Name: Date: Period: _____ Chapter 14 Study Guide Honors
advertisement

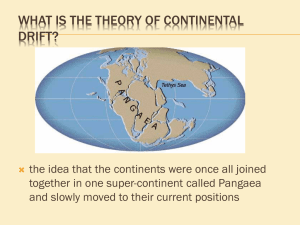
Name: ____________________ Date: ____________________ Period: _____ Chapter 14 Study Guide Honors Science Test Date: Friday, May 15th!! 1. At what rate do the plates move?1cm-12 cm per year 2. The presence of the same fossils and rocks on several continents supported the hypothesis of continental drift. 3. What does the hypothesis of continental drift state? The continents have slowly moved to their current locations. 4. What are formed when two continental plates collide? Mountain ranges 5.Mid-ocean ridge forms where two oceanic plates collide. 6. What is chemical weathering and how is it caused? Chemical weathering is the process of changing the composition of the rocks and minerals by exposure to water and the atmosphere and it is caused by acids and oxygen. 7. How does a volcano form? When layers of lava and volcanic ash erupt and build up to form a mountain. 8. What is a caldera? The top of a volcano collapses down 9. What is a subduction zone? The area where one plate slides under another 10. What causes tectonic plates to move? Convection in the mantle 11. What are the two types of evidence that scientists use to support the theory of plate tectonics? Continents fit together like puzzle pieces, same fossils are found on different continents and same geological formations found on 2 different continents 12. What reacts with iron, causing it to rust? Oxygen 13. What are lava flows? Long streams of molten rock from volcanoes 14. In what type of climate does chemical weathering occur the fastest? Hot and wet climates 15. What components make up soil? Weathered rock, mineral material, organic matter, water, and air 16. What happens to sediment eroded by water, ice, and winds when it slows down or stops moving? Sediment is deposited in a new location 17. What is an example of deposition by wind? Sand dunes 18. What is a hot spot? Locations where volcanoes form far from plate boundaries 19. Magma is less dense than the rock around it, so it is forced towards Earth’s surface. 20. What is a tsunami? Tsunamis are underwater earthquakes that as the ground pushes the water upward, huge waves form. The waves increase in height as they come closer to the shore. Essays How is chemical weathering different than physical weathering? Give one example of both physical weathering and chemical weathering. Chemical weathering is the process of changing the composition of the rocks and minerals by exposure to water and the atmosphere. Examples include acid rain, iron and minerals mixed in the atmosphere, and gases in the atmosphere. Physical weathering is the process of breaking rocks into small pieces without changing the composition of the rock. Some examples include frost wedging and tree roots breaking the sidewalk. Describe the three types of boundaries and the stress that is associated with each type of boundary. A convergent plate boundary is the boundary between two plates that move toward each other. The stress associated with a convergent boundary is compression. A divergent plate boundary is the boundary between two plates that move away from each other. The stress associated with a divergent boundary is tension. A transform plate boundary is the boundary between two plates that slide past each other. The stress associated with a transform boundary is shearing. What are the two types of evidence Wegner used to support his hypothesis of continental drift? Give one specific example for each type. Wegner used fossil evidence and geologic evidence. Geologists discovered that the same types of fossils on continents that are now separated by vast oceans. For example, the Mesosaurus has been found in South America and Africa. The continents are separated by the Atlantic Ocean and the Mesosaurus is a fresh water reptile. Rocks that are made of similar substances and mountains that formed at similar times are present on continents that are now far apart.