Learning activity section 3.5(a)
advertisement

Learning Activity
Score: KEY
MthSc 106
Section 3.5, Activity 1
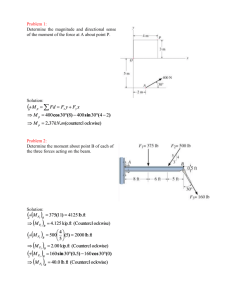
1. Find the derivative of the functions. You do not need to simplify.
a. y
= sin(x cos x)
y ´ = cos(x cos x) {[1]cos x + x [–sin x]}
= cos(x cos x) (cos x – x sin x)
b. y
dy
dx
=
cos(sin 2 x) = (cos(sin2x))½
= ½(cos(sin2x))-½ [–sin(sin2x)(2sin x cos x)]
= –sin(sin2x) sin x cos x (cos(sin2x))-½
sin(sin 2 x)sin x cos x
=
cos(sin 2 x)
2. The function h is the composite function defined as h(x) = f (g (x)). The following values
for the functions f, g, f ´, and g ´ are given:
g(3) = 6, g ´(3) = 4, f ´(3) = 2, and f ´(6) = 7
Find the value of h ´(3).
h(x) = f (g (x))
h ´(x) = f ´(g(x)) · g ´(x)
h ´(3) = f ´(g(3)) · g ´(3)
= f ´(6) · 4
= 7·4
= 28
3. Use the Chain Rule and the Product Rule to give an alternative proof of the Quotient Rule.
Quotient Rule: If f and g are both differentiable, then
d f ( x)
f ( x) g ( x) f ( x) g ( x)
=
dx g ( x)
[ g ( x)]2
Proof: Suppose f and g are both differentiable functions.
d f ( x)
dx g ( x)
d
{f (x) [g(x)]–1}
dx
= f ´(x)[g(x)]–1 + f (x){–1[g(x)]–2g ´(x)}
= [g(x)]–2[f ´(x)g(x) – f(x)g ´(x)]
f ( x) g ( x) f ( x) g ( x)
=
[ g ( x)]2
=