Geography Skills
advertisement

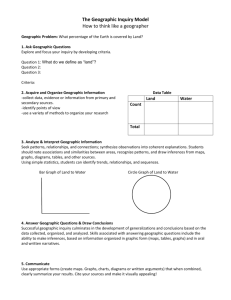
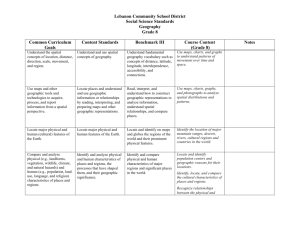
Geography Skills List Mapping Level 1 Level 2 For Level 1 and Level 2 from 2011, refer to the Teaching and Learning Guide for Geography, Ministry of Education at http://seniorsecondary.tki.org.nz. Précis Map Students will receive a drawn Students will receive a map with outline to work from some part of the outline drawn Level 3 Students will be required to locate aspects from a map Students will be required to locate aspects from an aerial photograph Students will be required to locate aspects from an oblique photo Students are presented with any topographical with full key Students are presented with more complex topographical without key Students should be able to read a basic key including scale Students should be able to read a more complex scale with representative fractions Students should be able to apply different scales through transfer Linear scale and measurement of straight line distance Students can calculate area Identification of key natural and cultural features Direction – read and find 8 points Direction – accuracy of bearings to 16 points Direction through the interpretation of data such from text or other sources Contour lines What are they? Identify different features using contour lines such as a hill and a valley Using contours to identify key features and determine difference between features such as a U shaped valley vs a V shaped valley Deductions are made from contour lines Simple cross-section drawn from map Cross-section drawn from map to demonstrate additional specific knowledge and skill Drawing a profile from a range of sources Locate and determine reference using 6 figures GR and degrees of longitude and latitude Locate and determine reference using degrees and minutes of longitude and latitude using 14 figure GR. Use of the GR is explicit Locate and determine reference using 14 figures GR and degrees of longitude and latitude. Use of the GR is implicit Students should be able to read and interpret a range of resources and apply them to the construction of maps such as Dot distribution maps Choropleth maps Proportional symbol Isoline maps Flow maps Students should be able to construct an appropriate statistical map from a range of resources Topographical Mapping Skills Students are presented with a New Zealand map with reduced key Other Maps Students should be able to read and interpret maps such as Dot distribution maps Choropleth maps Proportional symbol Isoline maps Flow maps Students will be expected to draw a précis map within a blank square Calculation of slope angles Visuals Level 1 Photographs Satellite Aerials – oblique and vertical Ordinary Level 2 Photographs Satellite Aerials – oblique and vertical Ordinary Level 3 Photographs Satellite Aerials – oblique and vertical Ordinary Photograph is related to map Direction is determined from a photograph Recognition and interpretation of detail, patterns and processes Student can identify key natural and cultural features using the photograph Student can locate an aerial photo on map Student can use an analysis of a photograph to support an argument and / or geographic idea Direction – read and find 8 compass points Student can calculate scale Student can use the photograph to develop a précis sketch Student can compare photos to explain geographic changes Student can recognise broad patterns Student can use the photograph to develop a précis sketch Student can evaluate the photo as a resource Students can compare and evaluate different types of photographs as a geographic resource Diagrams/models Student can read, and interpret relevant diagrams/models Diagrams/models Student can read, interpret and complete relevant diagrams/models Cartoons Student can identity and describe the characters, actions/events and symbolism in the cartoon Diagrams/models Student can read, interpret and construct and/or complete relevant diagrams/models Student can compare, evaluate and apply the diagrams/models to a real life situation Student can recognise and provide a detailed interpretation of patterns and processes Cartoons Student can explain the characters, actions/events and symbolism in the cartoon Student can provide an analysis of a diagram/model to support an argument/geographic idea Cartoons Student can provide an analysis of a cartoon to support an argument/geographic idea Valuing Skills - Opinions and perspectives Level 1 Student can identify and describe and explain a range of opinions or values Level 2 Student can identify and describe and explain a range of opinions or values Level 3 Student can identify and describe a range of opinions or values Resources would be simple such opinions for and against Resources would be more complex with a wider range of opinion Student needs to understand how aspects of the world are viewed from a range of perspectives Students would need to justify their own opinion Students would need to justify their own opinion Graphing Level 1 Students should be able to read and interpret and construct the following graphs Column/bar Histogram Line Pictograph Pie Percentage bar Scatter Climate Age/sex pyramid Positive/negative graph Level 2 Students should be able to construct, read and interpret the following graphs Triangular Scatter Positive/negative graph Compound graphs Level 3 Students should be able to construct read and interpret graphs which may include the following Multi-axis Positive/negative graph Multi-line graph using two scales Select the most appropriate for the context Statistical Level 1 Students show an understanding of the following Percentages Percentage change Mean Median Range Mode Data presentation Level 2 Students show an understanding of the following Percentages Percentage change Mean Median Range Mode Data presentation Level 3 Students show an understanding of how to use statistical information to determine patterns and to support an argument Use statistical information to make comparisons in a geographic context. Geographic Ideas Level 1 Student can provide a description of a GI within a directed geographic context. Level 2 Student can provide an explanation of a GI within a geographic context Level 3 Student select and then apply a GI in relation to a geographic context Students are provided with specific direction on how to apply a stated GI within a defined context Students are expected to apply a stated GI within a defined context Students are expected to select and apply a relevant GI within a defined context