Chapter 26 - Quantitative Genetics
advertisement

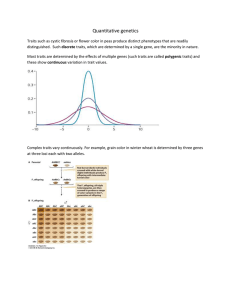
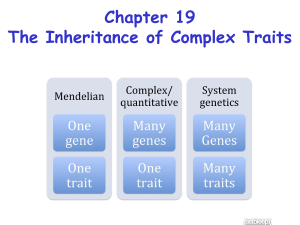
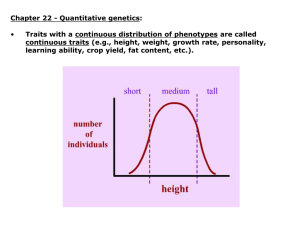
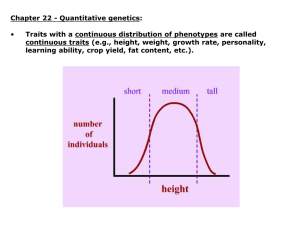
Chapter 26 Quantitative Genetics Study Outline 1. Overview of quantitative traits a. Many quantitative traits exhibit a continuum of phenotypic variation that follows a normal distribution 2. Statistical methods for evaluating quantitative traits a. Statistical methods are used to evaluate a frequency distribution quantitatively b. Some statistical methods compare two variables with each other 3. Polygenic inheritance a. Polygenic inheritance and environmental factors may produce a continuum of phenotypes b. Quantitative trail loci (QTLs) are now mapped by linkage to known molecular markers 4. Heritability a. Both genetic variance and environmental variance may contribute to phenotypic variance b. Phenotypic variation may also be influenced by interactions and associations between genotype and the environment c. Heritability is the relative amount of phenotypic variation that is due to genetic variation d. Heritability of dermal ridge count in human fingerprints is very high e. Heritability values are relevant only to particular groups raised in a particular environment 5. Selective breeding a. Selective breeding of species can alter quantitative traits dramatically b. Selective breeding provides a way of estimating heritability












![Quantitative genetics and evolutionary response to selection PowerPoint [similar to notes above but with images]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015396285_1-97c7e079eddce5063bdf93c6f1e31f5b-300x300.png)