Department of Engineering and Materials Sciences
Department of Engineering and Materials Sciences
Both engineering and materials sciences necessarily and significantly underlie the importance of national security, the improvement of people’s living standard and the sustainable development of the society and economy. Aiming at frontier science and meeting the national strategic demands of the social and economic development as well, research in the fields of engineering and materials sciences should pay full attention to scientific creativity and innovation, especially original creativity and innovation with independent intellectual property rights, in order to raise China’s international competitiveness in science and technology and to achieve a sustainable development of the society.
The Department will continue to strengthen its support to interdisciplinary areas and the exploration of frontiers and encourage original innovation, integrated innovation and re-innovation based on the absorption and digestion of existing knowledge, while considering the common features in the fundamental research of engineering and materials sciences. At the same time, the Department will pay attention to key scientific issues resulting from engineering application, especially those researches with such great significance that the industrial development can be promoted and international competitiveness be raised.
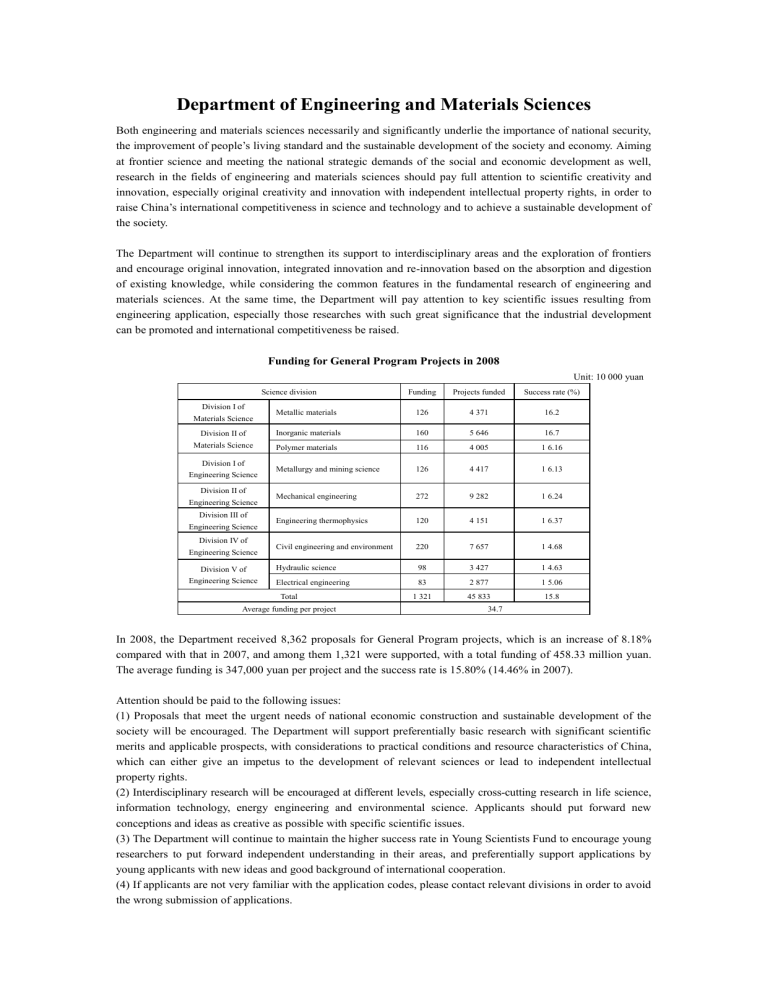
Funding for General Program Projects in 2008
Unit: 10 000 yuan
Science division Funding Projects funded Success rate (%)
Division I of
Materials Science
Division II of
Materials Science
Metallic materials
Inorganic materials
Polymer materials
126
160
116
4 371
5 646
4 005
16.2
16.7
1 6.16
Division I of
Engineering Science
Metallurgy and mining science 126 4 417 1 6.13
Division II of
Engineering Science
Division III of
Engineering Science
Division IV of
Engineering Science
Mechanical engineering
Engineering thermophysics
Civil engineering and environment
272
120
220
9 282
4 151
7 657
1 6.24
1 6.37
1 4.68
Division V of
Engineering Science
Hydraulic science 98 3 427 1 4.63
Electrical engineering 83 2 877 1 5.06
Total
Average funding per project
1 321 45 833
34.7
15.8
In 2008, the Department received 8,362 proposals for General Program projects, which is an increase of 8.18% compared with that in 2007, and among them 1,321 were supported, with a total funding of 458.33 million yuan.
The average funding is 347,000 yuan per project and the success rate is 15.80% (14.46% in 2007).
Attention should be paid to the following issues:
(1) Proposals that meet the urgent needs of national economic construction and sustainable development of the society will be encouraged. The Department will support preferentially basic research with significant scientific merits and applicable prospects, with considerations to practical conditions and resource characteristics of China, which can either give an impetus to the development of relevant sciences or lead to independent intellectual property rights.
(2) Interdisciplinary research will be encouraged at different levels, especially cross-cutting research in life science, information technology, energy engineering and environmental science. Applicants should put forward new conceptions and ideas as creative as possible with specific scientific issues.
(3) The Department will continue to maintain the higher success rate in Young Scientists Fund to encourage young researchers to put forward independent understanding in their areas, and preferentially support applications by young applicants with new ideas and good background of international cooperation.
(4) If applicants are not very familiar with the application codes, please contact relevant divisions in order to avoid the wrong submission of applications.
Division I of Materials Science
The Division mainly supports basic research on metals, alloys and metal matrix composites. In their proposals, applicants should give specific description and convinced analysis in the merits of focused scientific problems and their pertinent creative ideas to which a sound reasoning should be developed, targeting either at the international cutting-edge areas or at pushing forward the progress in the relevant areas that meets the national needs.
The funding spectrum of the Division covers broad areas, including compositions, microstructures, phases, surfaces and interfaces, scales effect, impurities and defects in metals, alloys, metal matrix composites, intermetallic compounds and metal-like materials, and their influence on mechanical, physical and chemical properties and performance of materials; basic issues in the processing of metallic materials; strengthening and toughening, phase transformation and alloy design, deformation and fracture, and strength theory of metallic materials; the fundamentals in energy materials, environment-friendly materials, biomaterials and recyclable metallic materials; the mechanism of interactions of metallic materials and environment, damage, functional degradation and consequent failure mechanism and relevant fundamentals; theoretical fundamentals on metallic materials; new-type metallic functional materials and structural materials and their theoretical basis, and the development of theoretical methods, calculating methods, modern analysis and test methods incorporating basic and applied basic researches of metallic materials.
In 2008, the Division received 1 172 proposals in total, which is an increase of around 9%. Through peer review and panel evaluation, 126 General Program projects were granted, with a success rate of 16% on average. It is noticed that proposals kept the leading place in such areas as metastable metals and alloys, functional materials and surface engineering. It is hoped that researchers pay attention not only to the frontiers and the hot areas, but also to other fundamental issues with scientific merits and creative ideas, especially those common key issues beyond materials systems. In addition, some attention should be paid to the new understanding of classic issues in basic materials. Applications in the field of composites and surface engineering should be improved in focusing scientific problems and proposing unique ideas.
The Division will continue to support basic research with creative ideas in all aspects in the funding spectrum specified above. New ideas revealing basic mechanism will be encouraged with respect to the Key Program areas supported in recent years (including areas to be supported in 2009). The Division also encourages and supports cross-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary research in which metallic objectives and materials science should be the mainstream, especially in such areas as energy, information and biology.
The Division will continue to prioritize those well-established research groups and institutions with good infrastructures in the field of metallic materials science and engineering in the process of evaluation. It will also continue to encourage and support young researchers to put forward creative thoughts and ideas, and to encourage and support researchers to carry out deeper research based on their previous good work.
Division II of Materials Science
The Division mainly supports fundamental researches on inorganic not-metallic and organic polymer materials.
Inorganic Non-Metallic Materials Science
The Division supports fundamental and applied researches which focus on inorganic non-metallic materials. With the development of material design theories, fabrication and characterization technologies, many novel materials have been discovered, including ceramic superconductors, smart ceramic materials, new energy materials, bio-medical materials, nano-materials and so on, which has greatly stimulated researches on inorganic non-metallic materials. At present, in the field of inorganic non-metallic materials, functional materials with high efficiency, reliability and sensibility, smartness and functional integration are being developed, and also high on the agenda are structure ceramics with multi-functionality, high toughness, specific strength, wear-resistance, corrosion-resistance, high-temperature endurance and low cost and high reliability. Meanwhile, conventional materials are also being remolded and upgraded. Furthermore, inorganic non-metallic materials are playing ever-increasingly significant roles in information technologies, life science, energy and environmental science, and
interdisciplinary research with other related areas.
A review of all the related proposals submitted in the past three years indicates that, in addition to an annual increase in the number of proposals, researches have been broader in range and more interdisciplinary in nature. In
2008, there were 1 471 applications for General Program, Young Scientists Fund and Fund for Less Developed
Regions, an increase of 9.4 % compared with those submitted in 2007. For General Program, 160 applications were supported, reaching a funding rate of 16.7 %. Among the applications, researches on functional materials accounted for 60.97% of the total. These applications unfolded many innovative ideas and induced the hot-spots of research on various areas including nano-materials, piezoelectric and ferroelectric materials, carbon and super-hard materials, photoelectric information functional materials, composite materials, photoelectric conversion and photo-catalysis materials and so on, among which applications from photoelectric information functional materials
(about 22.6 % of the total) ranked above all the others. There were also many applications from new energy materials, display materials, bio-medical materials and inorganic non-metallic based composite materials. The number of proposals on functional composite materials increased, however, the novelty of the proposals needs to be improved and further refinement about the scientific problems in inorganic non-metallic materials is needed.
The Division encourages substantially interdisciplinary research projects and supports the synthetic science and related fundamental application research on novel inorganic non-metallic materials in accordance with domestic resources, research on low-dimensional and nano-materials, including new fabrication techniques, property characterization, novel effects and applications related basic physical and chemical problems, research on the surface, interface and compatibility of inorganic materials, basic research on structural-functional integration materials, research on material synthetic science and techniques about high-performance, low-cost and high reliability materials, research on the composition, structure, performance and characterization features of smart materials, new energy materials, bio-medical materials and eco-environmental materials, basic theoretical research of design (at macro-, meso- and micro-scales, respectively) and corresponding fabrication science of inorganic non-metallic materials, and basic applied research on the improvement and remolding of conventional inorganic non-metallic materials based on new theories, with new techniques and through new processing science.
Organic Polymer Materials
In the field of organic polymer materials, the Division received 1 032 proposals in 2008 for General Program, 79 more than the figure in the previous year and an increase of 8.3%. Among them, proposals for opto-electronic functional materials, functional inorganic/organic composites, polymer- based nano-composites, biomedical materials and eco-environmental polymer materials reached 83, 105, 80, 136 and 88, respectively, representing
8.0%, 10.1%, 7.7%, 13.2% and 8.5% of the total.
At present, the main tasks and developing directions for organic polymer materials science are as follows:
(1) For general polymer materials, the focus is on the implementation of high performance and functional properties, the relationship between machine forming and congregation state textures, and the variation of materials textures and materials properties in their utilization;
(2) Functional polymer materials and organic solid functional materials;
(3) For polymer-based composites, the stress is on high performance, interface, new synthesis technology, computer aided technologies and low cost technology;
(4) Special polymer materials and engineering plastics;
(5) Polymer materials related to environment, energy resource and resource utilization.
Basic and applied basic researches in the following fields are encouraged: general polymer materials with high performance or functional properties, functional polymer materials and organic solid functional materials, preparation science and technical processes for polymer materials (e.g. new technique and new technology for material preparation and processing, new theories of reinforcement and toughening, fatigue and fracture, friction and lubrication, structures and performance of multi-component materials in congregation state, composite materials-based matrix resin and its interface properties, and computer aided design and forming), adhesives, coatings and assistants of new organic polymers, biomedical polymer materials, organic nano-materials, intelligent materials and bionic polymer materials, eco-environmental polymer materials including natural polymer materials,
environmental friendly polymer materials and renewable polymer materials.
The Division highly encourages fountainhead innovation, and promotes the interdisciplinary cooperation.
Division I of Engineering Science
The Division mainly supports fundamental researches in mining and metallurgy sciences, including such main fields as resource exploitation, safety science and engineering, mineral processing and separating, metallurgical and material physical-chemistry, ferrous and nonferrous metallurgy, material preparation and fabrication, eco-environment of mining and metallurgy, resource recycling, etc.
The research trends at present are as follows: Basic research scope in the above-mentioned fields has been increasingly extended and deepened. Many researches transfer from macro, middle scope to microscope, and each inosculate and intercrosses with another, from raw minerals to the recycling of resource, from metal to composite materials, even functional materials. Interdisciplinary differentiation and amalgamation have been strengthened.
With the interdisciplinary amalgamation and differentiation with life science, informatics, mechanical science, chemistry, materials science, managerial science, etc., new research fields such as resource recycling science, non-pollution process engineering, green catalyzing engineering, bio-metallurgy, environmental bio-chemical engineering, bio-chemical mining, computing metallurgy and physical-chemical metallurgy, metallurgical informatics and electro-magnetic metallurgy have appeared. Relationship between science and technology is getting increasingly closer. Equipment for mining and metallurgy, monitoring and controlling of system, metallurgical reaction engineering science and systems engineering, and metallurgical ecological technology, etc., are integrated with each other, and many new technologies, new methods and new branches of science have emerged. Researches have been carried out much more quantitatively and accurately, e.g. precisely analyzing the composition of molten salts and slag, and precise control of rolling process. Many important research areas are expected to be studied deeply and systematically.
In 2008, 1 214 proposals were received by the Division, 8% more than that of the previous year. 126 were supported and the funding intensity was 356 000 yuan on average. Among which, 60% dealt with the following research fields: materials preparation and fabrication, resource exploitation, safety science and engineering, mineral engineering, resource extraction and matter separations, powder engineering and powder metallurgy. The fields with fewer proposals were subterranean heat resource and exploitation, ocean and space metallurgy, other ways of resource utilization, underground and space engineering, metallurgical chemical engineering and equipments and metallurgical reaction engineering. Proposals on metallurgical and material physical-chemistry and mechanic metallurgy were limited. There were a few proposals dealing with special metallurgical methods and other new techniques, e.g., microwave, plasma, electromagnetism, laser and ultrasonic. With the adjustment of the application code, proposals in the fields of resource recycling decreased by half and proposals on special material preparation related with mechanical metallurgy such as fiber, foam, etc. were few. Now the hotspots are resource exploitation, material preparation and fabrication, safety science, etc.
The Division emphasizes process and engineering and will continuously promote interdisciplinary studies and the exploration of novel methods, encourage original ideas and creations, emphasize applied basic research, especially those that would enhance our competitiveness in mining and metallurgy industry. The funds will favor fundamental researches with theoretical importance, potential application and prior prospect, which might be the new field for knowledge production, and young scientists who have creative capability, good performance and good cooperation with others are encouraged. Researchers are suggested to work systematically and consistently in a specific research field to form their own features. More funding will be granted to projects of high cost and hard working environment (about 50-55 thousand yuan per project), such as mining, pyrometallurgy, electrochemical-metallurgy and plastic forming of metals.
Division II of Engineering Science
The Division mainly supports basic research in the fields of mechanical science and manufacturing engineering science. Mechanical science is a basic technology science aiming at functional comprehension, quantitative
description and performance control of the mechanism. Its main task is to study the unknown characteristics of mechanical systems and to develop all kinds of knowledge needed by mechanical systems into new design theory and method. Encouragement and support will be given to creative proposals in such fields as mechanisms and robotics, mechanical transmission, mechanical dynamics, mechanical structural strength, tribology and surface technology in mechanical engineering, mechanical design theory and methodology, mechanical bionics, micron/nano mechanology, etc. Manufacturing engineering science is mainly to study manufacturing products which meet the design requirement, and various manufacturing systems, processes, arts and crafts, equipment and methods. It includes forming, machining, manufacturing systems and automation, mechanical metrology and measurement instruments, MEMS/NEMS, and so on.
At present, the main tasks and development directions for mechanical science and manufacturing engineering science are as follows:
(1) Basic research aiming at national needs and disciplinary development, as well as industrial application;
(2) Resource-saving and environment friendly research on the integration of design and manufacture;
(3) Research aiming at processing mechanism and then process, equipment, technology and theory for superhigh precision and hi-tech equipment and instruments;
(4) Basic research aiming at macro/meso/micro/nano scale;
(5) Cross-disciplinary research among mechanism, electricity, hydraulic and magnetism.
Proposals for General Program submitted to the Division in 2008 reached 1 674, and 272 were funded with a total funding of 92.82 million yuan. The average funding rate is 341.2 thousand yuan per project, and the success rate is
16.24%. As to the distribution of research areas, the number of proposals still increased in mechanical dynamics, component forming, mechanical design, component manufacturing, and manufacturing systems and automation.
Meanwhile, proposals in the fields of mechanical structural strength, mechanical tribology and surface technology, mechanical metrology and measurement instruments also increased greatly. But the number of proposals in mechanical transmission decreased sharply.
While encouraging and supporting creative basic research proposals in the new frontiers of the discipline, the
Division will, in 2009, strongly support proposals on new principles and methods, new processes and technologies related to mechanical engineering in order to emphasize the fundamental research aimed to develop new mechatronics with self-own intellectual property rights and the frontier of the disciplinary. Proposals on new principles and methods, new processes and technologies on mechanical electrical systems and equipment with natural resource saving, environmental friendly and sustainable development will enjoy preferential support. Both joint proposals with enterprises and proposals with the background of engineering application are welcome.
Division III of Engineering Science
The Division supports fundamental research and part of applied research in the field of engineering thermo-physics and energy utilization that involves in engineering thermodynamics, refrigeration and cryogenics and dynamic characteristics of thermodynamic systems, aerothermodynamics, heat and mass transfer, multi-phase flow, combustion, thermo-physical properties and measurement, renewable energy utilization and other fundamental and innovative researches related to engineering thermo-physics and energy utilization.
Proposals in recent years demonstrate that research in the fields of engineering thermo-physics and energy utilization is very active. The research contents have gone deeper, research objectives more extensive and research achievements for wider applications. In 2007, 164 projects including General Program, Young Scientists Fund and
Fund for Less Developed Regions were supported with a success rate of 16.5%. In 2008, the Division received
1,083 proposals for General Program, Young Scientists Fund and Fund for Less Developed Regions, 92 more than that in 2007, with a remarkable increase in the areas of combustion related pollutant generation and pollution control, heat and mass transfer in micro- and nano-scale structures, radiation and phase-change heat transfer, and renewable energy utilization. In 2008, 120 projects including General Program, Young Scientists Fund and Fund for Less Developed Regions were supported. The average funding is 345 900 Yuan per project and the success rate is 16.37%.
The main development trends of the discipline are as follows. (1) Research on the basic issues has gone from macro-level to meso-level and micro/nano-level, from isolated studies to coupled studies, from common parameters to parameters under ultra- or extreme conditions, from routine thermo-physical problems to random, unsteady, multi-dimension, multi-phase and complicated thermo-physical problems and intercrossing research in the discipline. Moreover, research becomes more quantitative and precise. (2) Research has crossed traditional disciplinary borders and formed interdisciplinary projects with related disciplines (e.g. with physics, chemistry, life science, information science, materials science, environment and safety). Creative researches in the following areas are encouraged: the mechanism of new type thermodynamic cycles and non-equilibrium thermal dynamics, refrigeration and low temperature engineering, dynamics, optimization and control of complicated systems, turbulence properties of internal flows and properties and control of unsteady flows, porous media and micro-scale heat and mass transfer, radiation and heat exchange by phase transformation, clean, supersonic and micro-scale combustion, thermo-physical problems in the prevention of disasters, mechanism of interaction between phases and thermo-physical model in multi-phase flow, new principles and methods in thermo-physical measurement, and new thermo-physical principles in renewable energy transformation and utilization.
The Division requires that applicants provide detailed information on their research achievements obtained in all previous NSFC projects and the list of papers published on international and domestic journals in recent years. All the information provided must be impersonal and true, or it will directly affect the evaluation and approval of the applications.
Division IV of Engineering Science
The Division’s funding scope mainly covers architecture, environmental engineering and civil engineering. The development trends of architecture are research on the development of region, city and building, the innovation of construction techniques from the viewpoint of human-environment relationship, and research on basic theory, methods of planning and design, and construction technology innovation, based on sustainable development strategy. The emphasis of environmental engineering research is on water or air pollution control and quality amelioration, as well as theories and methods for the treatment, resourcelized and harmless disposal of various pollutants and wastes. Civil engineering stresses that studies should be closely combined with engineering practice to investigate basic theoretical issues and solve foresight key technological problems arising from engineering construction. The interdisciplinary interaction, application of advanced experiment and information technologies and adoption of new materials, new structures and new technologies are the major features in the development of these research fields.
In architecture, focus should be given to new scientific problems arising from urban construction, scientific method in urban planning and building design, and the exploration and innovation of new technologies and new methods. Research on environmental engineering emphasizes key scientific issues related to new theories and technical bases of new high-efficiency and low-consumption technologies, which includes water purification, wastewater treatment and utilization, municipal water supply and drainage system, urban refuse disposal and utilization, air pollution cleaning, and control and renovation of the polluted water environment. Other research subjects related to environmental science should be submitted to other relevant divisions. In civil engineering, more attention should be paid to innovative research on the analysis, design and reliability of complex structures.
Key scientific problems on the following topics are encouraged: intelligent structural systems and performance design theories in civil engineering, disaster effect, failure mechanism and performance control of civil infrastructure and structures, new structure systems and constructing technology, modern structure experiment, on-spot measurement and digital simulation technology, and health diagnosis and renovation of structures.
Research on structural disaster-resistance on the level of overall structural system should be strengthened, and efforts be made to improve the innovativeness and practicality in the study of seismic-resistant, fire-resistant and wind-resistant engineering structures. In the area of geo-technical engineering, researchers should focus their attention on the engineering properties of soil under complex conditions, and invalidation mechanism and control methods of geotechnical engineering. In traffic engineering, the emphasis is on the research of planning theory and key construction technology in traffic infrastructure.
Division V of Engineering Science
The Division is mainly responsible for funding projects in water sciences and water management, hydraulic engineering and ocean engineering, and electrical sciences and engineering.
Water Sciences and Water Management, Hydraulic Engineering and Ocean Engineering
It supports researches on hydro-science and hydraulic engineering, coastal engineering, naval architectures and ocean engineering, soil/rock mechanics and geotechnical engineering, water environmental engineering, water/soil science and irrigation engineering. Among them, naval architectures and ocean engineering, and coastal engineering are new and independent parts in the revised NSFC application code system.
The impact that climate change and human activities exert on water cycle and the relevant measures to deal with it are the most important research areas of the Division. Cross-disciplinary and integrative innovation is greatly encouraged since water has close and broad linkage with the population and society, resources and environment, energy and economy. Hot research themes include the physical mechanism, chemical mechanism and biological mechanism associated with water process, as well as water cycle’s impact on water resources, water environment and water eco-system. Much attention is paid to the academic issues related to major projects under construction, and the performance design and environment friendly design of hydraulic structure engineering. Researches on constitutive relationship, engineering behavior, fundamental principal and technical measures are the main tasks of geotechnical engineering. Naval architecture and ocean engineering have entered into a period of rapid development. The Division covers researches on ocean environment and its loading, design and construction of naval architecture and ocean structure, marine engine engineering, underwater acoustics engineering, and maritime security technology. China is in an urgent need of integrative and cross-disciplinary research in the above fields for its ocean resource exploitation and utilization.
Based on the proposals received during the last three years, the funding areas of the Division have extended gradually and tend to be more interdisciplinary. The number of proposals increases year by year. The annual increase of proposals for Young Scientists Fund is 15 to 30% higher than that of General Program. The annual increase of proposals on hydro-science and water resource, water environment engineering, geotechnical engineering, naval architecture and ocean engineering keeps at a rate of 10-40%, but that in some other areas is very low, or even negative.
In 2008, 670 proposals were received for General Program project, with an increase of 25% compared with that in
2007. Relatively large amount of proposals were received in the following areas: 206 proposals on geotechnical engineering with an increase rate of 54%, 142 on hydro science and water resource with an increase rate of 13%, and 138 proposals on water environmental engineering with an increase rate of 44%. The increase rate of proposals on naval architecture and ocean engineering, and hydraulic machinery was higher than 50%. Proposals on water/soil science and irrigation engineering, hydraulics and hydro-informatics decreased somehow compared with that in 2007. 98 projects were funded for General Program, with a total funding of 34.3 million yuan, an average funding of 350 000 yuan and a funding rate of 14.6%.
Electrical Engineering
The subject of electrical engineering includes two parts: electric (magnetic) energy science and the interaction between electromagnetic field and matters. The first one deals with the electrical energy conversion (mutual conversion between electric power and other kinds of energy) and its control, power system and automation, power electronics, high voltage and electrical insulation technology, superconducting technology, and pulse power technology. The second one includes engineering dielectrics, discharge and plasma technology, bio-electromagnetic technology, environmental electro-technology and electromagnetic compatibility. Furthermore, the two parts share some common basic research contents, such as electric network theory, electromagnetic field theory, electromagnetic measurement technology, and so on.
In 2008, 551 proposals were submitted for General Program in the field of electrical engineering, with an increase of 11.99% compared with that in 2007. By means of peer review and panel evaluation, 83 projects were funded with an average funding of 346 600 yuan per project and the success rate of 15.06%. Among them, proposals for
electromagnetic field and circuit theory accounted for 8.4% of the total, electric machine and its systems 13.3%, power systems 26.5%, electric engineering materials, apparatus, high voltage and insulation technologies 20.5%, power electronics 16.9%, pulsed power and discharged plasma technologies 7.2% and others 7.2%.
With the requirement of national energy security and sustainable development, the original and innovative research is encouraged. Priorities will be given to the following proposals: those on research principles, methodology and approaches in the field of electrical engineering and those attaching importance to the experimental verification and to the scientific aspect and quantification of experimental research.
The focus in electric energy science is on new theories, technologies and apparatus of high efficiency, flexibility, safety, reliability and environmental friendly for electrical energy conversion, transmission and utilization. They include high efficient conversion and utilization of electric energy, measurement of electromagnetic characteristics, power generation of new energy and renewable energy, safety and reliability of power systems and apparatus, power electronic converters and integration, and superconducting electrical technologies.
As to electromagnetics and the interaction between electromagnetism and matter, the focus is on new phenomena, the exploration of new principles, the establishment of new models and the discovery of new applications. They include electrical insulation under complicated and special conditions, microstructure and performance of nanocomposite dielectrics, time and space compressively transmission of electromagnetic energy, measurement of electromagnetic characteristics, coupling between electromagnetic pulsed energy and its applied objects, discharge and high active plasma generation, interaction between electromagnetic field and bio-matter, processing and utilization of biologic signals, and complicated transient electromagnetic fields.







