Cells of the 6 Kingdoms
advertisement

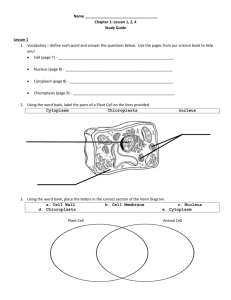
Biology Student EQ: Are there just plants and animals? Cells of the Six Kingdoms Lab Targeted Skills Preparing wet mount slides, using the microscope, making labeled drawings, recognizing relationships Enduring Understanding Living things are organized by similarities and differences. Broad Brush Knowledge Collect and classify, comparing the six kingdoms Concepts Important to Know and Understand Organization of Living Things, patterns Core Objectives 13. Categorize the six kingdoms by major characteristics. PURPOSE: Review the proper way to prepare wet mount microscope slides. Use a microscope to observe cells from the six kingdoms. Make labeled drawing of cells. Compare similarities and differences in cell structure and function. Recognize characteristics of each of the six kingdoms. A plant looks and behaves very differently from the insects that might feed on it and from fungi that might grow in its roots. Likewise, different types of single-celled organisms, such as Amoebas and bacteria, vary in appearance. Differences in the cells of organisms ultimately account for these variations. As the functional units of life however, all cells have common characteristics. For example, every cell contains genetic material, cytoplasm and ribosomes and is surrounded by a cell membrane. In this investigation, you will examine cells representing organisms from each of the six kingdoms. MATERIALS: microscope, microscope slides, coverslips, prepared microscope slides of various specimens, pencil, colored pencils GENERAL PROCEDURES: 1. Draw a few cells for each specimen under HIGH power. 2. Color the cell the color that you see it. 3. Label parts as directed. 4. List total magnification under each drawing in the appropriate place. DATA: KINGDOMS EUBACTERIA AND ARCHAEBACTERIA 1. Obtain a prepared slide that contains the 3 shapes of bacteria. In the circles below, draw each cell shape under high power. Label the shape underneath the drawing as coccus (round), bacillus (rod) or spirilli (spiral). In addition, label the cytoplasm , cell membrane and cell wall on each cell. ___________ X ___________ X ___________ X ___________ Cell Shape ___________ Cell Shape ___________ Cell Shape Cells of the Six Kingdoms Lab - Student p. 1 Comparison Study: Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote 2. Obtain a prepared slide of a Prokaryote/Eukaryote. Find the prokaryote under low power first and then switch to high power and draw it in the space provided. Determine the shape of the bacteria and record in the space provided. Label the cytoplasm, cell membrane. ___________ X ___________cell shape 3. Now look at the Eukaryotic cell. Find the cell under low power first and then switch to high power and draw it in the space provided. Determine the shape of the bacteria and record in the space provided. Label the cytoplasm, cell membrane. ___________ X ___________cell shape Observation: What are some of the main differences between a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ KINGDOM PROTISTA 5. Obtain a prepared slide of Paramecium 6. List the major characteristics of Kingdom Protista. caudatum. What must be present in order for a protest to Find the Paramecium under low power first and survive? then switch to high power and draw 1-2 cells in the space provided. Label the cytoplasm, cell membrane, chlorophyll and cell wall. ___________ X Cells of the Six Kingdoms Lab - Student p. 2 KINGDOM FUNGI 7. Is Kingdom Fungi autotrophic or heterotrophic? Is this Kingdom multicellular or unicellular? Explain. 8. Obtain a prepared slide of yeast. Find the specimen under low power first and then switch to high power. Draw 2-3 cells in the space provided under high power. Label the cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm and budding. ___________ X KINGDOM PLANTAE & KINGDOM ANIMALIA 9. Obtain a prepared slide of a general Plant cell. Draw a plant cell in its entirety under high power. Label the cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts, cytoplasm and nucleus. ___________ X 10. Obtain a prepared slide of an general animal cell. Draw an animal cell under high power. Label the cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm and nucleus. ___________ X 11. Make a list of the similarities and differences between a plant and an animal cell. Use your book as a reference. Cells of the Six Kingdoms Lab - Student p. 3 This is the end of the laboratory investigation. Turn off your microscope. Clean and dry all slides and coverslips. Follow your teacher’s instructions for properly putting your microscope away. Once you are checked out, complete the data analysis and conclusion. DATA ANALYSIS: 1. Complete the table below. Write the cell type (prokaryote or eukaryote) in the appropriate box. Describe the general size and shape of cells from each kingdom. Place a check () in the cell structure column if the structure is present in cells of that kingdom. (You may not have seen all of these structures, so look in your foldable for help.) COMPARING CELLS FROM THE SIX KINGDOMS Kingdom Cell Type Size & Shape Cell Structures Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Genetic Material Nuclear Membrane Chloroplasts Cell Wall Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plant Animal Cells of the Six Kingdoms Lab - Student p. 4 CONCLUSION 1. Complete the Venn diagram below to compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Use the terms below and write them in the correct place on the diagram. Areas that overlap suggest common characteristics between pro- and eukaryotes, while separate regions suggest differences between pro- and eukaryotes. Genetic material, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cell membrane, nuclear membrane, chloroplasts, ribosomes PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES 2. Which kingdoms have organisms that are prokaryotes? ____________________________________ 3. Which kingdoms have organisms that are eukaryotes? ____________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which kingdom is believed to be the ancestor of all eukaryotes? ____________________________ 5. Most kingdoms have organisms that have cell walls except one. Name this kingdom. ____________ 6. Members of the animal and plant kingdoms are eukaryotic and multicellular. What are some ways that one can differentiate between a plant cell and an animal cell? ______________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Describe what an autotroph can do that a heterotroph cannot do? ___________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Write the names of the kingdoms in the Venn diagram below. This diagram compares which kingdoms have organisms that are heterotrophic, autotrophic or both. The area that overlaps would contain the name of the kingdoms where there are organisms that could be autotrophic or heterotrophic. Refer to your foldable as a reference. AUTOTROPHS Cells of the Six Kingdoms Lab - Student HETEROTROPHS p. 5