Skin Assessment - My Illinois State
advertisement

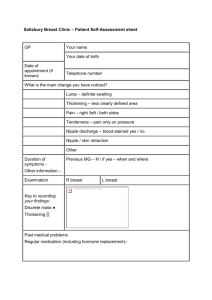
Skin and breast assessment 1 MENNONITE COLLEGE OF NURSING AT ILLINOIS STATE UNIVERSITY Diagnostic Reasoning for Advanced Practice Nursing 431 Skin and Breast Assessment Skin Assessment Anatomy and Physiology of the Skin, Hair, & Nails review Major function – body homeostasis o Protects underlying structures o Modulates temperature o Synthesized vitamin D Largest and heaviest (16% of body weight) organ of the body 3 layers (contain sebaceous and sweat glands) o Epidermis o Dermis o Hypodermis Hair Nails Sebaceous glands o On all surfaces except palms/soles o Secrete fatty substance through hair follicles Sweat glands o Eccrine – widely distributed, open onto skin surface, control body temp o Apocrine – in axilla & groin, stimulated by emotion Age Changes Infant Adolescents Pregnancy Adult Older adults Skin Lesions: Primary Flat o macule (freckle) o patch (vitiligo) Elevated o papule (<0.5 cm) o plaque (> 0.5 cm) o nodule o tumor o wheal o keloid (scars, piercings) Elevated, containing free fluid Skin and breast assessment 2 o o o vesicle (< 0.5 cm) bulla (> 0.5 cm) pustule Skin Lesions: Secondary Loss of Skin Surface o erosion o ulcer o fissure Material on the Skin Surface o Crust o Scale Skin Cancers Basal cell – shiny, translucent, slow growing, rarely metastasize, 80% Squamous cell – crusted, scaly, ulcerated, can metastasize, 16% Melanoma – 4% and rising o Screen using ABCDE (asymmetry, borders irregular, color change/variation, diameter ≥6 mm, elevated/enlargement o Risk factors – previous melanoma, age > 50, male, mole change, light eye/skin/hair color, sun exposure, family history Subjective; History CC – common concerns rash, hair loss, moles HPI PMH – skin cancer (most common cancer in U.S.) FH - melanoma SH – sun exposure (hands, neck, head) ROS – rashes, lumps, size/color/location of moles; changes in hair, skin, moles, new moles Prevention – regular self-exam, reporting changes in moles, moisturizing, use of sun screen/hats/sunglasses Objective; Physical Exam Examination begins with General survey (hair and nails discussed previously) Inspection and Palpation o Best done in gown with good light o Note characteristics – color, moisture, temperature, texture, turgor o Describe lesions color location pattern (arrangement) shape type o Use proper terminology! See Dains, chapter 25. Buy a good book and use in clinic. Example: Skin – warm, moist; no rashes, suspicious nevi, petechiae or ecchymoses. Nails-no clubbing or cyanosis. Hair – normal distribution, moderate (fine or thick) texture, no scalp scaling or nevi. Article – Lyons, F. (2012). Solving skin rash in primary care. Advance for NPs & PAs; April 2012: 30-33. Skin and breast assessment 3 Breast Assessment Anatomy Breast tissue made up of: o glandular tissue o fibrous tissue o subcutaneous tissue o fatty tissue Most concerned with glandular tissue Glandular tissue There are 15-20 lobes/breast Each lobe has 20-40 lobules Each lobule has milk-producing acini cells that lead to the lactiferous ducts that lead to the nipple Breast Anatomy Each breast has o 4 quadrants; UOQ, UIQ, LIQ, LOQ o Tail of Spence o Nipple Lymph nodes o Central (deep in axilla) o Pectoral (anterior) o Subscapular (posterior; lateral border of scapula) o Lateral (upper humerus; flow into infraclavicular and supraclavicular) Breast Cancer 12.28% lifetime risk of breast cancer in women Risk increases with aging Cure rate = 90% when nonpalpable, but found on mammography Most tumors in upper outer quadrant and Tail of Spence Breast Cancer: Risk Factors Age First degree relative Personal history of GYN, colon or thyroid cancer Early menarche (<12) Late menopause (>55) Nulliparity First child after age 30 Age Changes Tanner changes Adult female Pregnancy Menopause and after Male breast - gynecomastia Male breast cancer (ACS website) Skin and breast assessment 4 1/1000 lifetime risk, 1% of all breast cancers S/S – commonly a firm, non-painful mass below nipple, nipple change/discharge Increased risk with increased by elevated levels of estrogen, previous radiation exposure, and a family history Subjective; History CC – common concerns lump or mass, breast pain, nipple discharge HPI PMH – hormonal drugs, history of breast cancer, calcifications on mammograms, menstrual history, breast feeding, HRT, LMP FH – 1st degree relatives, early age SH – alcohol, diet/exercise, caffeine, tobacco ROS – breast pain/discomfort, lumps, nipple changes/discharge, self-exam, clinical exam, mammograms Prevention- reduce modifiable risk factors Objective; Physical Exam Inspection o Positions – arms at side, overhead, pressed on hips, leaning forward o Breast and nipple; skin color, size, shape, symmetry, discharge (drug related?) Palpation o Position – supine, arm above shoulder, position roll to flatten breast tissue; sittingmales o Systematic pattern – vertical strip or concentric circles o Nodules – describe o Nipple o Axilla nodes – sitting Breast Care (Controversy exists on the appropriate intervals for screening due to the evidence; consider guidelines below, patient desires and your assessment from H&P) Self-breast examination o Not recommended (ACS) o Advises against (USPSTF) Clinical exam o Ages 20-39, every 3 years; ages 40+, yearly; no upper age limit (ACS) o Ages 20-39, insufficient evidence; age 40+ consider (USPSTF) Mammogram o 40+ and no upper limit, annually (ACS) o 40-59 biannually (individual basis), 50-75 biannually, >75 insufficient evidence (USPSTF) Ultrasound Biopsy Case study-Lump, 2 Multiple Choice Questions & 4 Matching to be done in groups. Demonstration & practice of physical examination on model.