carbonate. The calcium carbonate is a white solid precipitate that sinks to the bottom of the water. As the precipitate is formed, the bicarbonate breaks down first to make hydrogen ions, an acid. This acid then converts some of the bicarbonate to carbon dioxide gas which begins to blow up the plastic bag. It can also be observed as a fizzing or bubbling. The phenol red turns yellow when the CO2 produced dissolves in water to produce carbonic acid. The balanced chemical reaction is: 2 NaHCO3 + CaCl2 => CaCO3 + CO2 + 2 NaCl + H2O. Also, as part of the chemical reaction between these two solids, changes in temperature can be felt--an exothermic reaction causes the calcium chloride to get warm, while the endothermic reaction makes the baking soda get cold. For a relatively simple explanation, see: What Do Calcium Chloride & Baking Soda Make? | eHow.com http://www.ehow.com/how-does_5498056_do-amp-baking-sodamake.html#ixzz1uEDHM6n4 Additional Teacher Information Calcium chloride + baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) --- calcium carbonate + sodium chloride + hydrogen ions CaCl2 + 2 NaHCO3 ---> CaCO3 + 2 NaCl + H+ ions Hydrogen ions + sodium bicarbonate ---> carbon dioxide + water + sodium ions H+ ions + NaHCO3 ---> CO2 + H2O + Na+ A chemical reaction involves the breaking of bonds in the reactants and the making of bonds in the products. It takes energy to break bonds (endothermic; feels cold) and that energy is released when bonds are formed( exothermic; feels warm/hot). In an endothermic reaction, it takes more energy to break the bonds of the reactants than is released when the bonds in the products are formed. In an endothermic reaction, the temperature goes down. Additional Explanation: From: http://agpa.uakron.edu/p16/lesson.php?id=ziplock_chem&pg=procedures The solution gets warm because heat is given off when calcium chloride dissolves in water (not a chemical reaction). This process is exothermic. When sodium bicarbonate dissolves in water, heat is absorbed and the solution gets colder. This process is endothermic. The phenol red turns yellow when CO 2 produced dissolves in water to produce carbonic acid. Note: the addition of some solutes to a solvent will raise the temperature of a solution, while others will have no noticeable effect. This behavior depends on the heat of solution of the solute in a given solvent. The heat of solution, i.e., the amount of heat given off or absorbed during the process of solution, is equal to the difference between the energy that must be supplied to break up the crystals of the solute and the energy that is released when the solute particles are taken into solution by the solvent. If more energy is required to break up the crystals than is released in forming the solution, the temperature will decrease. If more energy is released in forming the solution than in breaking up the crystals, the temperature will increase. The following is for your information and may be too detailed for your students: The gas evolved is carbon dioxide. The bicarbonate ion (HCO 3-) is a weak acid and partially ionizes in solution: HCO3- ↔ H+ + CO32The calcium ion (Ca2+) from the calcium chloride reacts with the carbonate ion (CO 32-) to form insoluble calcium carbonate: Ca2+ + CO32- ↔ CaCO3 The hydrogen ions react with the bicarbonate ion to yield carbon dioxide: H+ + HCO3- ↔ H2O + CO2 The indicator changes colors because the carbon dioxide dissolves in water to produce an acidic solution. Phenol red is red in basic solutions and yellow in acidic solutions. CO2 + H2O ↔ H2CO3 ↔ H+ + HCO3-