Answers to the RI and UC questions
advertisement

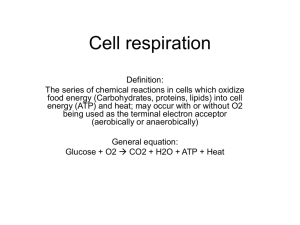
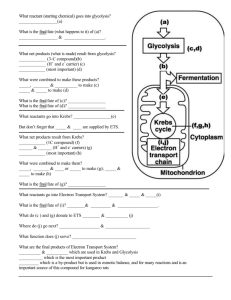
Answers to the RI and UC questions Reviewing Ideas 1. How are membranes involved in respiration? Membranes are the site of the electron transport system in the mitochondria. Also, many Krebs-cycle enzymes are membrane-bound. The plasma membrane serves a similar function in prokaryotes. 2. Where in a cell does each part of cell respiration take place? Describe how the location of each part of the process is different in bacteria an din more complex cells. The cytosol is the site of glycolysis in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The mitochondrion is the site of the Krebs cycle and the electron transport system in eukaryotes, while the plasma membrane serves that function in bacteria. 4. What are the biological functions of these processes? a. Cell respiration: breaks down food molecules in steps that allow the cell to conserve the food’s energy in usable packets of ATP b. glycolysis: produces stored energy in the form of ATP, NADH needed for ATP synthesis, carbon skeletons for biosynthesis and pyruvate needed for the Krebs cycle c. Krebs cycle: forms ATP for energy, NADH an dFADH for ATP synthesis, and carbon skeletons for biosynthesis. d. electron transport chain: forms ATP for energy 5. Discuss the ways in which biosynthesis depends on cell respiration? Biosynthesis depends on cellular respiration for energy in the form of ATP and for carbon skeletons to be used as building blocks during biosynthetic reactions 6. How does the Krebs cycle depend on glycolysis? How does the electron transport chain system depend on the Krebs cycle? The Krebs cycle depends on glycolysis for a supply of pyruvate. The electron transport system depends on the Krebs cycle for hydrogen atoms supplied in the form of NADH and FADH2 Understanding Concepts 2. Why would you not expect to find mitochondria in anaerobic organisms? Anaerobic organisms live by fermentation, which occurs in the cytosol. Mitochondria provide the sites for the Krebs cycle and the electron transport system, which are not used by bacteria 6 and 8 on page 2 6. Some cells contain no mitochondria at maturity. If these cells receive ample glucose, could they use it for energy? Would they release carbon dioxide? Could these cells use fat as a source of energy? Explain your answers. Cells lacking mitochondria can use glucose to produce energy. Since they cannot carry out the Krebs cycle or electron transport, they do not produce carbon dioxide. Such cells could not use fat as a source of energy because fats enter respiration through the Krebs cycle. 8. The complete oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide produces about 686 kcal of free energy. Oxidation of a molecule of glucose in a cell generates a maximum of 38 molecules of ATP. ATP provides about 7.3 kcal of energy. Calculate the efficiency of the ATP energy yielded from the complete aerobic respiration of glucose. What happens to the rest of the energy? Using the values provided, the efficiency of aerobic respiration of glucose is about 40%. The rest of the energy is converted to heat.