L2: Lenses
advertisement

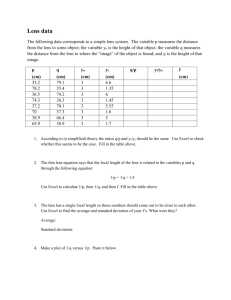
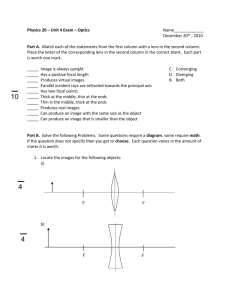
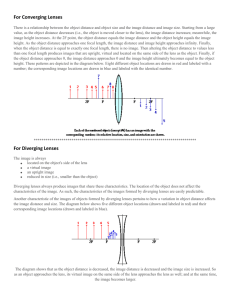
L2: Lenses Theory The source distance s, image distance i, and focal length f of a thin lens are related by 1/s + 1/i = 1/f. In this lens experiment you will investigate some of the consequences of this equation. For example, if the source is very far from the lens (s=), then i=f. Also, if s and i are both positive (therefore the image is real), then the source and image may be interchanged and the equation will still be satisfied. The lateral magnification of the image is given by M(image height/source height)=i/s. Procedure 1. Obtain a converging lens. How did you determine that it was a converging lens? Determine its focal length using two different methods. Record your measurements and results for the focal lengths. 2. Make a ray diagram for each of the methods used in 1. 3. Using the optical bench equipment, find two lens positions which will form an image on the screen when the lens is converging and the object and screen do not move. Measure and record the two source distances, s1 and s2. (Measure from the front of the light source.) 4. Measure and record the sizes of the two images in step 3 as well as the source. Use this data to calculate the two corresponding magnifications, M1 and M2. 5. Obtain a diverging lens. How can you verify that it really is a diverging lens? Attempt to form an image on the screen. Were you able to do it? 6. Take the diverging lens in your hand and look through it at the trees outside the window. What kind of an image are you seeing, real or virtual? Upright or inverted? Enlarged or reduced? Analysis 7. Show mathematically that there should be two converging lens positions in step 3 which produce images on the fixed screen. Also show that theoretically M1=1/M2. 8. How well do your two experimental magnifications from step 4 obey the theoretical reciprocal relation in step 7? (Calculate the percent error.) 9. Calculate the percent difference for your two focal lengths for the converging lens in step 1. Use %-difference=100%|difference|/(average value). 10. Using the lens equation, explain why you were unable to form an image on the screen with the diverging lens in step 5. (Hint: The focal length for a diverging lens is negative.) 11. Summarize what you did and what you found out.