outline24071
advertisement

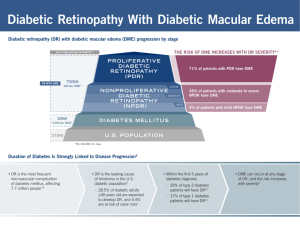
Cornea to Contact Lens Related Cases SEAL, CLARE, VLK Signs and Symptoms Pain vs irritation Hyperemia status and location Value of NaFl staining and filter use Demographics The issues Lens material, lens design, dry eye dysfunction Systemic and ocular disease influences Differential Diagnosis Dellen, pterygium, infectious keratitis, CLSLK and foreign body staining. Treatment Plan Contact lens material and design features as well as therapeutic interventions Chemical trauma Cases Determine agent If combo element determine all chemical constituents Lavage, lavage, lavage Check pH of in cul-de-sac with strip Decrease inflammation Steroids x 2 weeks (acute phase) Cycloplegics and antibiotic Role of oral doxycycline Infectious Keratitis Cases The challenging ones Fungal and Acanthamoeba Demographics and risk factors May look like bacterial/viral ulcerative keratitis Can be indolent with periods of waxing and waning The role of auxiliary instrumentation and tests such as in vivo confocal microscopy and laboratory analyses. When should they be ordered? Signs and Symptoms Differential diagnosis Treatment and Management Balancing treatment effects with adverse reactions Knowing when to refer Corneal dystrophy Cases Demographics and Prevalence Genetics Heterogeneity and penetrance Signs and Symptoms Visual acuity Biomicroscopy Hints The role of auxiliary instrumentation Histopathology Aberrant basement membrane formation Amyloid, cholesterol and hyaline Thickened posterior limiting lamina abnormal endothelial products collagen variants Prognosis Treatment Options Monitor Rationale for contact lens options Therapeutic indications PKP, DSAE, DLEK and others Retina Diabetic Retinopathy Case Pathogenesis Risk factors for retinopathy Severity scale Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) Diabetic macular edema Focal Diffuse Diagnostic testing Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Fluorescein Angiography (FA) Treatment Diabetic clinical trials Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) Diabetic Retinopathy Study (DRS) Diabetic Retinopathy Vitrectomy Study (DRVS) Laser Focal Pan Retinal Photocoagulation (PRP) Intravitreal injection Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Case Pathogenesis Risk factors Classification Perfused Clinical features / findings Complications Non-perfused Clinical features / findings Complications Diagnostic testing FA OCT Treatment Central Vein Occlusion Study (CVOS) Observation PRP Prognosis Age-Related Macular Degeneration Case Pathogenesis Risk factors Classification Non-exudative Clinical features / findings Exudative Clinical features / findings Complications Diagnostic testing FA OCT Treatment Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) Intravitreal injection Prognosis Cystoid Macular Edema Case Etiologies Clinical presentation / features Diagnostic testing FA OCT Treatment Topical Oral Injection Macular Hole Case Etiologies Types Full thickness Clinical features / findings Partial thickness Clinical features /findings Stages I II III IV Diagnostic testing OCT FA Treatment Pars plana vitrectomy with gas/fluid exchange Prognosis