Homework 10 Forms and Twins l
advertisement

Homework 10
Forms and Twins
Follow along in the PowerPoint and answer the following:
1. Define Form
2. Define Zone
3.
Miller Indices are enclosed in parentheses (111), zones in
square braces [111], and forms in curly braces {111}. True or
False?
4. Using sketches, explain the difference between trapezohedron
(Garnet) and scalenohedron (Calcite) forms.
5. Using sketches, explain the difference between pyritohedron
(Pyrite) and dodecahedron (Garnet) forms.
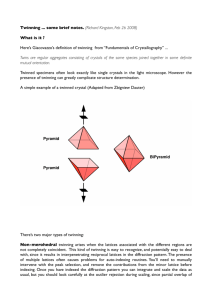
6. Define composition plane with respect to twinning.
7. Define Polysynthetic Twins
8. Polysynthetic twins are typical of Calcite and
________________.
9. Plagioclase commonly shows Albite Twinning. The Albite Twin
Law has the form {010} as the twin plane. Such twinning is one
of the most diagnostic features of plagioclase. True or False?
10. The combination of albite twinning {010}, a form, and pericline
twinning [010], a zone, in Microcline results when the high
temperature feldspar e.g. Sanidine (monoclinic) transforms to
low temperature microcline (triclinic). True or False?
11.Albite twinning {010}, and pericline twinning [010] are
perpendicular to one another. True or False?
12. The combination of albite twinning {010}, and pericline
twinning [010], results in a "tartan" twinning, the most
characteristic diagnostic property for the identification of
microcline under the polarizing microscope. True or False?
13. Aragonite has contact and __________ twinning. This gives
Aragonite a hexagonal appearance, but Aragonite actually falls
into the __________________ Crystal System.
14. Carlsbad twins [001] can occur in monoclinic Orthoclase,
KAlSi3O8. True or False?
15. Swallow-tail (aka Fish-tail) twins {100} can occur in
__________,
an evaporite mineral that has a chemical formula of CaSO4 . 2H2O.