Honors Chem Equilibrium q`s
advertisement
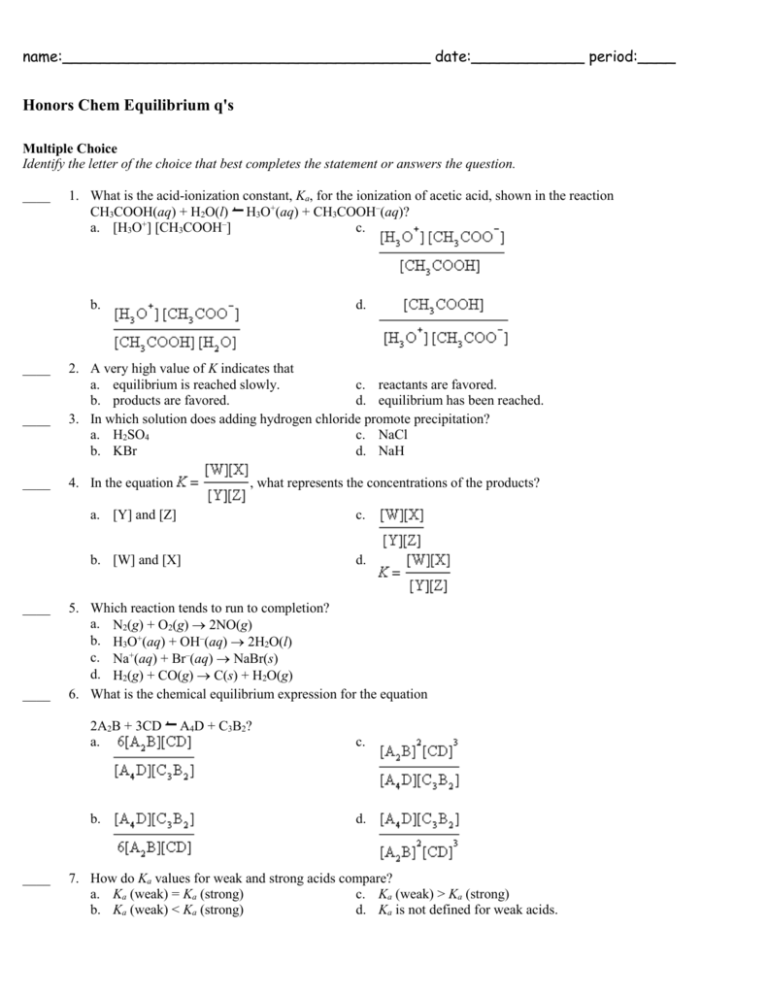
name:_______________________________________ date:____________ period:____ Honors Chem Equilibrium q's Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What is the acid-ionization constant, Ka, for the ionization of acetic acid, shown in the reaction CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + CH3COOH–(aq)? a. [H3O+] [CH3COOH–] c. b. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 2. A very high value of K indicates that a. equilibrium is reached slowly. c. reactants are favored. b. products are favored. d. equilibrium has been reached. 3. In which solution does adding hydrogen chloride promote precipitation? a. H2SO4 c. NaCl b. KBr d. NaH 4. In the equation , what represents the concentrations of the products? a. [Y] and [Z] c. b. [W] and [X] d. 5. Which reaction tends to run to completion? a. N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g) b. H3O+(aq) + OH–(aq) 2H2O(l) c. Na+(aq) + Br–(aq) NaBr(s) d. H2(g) + CO(g) C(s) + H2O(g) 6. What is the chemical equilibrium expression for the equation 2A2B + 3CD a. b. ____ d. A4D + C3B2? c. d. 7. How do Ka values for weak and strong acids compare? a. Ka (weak) = Ka (strong) c. Ka (weak) > Ka (strong) b. Ka (weak) < Ka (strong) d. Ka is not defined for weak acids. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 8. Which reaction tends to run to completion? a. N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) b. Na+(aq) + Cl–(aq) NaCl(s) c. 2CO(g) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) d. H2CO3(aq) H2O(l) + CO2(g) 9. The common-ion effect promotes a. dissolving. c. boiling. b. precipitation. d. ionization. 10. Which reaction tends to run to completion? a. K+(aq) + Cl–(aq) KCl(s) c. Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq) AgCl(s) b. 2NO2(g) N2O4(g) d. H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) 11. The equilibrium constant depends on changes in a. pressure. b. concentrations. c. temperature. d. pressure, concentrations, and temperature. 12. At equilibrium, a. the forward reaction rate is lower than the reverse reaction rate. b. the forward reaction rate is higher than the reverse reaction rate. c. the forward reaction rate is equal to the reverse reaction rate. d. no reactions take place. 13. If the temperature of the equilibrium system CH3OH(g) + 101 kJ CO(g) + 2H2(g) increases, K a. increases. c. increases or decreases. b. decreases. d. does not change. 14. How do coefficients from a chemical equilibrium appear when the chemical equilibrium expression is written? a. as coefficients c. as subscripts b. as exponents d. They do not appear. 15. A reaction in which products can react to re-form reactants is a. at equilibrium. c. buffered. b. reversible. d. impossible. 16. At equilibrium, a. all reactions have ceased. b. only the forward reaction continues. c. only the reverse reaction continues. d. both the forward and reverse reactions continue. 17. A value of K near 1 indicates that at equilibrium probably a. only products are present. b. only reactants are present. c. significant quantities of both products and reactants are present. d. the reactions occur at a moderate rate. 18. If the pressure on the equilibrium system 2CO(g) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) is increased, a. the quantity of CO(g) increases. b. the quantity of CO2(g) decreases. c. the quantity of CO2(g) increases. d. the quantities in the system do not change. 19. The value of K for a system a. can be calculated from the molar masses of products and reactants. b. can be calculated from the heats of the forward and reverse reactions. c. can be calculated from the chemical properties of products and reactants. d. must be measured by experiment. 20. What is the symbol for the ion-product constant for water? a. Kw c. K b. Ka d. Ksp ____ 21. At equilibrium, the total amount of the product(s) a. is always equal to the total amount of the reactants. b. is always greater than the total amount of the reactants. c. is always less than the total amount of the reactants. d. may be equal to, greater than, or less than the total amount of the reactants. ____ 22. Which two processes are at equilibrium in a saturated sugar solution? a. evaporation and condensation c. decomposition and synthesis b. dissolving and crystallization d. ionization and recombination ____ 23. Adding sodium acetate to an acetic acid, CH3COOH, solution a. increases pH and lowers [H+]. c. decreases pH and lowers [H+]. + b. increases pH and raises [H ]. d. decreases pH and raises [H+]. ____ 24. The pH of a solution is 9. What is its H3O+ concentration? a. 10–9 M c. 10–5 M –7 b. 10 M d. 9 M ____ 25. If the system 2CO(g) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) has come to equilibrium and then more CO(g) is added, a. [CO2] increases and [O2] decreases. c. [CO2] decreases and [O2] decreases. b. [CO2] increases and [O2] increases. d. both [CO2] and [O2] remain the same.