Lab Plant Reproduction - Jocha
advertisement

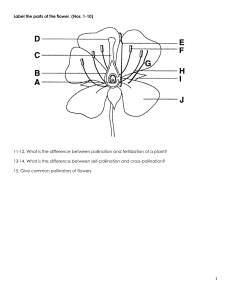
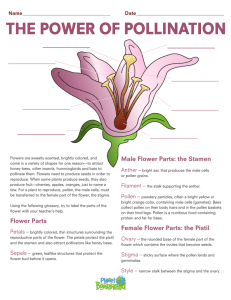
STUDY GUIDE LAB 8: Plant Reproduction Most answers can be pulled out from your lab manual and results obtained during the lab. For some concepts, you might need to check your book or Google the definition online! FLOWER STRUCTURE 1. The flower is the plant structure “designed” for sexual reproduction, as it normally possesses both the female and male reproductive parts. Use a diagram of a flower to understand all the structures that are part of most flowers (receptacle, sepals, petals, corolla, calyx, carpel, stigma, style, ovary, anther, filament, stamen, pollen) a) Which ones of the previous structures are strictly connected with reproduction? b) Which ones are connected with attracting pollinators? c) Which ones provide support for the flower? (but are not used for a or b) d) On the Lily flowers used in the lab, how are sepals distinguished from the petals if both actually look identical? POLLINATION 2. What “resources” do flowers use in order to attract pollinators? 3. What are the different types of pollinators and what is each attracted to? 4. If a plant is wind pollinated, what changes are expected regarding the flower design and the amount of pollen released by the plant? GERMINATION and DOUBLE FERTILIZATION 5. Briefly, describe the three steps seen in the lab, from the moment the pollen grain lands on the flower to the actual fertilization process 6. Why is it called “double fertilization”? DISPERSAL 7. The seed is one the structures “designed” for dispersal in plants, which one is the other one? 8. Explain the different seeds dispersal methods and give at least one example of a specialized feature that allows plants to disperse the seeds. 9. If you have not answered question 7 yet, the fruit is the answer you were supposed to give! Familiarize yourself with examples of different fruit types and whether they hold one, several or multiple seeds 10. How is a simple fruit different from an aggregate fruit? 11. If the fruit is simple, will it always have just one seed inside? Explain Instructor: Dr. Jose Bava