METHODS TO REDUCE PIXEL EXPANSION WITHOUT CHANGING
advertisement

METHODS TO REDUCE PIXEL EXPANSION WITHOUT
CHANGING THE IMAGE QUALITY
D.V SATISH KALADHAR REDDY1, CH.PRAVEEN KUMAR2, Mr R. KONDA REDDY 3
¹M.Tech 2ndyear, Dept. of CSE, ASCET, Gudur, India
2
M.Tech 2ndyear, Dept. of CSE, ASCET, Gudur, India
3,
1
Associate Professor, Dept. of CSE, PBR VITS, K a v a l i , In d ia
satheeshreddy562@gmail.com;2 praveenkumar539work@gmail.com;3rkondareddy75@gmail.com
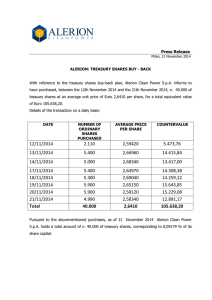
Abstract: Visual cryptography scheme (VCS) is one
sharing secret images. In the proposed mechanism,
of the techniques for secret sharing and encoding
using visual cryptography scheme, the idea is to split
the image into n shares distributed to n participants.
Only a set of qualified participants recover the
secret image without any cryptographic knowledge.
Extended visual cryptography scheme (EVCS) a
type of VCS which consists of shares stacked
together based on their associations (meaningful) as
against
random
Embedded
EVCS
shares
has
in
Traditional
provided
the
VCS.
better
competitive visual quality than with the other
EVCS’s.
In Embedded EVCS, there exists two
trade-offs between the large share pixel expansion
and visual quality of shares and between the secret
pixel expansion and visual quality of the shares. We
propose a solution in Embedded EVCS with reduced
pixel
expansion
and
improved
quality
by
introducing a Step construction to construct
VCSOR and VCSXOR [5] which have optimal pixel
expansion and contrast.
A secret image into two random shares (printed on
transparencies),
where
individual
transparencies
reveal no information about the secret image other
than the size of the secret image. The secret image
can be revealed by stacking the two shares. The
logical operation used for perfect reconstruction of
secret image. Traditional VCS [1] takes a secret
image as input, and gets shares as outputs to satisfy
two conditions:
Minimum number of shares can recover the
secret image, these shares are qualified
shares.
Other than qualified subset of shares, no
other shares can produce or reveal the
secret image other than size of the original
image.
Compared with the shares of the VCS,
Extended VCS (EVCS) is the one which is capable of
Keywords: secret sharing, visual quality, pixel
generating meaningful shares introduced by Naor et
expansion, Step Construct, VCSOR and VCSXOR.
al [4].The EVCS takes a secret image and the
INTRODUCTION
The principle of visual cryptography scheme
(VCS) was first introduced by Naor and Shamir. VCS
is for sharing secret information that focuses on
original share images as input and generates shares
that can satisfy the criteria given below.
Secret image can be recovered from any
subset of shares.
Forbidden shares can’t be used to obtain
secret image.
All the shares are meaningful images.
al [4] introduced extended VCS suitable for natural
According to the Wang et al, EVCS have
images to improve quality of output image. To
general access structure and suffer from pixel
improve the visual quality of natural images to apply
expansion problem that will enlarge the size of the
affine transformation to reduces the contrast of input
shares and decrease the contrast of recovered image.
images. In EVCS have limitations:
In embedded EVCS [4], an EVCS was
1. Computation expensive.
constructed by embedding random shares of secret
2. Void and cluster algorithms makes positions of the
image into the meaningful covering shares. The
secret pixels dependent on content of share images.
shares of EVCS are meaningful images, and stacking
3. Pair of complementary images is required.
of a qualified subset of shares will recover the secret
Generating the covering shares by using dithering
image visually.
matrices and then extended to general access
In traditional VCS, same pixel expansion is
structure. To improve the quality of image and
applied for all share images and each participant has
contrast to introduce embedded EVCS. Embedded
one share image. According to velumurugan et al [5]
EVCS has provided the better competitive visual
each participant may have multiple share images with
quality than with the other EVCS’s. In Embedded
different pixel expansions. In his paper, they focus on
EVCS, Two trades-offs between the share pixel
black and white images, white pixel is denoted by 0
expansion and visual quality of shares and between
and black pixel is denoted by 1. Using values 0’s and
the secret pixel expansion and visual quality of the
1’s the OR and XOR operation used to recover the
shares.
secret image. For each participant, average pixel
expansion (APE) of share images are calculated that
The embedding process:
each participant holds. Here they use quantum key
Input: The n covering shares constructed in the
distribution protocol which works on network
corresponding VCS (C0, C1) with pixel expansion m
security by the use of key agreement. Trusted center
and the secret image I.
provide a unique secret key and shared by each user
Output: The n embedded shares e0, e1….en-1.
and generate a key with the help of algorithms and
Step 1: Dividing the covering shares into blocks that
quantum mechanics for network security. We can
Contain t sub pixels each.
apply the concept of APE of shares in Embedded
Step 2: Choose m embedding positions in each block
EVCS and get optimal Pixel expansion and improved
in the n covering shares.
contrast image. This helped us in eliminating the
Step 3: For each black (respectively, white) pixel in I,
trade-off between the pixel expansion and the visual
randomly choose a share matrix M€C1 (respectively,
quality of the image.
M€C0).
Step 4: Embed the m sub pixels of each row of the
EXISTING SYSTEM
Extended VCS is a kind of cryptography
which encodes a number of images and stacking
meaningful images to get original image. Nakajima et
share matrix M into the m embedding positions
Chosen in Step 2.
According to Lee and Chiu et al [7]to solve the pixel
expansion problem
introduced a two-phased
encryption algorithm of (ҐQual, ҐForb), EVCS for
GASs. In the solution procedures first phase, it
generates intermediate shares of (ҐQual, ҐForb) VCS.
These intermediate shares have no appropriate
appearance and no pixel expansion. In the second
phase, cover images I1, I2 will be added in these Ishares to yield the resultant shares of (ҐQual, ҐForb).
Fig: Embedding process
Advantages:
From GAS Solver by taking secret image it encrypts
the image and forward to share synthesizer and this
Deal with gray-scale input images.
synthesizer will encrypt the images into shares. These
Applied on general access structure.
shares are embedded into the images I1, I2 by the
Not require pair of complementary input
stamper.
share images and participants needs only to
take one share.
Disadvantages:
Large pixel expansion.
Bad visual quality of recovered secret
image.
PROPOSED SCHEME
An Extended VCS is kind of VCS, which
adds a meaningful cover image in every share to
address the management problem as against random
shares in Traditional VCS. Of the limitations in
EVCS 2 of them according to Wang et al [4] are 1)
Large pixel expansion 2) Bad visual quality of shares
and recovered secret image. In proposed scheme,
each participant has multiple share images with
different pixel expansions. Then finally compute
average pixel expansion .In this paper, introduced a
step construction which have optimal pixel expansion
and contrast to construct VCSOR and VCSXOR for
each qualified set in general access structure by
applying (2,2)-VCS [5]recursively, than a participant
may receive multiple share images. To reduce
average pixel expansion (APE) our proposed scheme
applies a technique to simplify the access structure.
Fig:Solution procedures for EVCS
Advantages:
Reduces pixel expansion.
Improves quality of recovered secret image.
PROPOSED ALGORITHMS
There are mainly two major differences in stamping
algorithm to stamp cover images on I-shares
produced in first phase. These are:
1.
The solution procedure for EVCS is mainly
rather than redesign a code book for a
two phases. In first phase, generates intermediate
particular VC scheme than no pixel
shares (i.e. I1… In) of (ҐQual, ҐForb)-EVCS. I-shares
have a meaningless appearance and no pixel
expansion.
To locate cover images on shares directly
expansion occurs.
2.
Black pixel density of the cover images
can be adjusted on demand in a finegrained fashion.
Our proposed approach has better performances
in display quality of the recovered image, which
includes contrast, perfect reconstruction of black
secret pixels, and maintenance of the same aspect
ratio as that of the original secret image. The
proposed algorithms have four advantages:
In second phase, these cover images are
Generic approach: All existing schemes
added to the I-shares to get the resultant shares of
(ҐQual, ҐForb)-EVCS (i.e. P1…Pn).
modified
with extended VC schemes
without
redesigning codebooks.
Modularity: Each phase in the encryption
procedure is individually designed and also
can be replaced separately.
The first phase applicable not only to the
extended
VC
schemes
but
also
for
conventional VC schemes.
It is very helpful for modifying the display
quality of the cover images because the
density of the cover images is adjustable.
RESULTS
In this approach estimate the performance of
EVCS optimization model by comparing with other
VC results for GASs. In below table shows
Ateniese’s and Liu’s approaches have the same pixel
expansion for recovered image. By combining Liu’s
partition results, Ateniese’s approach has smaller
pixel expansion. To apply the EVCS encryption in
our approach is still pixel-expansion-free.
Fig: contrast (%) of recovered image.
CONCLUSION
In the existing embedded EVCS system,
shares are meaningful images and recover the secret
image visually by stacking qualified subset of shares.
Embedded EVCS has higher pixel expansion and
small contrast. Our approach successfully resolves
the two trade-offs between the share pixel expansion
Compare to other two approaches, EVCS encryption
and visual quality of shares and between the secret
approach
pixel
pixel expansion and visual quality of the shares. In
expansion of recovered image which includes
the modified Embedded EVCS, step construction
contrast, perfect reconstruction of black secret pixels
generates VCSOR and VCSXOR which have optimal
and maintenance of the same aspect ratio as that of
pixel expansion and contrast for each qualified set in
secret image.
general access structure by applying (2,2)-VCS
gives
better
performance
for
recursively, apart from the underlying operation OR
or XOR, where a participant may receive multiple
share images. Also, our proposed approach, a twophase encryption algorithm for the EVCS for general
access structures, solves pixel expansion problem and
improves quality/contrast of secret image.
REFERENCES
1.
Fig: comparison of APE.
2.
3.
M.
Naor and A. Shamir, “Visual
Cryptography,” in {EUROCRYPT’94},
Berlin, 1995, vol 950, pp. 112, SpringerVerlag, LNCS.
S. Droste, “New results on visual
cryptography,” in CRYPTO’96, 1996, vol.
1109, pp. 401-415, SpringerVerlagLNCS.
D.S.Wang, F.Yi, andX.B.Li, “On general
construction
for
extended
visual
4.
5.
6.
7.
cryptography schemes,” Pattern Recognit.,
vol. 42, pp.3071–3082, 2009.
Feng Liu and Chuankun Wu, Senior
Member, IEEE, “Embedded Extended
Visual Cryptography
Schemes,” IEEE
transactions on information forensics and
security, vol. 6, no. 2, June 2011.
Velmurugan.N, Vijayaraj.A, “Visual Pixel
Expansion of Secret Image”, Global Journal
of Computer Science and Technology,
Volume 11 Issue 20 Version 1.0 December
2011.
K.g.ilavarasan, R.malavika, “A multiple
level visual cryptography scheme for
biometric privacy
without pixel
expansion” International Journal of
Communications and Engineering, Volume
04 – No.4, Issue: 01 March2012.
Kai-Hui Lee and Pei-Ling Chiu,“ An
Extended Visual Cryptography Algorithm
for General Access Structures” ieee
transactions on information forensics and
security, vol. 7, no. 1, February 2012.
AUTHORS
D.V
Sateesh
Kaladhar
Reddy received B. Tech in
Computer
Sciences
Engineering from the PBR
Visvodaya Institute of Science
& Technology affiliated to the
Jawaharlal
Nehru
technological
university
Anantapur, in 2011, and
pursing M. Tech in Software Engineering
from the Audisankara College of
Engineering and Technology engineering
affiliated to the Jawaharlal Nehru
technological university Anantapur in 2014,
respectively. He Published SIX International
Journals and He Participated TWO
International conferences and SIX National
conferences and He Participated SEVEN
National Level Paper Symposiums in
different Colleges. His interests are
Computer Networks, Mobile Computing,
Network Programming, and System
Hardware. He is a member of the IEEE.
CH.
Praveen
Kumar
received
B.Tech
in
Computer
Science
Engineering from the PBR
Visvodaya
Institute
of
Technology
&
Science
affiliated to the Jawaharlal
Nehru
technological
university Anantapur, in
2013, and pursuing M.Tech in Computer
Science Engineering from the Audisankara
College of Engineering and Technology
affiliated to the Jawaharlal Nehru
technological university Anantapur in 2015.
He Published THREE International Journal
and TWO National conferences. And
Participated THREE National Level Paper
Symposiums in different Colleges. He is a
member of the IEEE.
Mr.R.KondaReddy
has
received his MCA Degree at
Sri
Krishna
Devaraya
University Campus College
affiliated to Sri Krishna
Devaraya University in 2000
and M.Tech Degree in
Computer science
from
Allahabad
Agriculture
Institute –Deemed University
in 2006. Now He is pursuing
Ph.D. from Rayalaseema University. He is
dedicated to teaching field from the last 11
years. He has Guided 15 P.G and 40 U.G
students. His research areas Included
Computer Networks/Mantes Routing. At
present he is working as Associate Professor
in PBR Visvodaya Institute of Technology
& Science, Kavali, and Andhra Pradesh,
India.