Chem 2.6 Assess schedule 08
advertisement
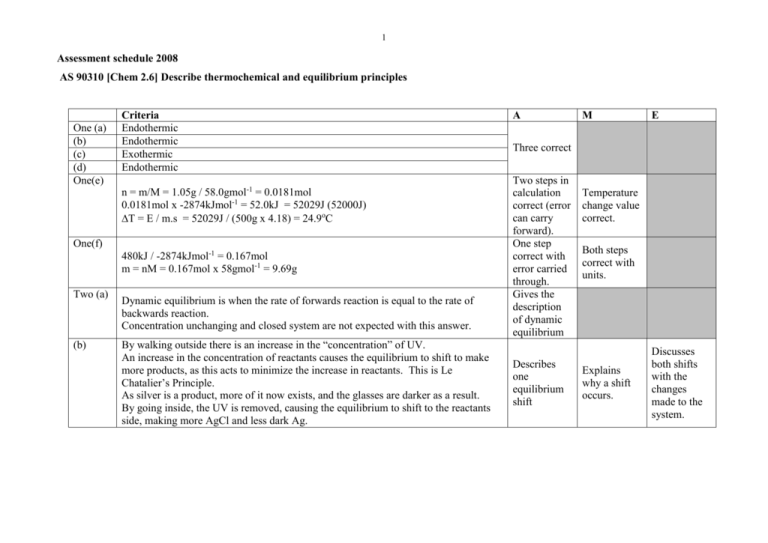
1 Assessment schedule 2008 AS 90310 [Chem 2.6] Describe thermochemical and equilibrium principles One (a) (b) (c) (d) One(e) Criteria Endothermic Endothermic Exothermic Endothermic n = m/M = 1.05g / 58.0gmol-1 = 0.0181mol 0.0181mol x -2874kJmol-1 = 52.0kJ = 52029J (52000J) T = E / m.s = 52029J / (500g x 4.18) = 24.9oC One(f) 480kJ / -2874kJmol-1 = 0.167mol m = nM = 0.167mol x 58gmol-1 = 9.69g Two (a) (b) Dynamic equilibrium is when the rate of forwards reaction is equal to the rate of backwards reaction. Concentration unchanging and closed system are not expected with this answer. By walking outside there is an increase in the “concentration” of UV. An increase in the concentration of reactants causes the equilibrium to shift to make more products, as this acts to minimize the increase in reactants. This is Le Chatalier’s Principle. As silver is a product, more of it now exists, and the glasses are darker as a result. By going inside, the UV is removed, causing the equilibrium to shift to the reactants side, making more AgCl and less dark Ag. A M E Three correct Two steps in calculation correct (error can carry forward). One step correct with error carried through. Gives the description of dynamic equilibrium Describes one equilibrium shift Temperature change value correct. Both steps correct with units. Explains why a shift occurs. Discusses both shifts with the changes made to the system. 2 Three(a) Expect six CO, three O2, one CO2 (based on two CO2’s converting) or similar. When temperature is increased, the equilibrium acts to minimize this increase. Endothermic reactions (in this case backwards reactions) occur. This decreases the concentration of CO2 and increases the concentration of CO and O2. (b) Expect no change drawn (therefore four CO, two O2 and three CO2). A catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium position / concentration of the species. The catalyst does speed up the rates of forwards and backwards reactions. (c) Expect two CO, one O2 and five CO2 (based on two CO’s and one O2 converting). When the pressure is increased the system acts to reduce that pressure. The equilibrium will shift to the side with the fewest gaseous particles; in this case the forwards reaction is favoured. This increases the concentration of CO2 and decreases the concentration of CO and O2. Four(a) [CO2 ]2 Kc [CO]2 [O2 ] (b) A high value of Kc like 2.48 x 106 suggests a very high concentration of products (CO2) and low concentrations of reactants (CO and O2), because a large numerator in the Kc expression causes a large Kc value. (c) (d) Five(a) [ N 2O5 ]2 Kc [ NO2 ]4 [O2 ] NO2 will be circled. With a very small Kc value in this equilibrium, it means that the denominator of the Kc expression is large, therefore a high concentration of NO2 (and O2) and a small concentration of N2O5. 4 x 10-13 0.0250 12.4 -11 -4 1.58x10 6.31x10 10.8 0.00568 1.76x10-12 2.2 Has drawn two correct sketches Has two of (a), (b) or (c) correct, including the sketches OR OR Any one of (a), (b) or (c) fully correct. Has all three correct with appropriate detail. All three correct but lack detail. Kc expression correct OR description of what it means. All parts correct. Kc expression correct OR description of what it means. All parts correct. Two correct Four correct Six correct 3 Five(b) Six(a) (b) NaOH is a strong base, and NH3 is a weak base. A strong base, when it dissolves completely, creates the same concentration of hydroxide ions as the concentration of the solution. NaOH Na+ + OHA weak base, when it completely dissolves, only partially dissociates with water, creating a low concentration of hydroxide ions in water. NH3 + H2O <-> NH4+ + OH-. It is the concentration of hydroxide ions that creates the pH, not the concentration of the solution. A high concentration of hydroxide ions leads to a much higher pH, therefore NaOH has a higher pH. HCl + NaHCO3 NaCl + H2O + CO2. (State symbols not required) Because the same mass of NaHCO3 was used for each reaction the amount of substance is the same. Therefore with acid in excess the same volume of gas would be produced. The HCl has a higher concentration of H+ ions available at any one time to react with the NaHCO3, therefore there is a greater chance that an effective collision occurs, making the rate greater. The reaction will be completed sooner. The fruit acid has a lower concentration of H+ ions available at any one time, therefore there is a lesser chance that an effective collision occurs, making the rate slower. Volume of CO2 (mL) (e) Fruit acid - - - HCl ________ Time (s) Has identified strong vs weak Explains the link between strong/weak and hydroxide concentration OR link from OH- to pH Correct Describes a difference or similarity between the two reactions. Explains both a difference and a similarity. Diagram of rate clearly has the fruit acid line below the HCl line OR Same volume of gas clearly shown. Both comparative lines and same final volume correct. Fully labeled. Discusses in full as per evidence or similar. Equations necessary. Discusses why the difference and similarity exist, with links to the acid strength. 4 Seven(a) Carbonic anhydrase is a catalyst / catalytic enzyme. It lowers the activation energy required for reaction to occur / provides an alternative reaction pathway / provides a surface to react on / orientates reactants for correct collision. (b) Because the particles are of different sizes, there is a greater surface area on 1mm particles than 2mm and then 3mm. By having a greater surface area, more surface of the egg shell is available to collide with the acid at any one time. An increase in collisions means a greater chance that effective collisions occur, meaning that the production of CO2 will be faster. (c) A higher temperature means that the acid particles are traveling with greater kinetic energy. A faster particle has a better chance of overcoming activation energy when it collides, so there is a greater chance that the collisions are effective. If more collisions are effective then production of CO2 will be faster. (a) is correct OR Aspects of either (b) or (c) are correct. Either (b) or (c) are completely correct OR Incomplete explanations for both are given. All parts (a), (b), (c) are correct with appropriate detail. Judgement statement Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence SEVEN questions answered correctly. EIGHT questions answered correctly, including at least FIVE at Merit level. Minimum of 7 x A. Minimum of 5 x M + 3 x A. EIGHT questions answered correctly, including at least THREE at Excellence level and THREE at Merit level. Minimum of 3 x E + 3 x M + 2 x A.








