planning/buying media -
advertisement
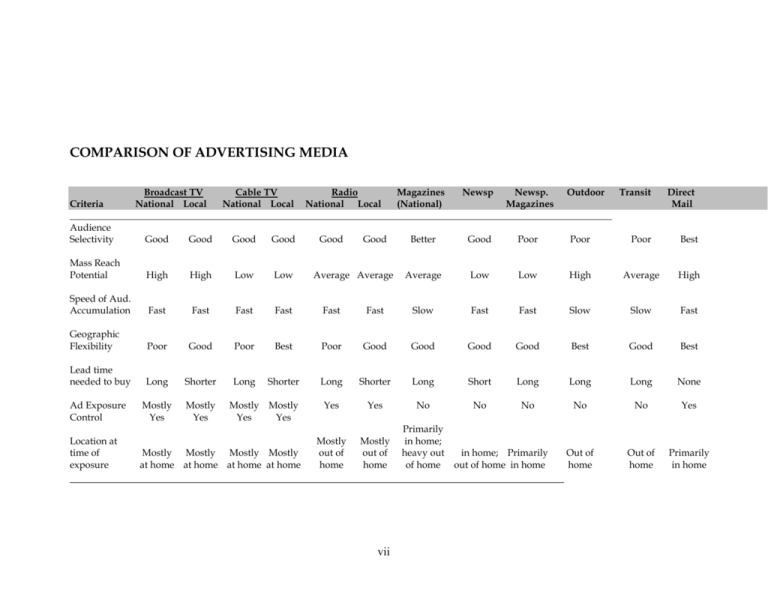
COMPARISON OF ADVERTISING MEDIA Broadcast TV Cable TV Radio Magazines Newsp Newsp. Outdoor Transit Criteria National Local National Local National Local (National) Magazines _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Audience Selectivity Good Good Good Good Good Good Better Good Poor Poor Poor Mass Reach Potential High High Low Low Speed of Aud. Accumulation Fast Fast Fast Fast Fast Geographic Flexibility Poor Good Poor Best Lead time needed to buy Long Shorter Long Shorter Ad Exposure Control Mostly Yes Mostly Yes Location at time of exposure Mostly Mostly Yes Yes Mostly Mostly Mostly Mostly at home at home at home at home Average Average Direct Mail Best Average Low Low High Average High Fast Slow Fast Fast Slow Slow Fast Poor Good Good Good Good Best Good Best Long Shorter Long Short Long Long Long None Yes Yes No No No No No Yes Mostly out of home Mostly out of home Primarily in home; heavy out of home Out of home Out of home Primarily in home in home; Primarily out of home in home _____________________________________________________________________________________ vii PLANNING/BUYING MEDIA -- NEWSPAPERS I. CLASSIFICATION (7 Categories) A. Daily Total --- _______ in U.S. [about 70% are chains] Predominantly ________ (in $) -- Use of dailies (and weeklies) is logistically prohibited for national advertisers National (daily) newspapers include: B. Sunday -- around ______ Do people read Sunday papers differently from dailies? How? C. Weeklies -- around 8,000 Two types (rural and suburban) and their media implications: D. Special Interest Include foreign language, religious, African-American, labor, financial papers, etc. Have magazine-like characteristics: i Noted for audience selectivity. E. Supplements or Supps [Sunday magazines] National -- using Local [Most] -- using F. Sunday Comics National (Metro-Puck) Local -- Bought thru "_________" G. Pre-Print Advertising/Inserts -- typically distributed through supplements Magazine-like color reproduction Two Color Options (Strengths/Weaknesses) ROP (Run-of-Paper or Run-of-Press): Pre-print inserts: Current examples: multi-page inserts, free-standing inserts (FSI), cards, envelopes, product sample, etc. ii II. WHY USE NEWSPAPERS? Read the textbook and fill in the space following iii III. TACTICS OF BUYING NEWSPAPERS A. Who provides newspaper information? [See the "Source of Media and Market Information" ] Circulation information: Audience information: Rates (cost) information: Also, refer to SB book, p. 338, Exhibit 12-13. B. What ad sizes are available? SAU (Standard Advertising Unit) system for determining ad sizes and rates: [See Handout] C. Advertising Rates -- Column inch is the basis 1. One column inch = 1 column (width) by 1 inch (depth) 2. Open Rate vs. Flat Rate Distinction Flat rate: Open rate: iv 3. Short Rating and Rebating: _______: advertiser pays for the rate difference when the volume or space actually purchased is less than that signed for the year; ________: vehicle pays for the rate when the actual purchase is more than that singed for. Examples: Suppose you contracted for 10,000 inches of buy in Morning edition of Times for the fiscal year of 1996. If you, however, end up buying 8,000 inches, a) which rate system is applicable to your buy? b) What is the total rate difference? c) What rate system applies and d) how much is the difference in rates if you end up buying 12,000 column inches? 4. Color Rates ("extra" charges to be added to the B&W rates: see GS 8) -- Note the color "add-on" charge shown applies to each ad run v D. Costing a Newspaper Buy Example: (GS 8) vi IV. SOME ADDITIONAL MATTERS/SIGNIFICANT TRENDS A. Rate Differential: National advertisers pay _______% more than retailers. B. Newspaper Readership [done yearly by SMRB] -- who reads newspapers? ____% of all adults read a daily newspaper Readership vary by selected demographics (declining readership over the years): 45 to 64 -- 65% [vs. 18-24 -- 52%] Graduate college -- 70% [ vs. 40% did not attend H.S.] $50K+ HH income -- 72% [vs. 41% less than $10K] Summarizing the pattern of newspaper readership (in your own words): C. Some Notable Trends Zone editions [see GS 8]: TMC by advertisers: vii MAGAZINES I. CLASSIFICATION -- 3 Categories: A. Consumer magazines-- over 200 vehicles & over 20 editorial classes B. Farm (Agricultural) publications C. Business publications [separate SRDS] 1. Industrial 2. Merchandising (Trade) 3. Professional II. WHY USE MAGAZINES? Read the textbook and fill in the space following Additional Characteristics: 1. Relatively "easy to buy" medium, why? a. b. viii 2. Guaranteed circulation -- Rate base: III. TACTICS OF BUYING MAGAZINES A. Who provides magazine information? 1. Circulation: Consumer magazines: Farm Publications: Business Publications: 2. Audiences (extensive audience data is available for consumer magazines): 3. Rates: Also, refer to SB book, pp. 335-337 for year 2000 data, or VISIT www.mriplus.com for additional and updated data. C. Some Important Terms 1. Total Audience = Primary + Secondary (Pass-Along) Audience Primary Audience: Secondary (Pass-Along) Audience: How helpful are they to a media planner? ix 2. Readers Per Copy = Example: If Readers Digest has audience of 40 million, and circulation of 18 million, what is RPC (readers per copy) for Readers Digest? D. Costing Magazine Buys Example: x