Cornell_Notes_Intermediate_Inheritance_Patterns
advertisement
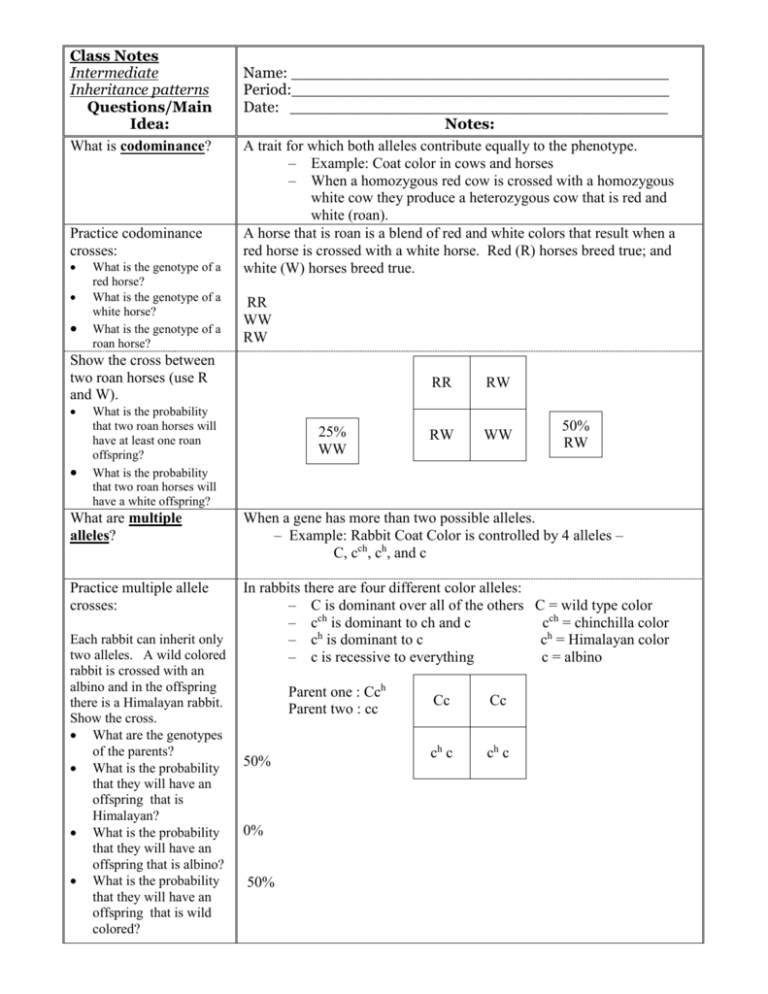
Class Notes Intermediate Inheritance patterns Questions/Main Idea: What is codominance? Practice codominance crosses: What is the genotype of a red horse? What is the genotype of a white horse? What is the genotype of a roan horse? Name: _______________________________________ Period:_______________________________________ Date: _______________________________________ Notes: A trait for which both alleles contribute equally to the phenotype. – Example: Coat color in cows and horses – When a homozygous red cow is crossed with a homozygous white cow they produce a heterozygous cow that is red and white (roan). A horse that is roan is a blend of red and white colors that result when a red horse is crossed with a white horse. Red (R) horses breed true; and white (W) horses breed true. RR WW RW Show the cross between two roan horses (use R and W). What is the probability that two roan horses will have at least one roan offspring? What is the probability that two roan horses will have a white offspring? 25% WW RR RW RW WW 50% RW What are multiple alleles? When a gene has more than two possible alleles. – Example: Rabbit Coat Color is controlled by 4 alleles – C, cch, ch, and c Practice multiple allele crosses: In rabbits there are four different color alleles: – C is dominant over all of the others C = wild type color – cch is dominant to ch and c cch = chinchilla color – ch is dominant to c ch = Himalayan color – c is recessive to everything c = albino Each rabbit can inherit only two alleles. A wild colored rabbit is crossed with an albino and in the offspring there is a Himalayan rabbit. Show the cross. What are the genotypes of the parents? What is the probability that they will have an offspring that is Himalayan? What is the probability that they will have an offspring that is albino? What is the probability that they will have an offspring that is wild colored? Parent one : Cch Parent two : cc 50% 0% 50% Cc Cc ch c ch c What is incomplete dominance? Practice incomplete dominance: Red Plant Genotype? White Plant Genotype? Show the results of a cross between a Four O’Clock with red flowers and a Four O’Clock with white flowers. Are the F1 flowers purebred or hybrid? What is the phenotype of the F1? What is a polygenic trait? What is multifactorial inheritance? Summary: Results in a heterozygous phenotype that is a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes. – Examples: mirabilis (four o’clock) plants, coat color in horses – When a homozygous chestnut horse is crossed with a homozygous white horse, they produce a heterozygous tan (palomino) horse. In Four O’Clocks, the gene for red flowers (r) is incompletely dominant to the gene for white flowers (w). The heterozygous condition results in pink flowers. Rr ww hybrid pink rw rw rw rw A trait that is controlled by the interaction between 2 or more genes. – Examples: skin color, eye color, height, hair color – Results in a continuum of expressed phenotypes. The phenotype is a result of an interaction between your genotype and certain environmental factors. The expression of most all genes is influenced by environmental conditions. Examples: – Diabetes – Height – Heart Disease Can inherit a predisposition to all of these diseases/characteristics. Their development (phenotype) is influenced by environmental factors such as proper nutrition, exercise, quality medical care, etc.