Climate Zone Assignment CGC1P
advertisement

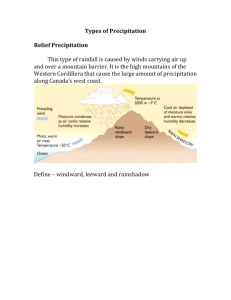
Climate Zone Assignment CGC1P Part 1: Complete the map of Canada’s Climate Zones provided to you. For each climate zone identified, graph the climate information (precipitation and temperature) of one city that is located in each zone. Part 2: Using the table below to display your information, calculate climate statistics of average annual temperature, annual temperature range, total annual precipitation, and annual precipitation distribution. Climate Zone and city name Avg. annual precipitation Temperature Total annual range precipitation Precipitation distribution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Part 3: On a separate piece of paper write a paragraph on where in Canada you would like to live, based on Climate and what climate factors would influence your decision to move there. Geography, Gr. 9 Natural Systems – Climate Canadian Climate Region Assignment Climate varies greatly across Canada and it is sometimes difficult to compare the similarities in temperature and precipitation across the country. One method of displaying climate data in a way that allows for easy comparison is called a Climatograph. A Climatograph is a special type of graph that displays the average annual distribution of temperature and precipitation in any location. In a Climate graph the temperature data is always represented by a line and precipitation data is always represented by a set of bars. An example is shown below: Note: all precipitation data is recorded in millimeters (mm) and all temperature data is recorded in degrees Celsius (C) Many statistics can be used to evaluate the climate of an area. The following descriptors are the most commonly used by climatologists to classify climates: Highest Monthly Temperature (HMT) – refers to the highest average monthly temperature for a year Lowest Monthly Temperature (LMT) – refers to the lowest average monthly temperature for a year Temperature Range – the number of degrees difference between the HMT and LMT Average Annual Temperature – the total average temperature for the year (add all monthly averages together and divide by 12) Snow Fall Equivalent – total snowfall for a year can be estimated by taking each month with an average temperature below 0C and multiplying the monthly precipitation to get the snowfall equivalent (ie. 10mm precipitation = 100mm snow fall) Length of Growing Season – can be estimated by taking each moth with an average temp. of 6C or more and tallying the days this would represent, depending on the number of days in each month. Temperature and moisture classification – See Fig 12-19 on page 141 in your textbook to determine if a location is considered Maritime or Continental based on it’s climate data. Seasonal distribution of precipitation – what part of the year receives the most precipitation (See Fig 12-19). Assignment: Using the climate data provided, complete the Canadian Climate Information Organizer and neatly complete the climatographs for the cities indicated on the Climate Regions of Canada map.