Proteins and Enzymes
advertisement
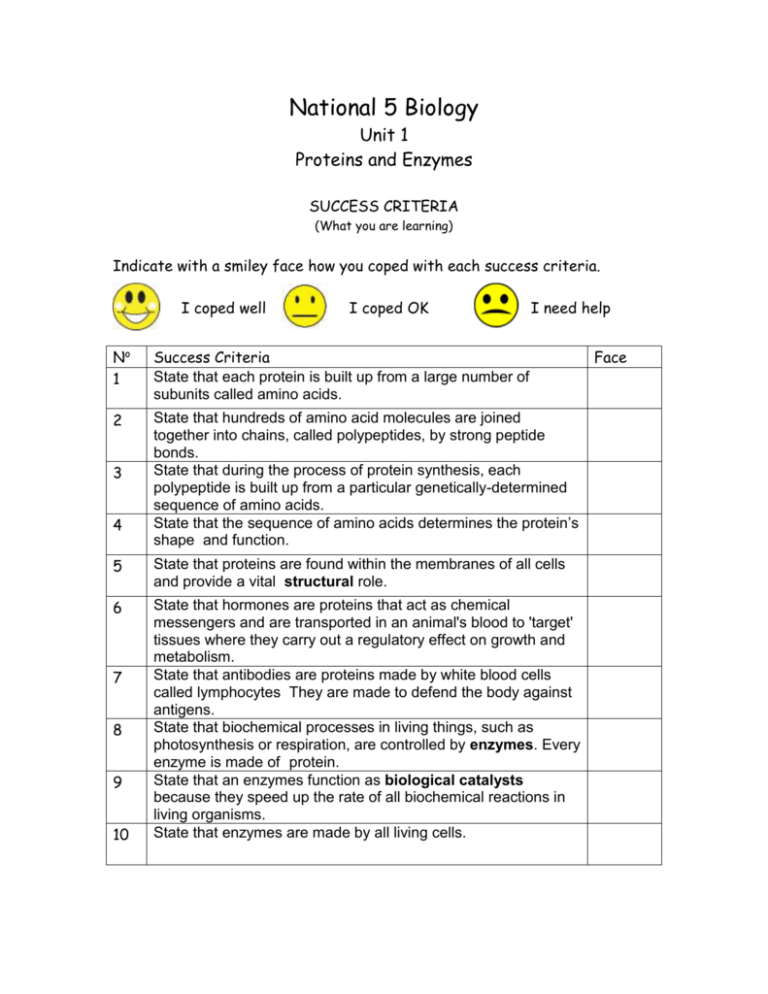
National 5 Biology Unit 1 Proteins and Enzymes SUCCESS CRITERIA (What you are learning) Indicate with a smiley face how you coped with each success criteria. I coped well I coped OK I need help No 1 Success Criteria State that each protein is built up from a large number of subunits called amino acids. 2 State that hundreds of amino acid molecules are joined together into chains, called polypeptides, by strong peptide bonds. State that during the process of protein synthesis, each polypeptide is built up from a particular genetically-determined sequence of amino acids. State that the sequence of amino acids determines the protein’s shape and function. 3 4 5 State that proteins are found within the membranes of all cells and provide a vital structural role. 6 State that hormones are proteins that act as chemical messengers and are transported in an animal's blood to 'target' tissues where they carry out a regulatory effect on growth and metabolism. State that antibodies are proteins made by white blood cells called lymphocytes They are made to defend the body against antigens. State that biochemical processes in living things, such as photosynthesis or respiration, are controlled by enzymes. Every enzyme is made of protein. State that an enzymes function as biological catalysts because they speed up the rate of all biochemical reactions in living organisms. State that enzymes are made by all living cells. 7 8 9 10 Face 11 State that they take part in a reaction but remain unchanged at the end of it. 12 State that the active site of an enzyme is the place on the enzyme's surface which matches the shape of the substance that it works on (its substrate). State that an enzyme is said to be specific to its substrate as each enzyme is able to act on only one type of substrate. 13 14 15 State that the substrate is the only substance whose molecules exactly fit the enzyme's active site. So the substrate's molecular shape is said to be complementary to the enzyme's active site. State that at very low temperatures, enzyme molecules are inactive but undamaged. 16 State that as the temperature increases, the rate of reaction increases. 17 State that the temperature at which the enzyme works at its fastest rate is called the optimum temperature. The optimum temperature for most human body enzymes is 370C. State that enzymes are proteins and the structure of proteins is easily changed by heating, e.g. as seen when boiling an egg. This results in a change in their shape. This effect is permanent. The protein is said to be denatured, and this is irreversible. State that beyond the optimum temperature, as more and more enzyme molecules become denatured, the rate of reaction decreases rapidly. State that enzymes work within a range of pH values. Each enzyme works best at its optimum pH 18 19 20 21 State that the shape of an enzyme, or protein, can be changed by changes in the pH of the solution it is in. This will affect the rate of reaction between the enzyme and substrate and may result in the enzyme becoming denatured.









