Earth`s Structure and Processes Test 1 1. What are the only things
advertisement

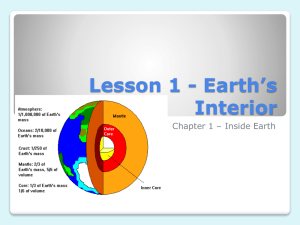
Earth’s Structure and Processes Test 1 1. A B C D What are the only things found in the lithosphere? Piedmont and Sandhills region oceans and rivers barrier islands and beaches crust and parts of the mantle 2. Below the uppermost brittle, rigid Earth layer there is a soft, plastic-like layer that contains hot, slowly flowing A B C D material. What is this layer called? outer core asthenosphere inner core lithosphere 3. A B C D The crust and uppermost part of the Earth’s mantle form a brittle, rigid layer. What is this layer called? outer core asthenosphere atmosphere lithosphere 4. A B C D What is the correct order of the three interior layers of Earth from outermost layer to innermost layer? core, mantle, crust mantle, core, crust crust, mantle, core crust, core, mantle 5. A B C D What are the two most common elements in Earth’s crust? oxygen and silicon oxygen and hydrogen carbon and iron carbon and sulfur 6. A B C D As you go deeper and deeper into Earth’s interior, what happens to the pressure and temperature? both decrease pressure increases and temperature decreases temperature increases and pressure decreases both increase 7. A B C D Which answer describes Earth’s crust? the thinnest layer of Earth the thickest layer of Earth made of molten iron and nickel made of solid, compressed, melted metals 8. A B C D Which answer describes Earth’s outer core? the thinnest layer of Earth the thickest layer of Earth made of molten iron and nickel made of solid, compressed, melted metals 9. A B C D Which answer describes Earth’s mantle? the thinnest layer of Earth the thickest layer of Earth made of molten iron and nickel made of solid, compressed, melted metals 10. A B C D Which pair matches a type of seismic wave with its correct abbreviation? E - Coastal K - Convergent P – Primary X – Tectonic 11. A B C D How do surface waves compare to other seismic waves? Surface waves are the longest lasting. Surface waves are the most common. Surface waves are the most damaging. Surface waves are the fastest moving. 12. A B C D What are the three types of seismic waves produced by earthquakes? primary, secondary, tertiary primary, secondary, surface surface, underground, oceanic surface, underwater, atmospheric 13. Which type of seismic wave moves through solid rock and moves at a right angle to primary waves, causing rocks to A B C D move up and down and side to side? surface primary secondary tertiary 14. Earthquake waves travel faster through Earth’s mantle than through the crust. What does this information tell us A B C D about Earth’s mantle? The mantle is less dense than the crust. The mantle is the same density as the crust. The mantle is denser than the crust. The mantle is the same density as the core. 15. A B C D What causes Earth’s magnetic field? the movement of materials in the outer core of Earth the movement of materials in Earth’s crust the movement of seismic waves the movement of iron and nickel in the mantle 16. A B C D Which phenomenon is believed to be the cause of Earth’s magnetic field? The iron in the ocean floor lines up from the North Pole to the South Pole. Earth’s atmosphere holds in all magnetic particles. A solid inner core spins inside a molten moving outer core. A molten inner core moves inside of a solid outer core. 17. A B C D How does a compass always respond to Earth’s magnetic field? It always spins in circles. It always points south. It always points in the direction that you are walking. It always points north. 18. Seismologists monitored the behavior of seismic waves through a certain area. They observed that the S waves did A B C D not travel through this area. Using this information, what could they infer about the type of material in this area? The area is composed of gravel. The area is composed of solid iron. The area is composed of solid rock. The area is composed of molten rock. 19. A B C D What type of instrument measures and records seismic waves? seismometer seismograph seismogram seismonitor 20. Using the map below and the triangulation method, approximately where is the epicenter of this earthquake? W X A B C D W X Y Z Y Z The diagram below represents how seismologists plot circles on a map and use the triangulation to determine the epicenter of an earthquake. Use this diagram to answer the next 3 questions. New York Seismograph A Tennessee Seismograph B C Alabama D Seismograph 21. A B C D What does the circle around a seismographic station represent? The distance of the earthquake’s focus from the seismographic station. The time it took for the P waves to reach the seismographic station. The time it took for the S waves to reach the seismographic station. The distance of the earthquake’s epicenter from the seismographic station. 22. A B C D Which point on the diagram marks the epicenter of the earthquake? A B C D 23. A B C D The epicenter cannot be determined with only New York and Alabama’s seismographic data. Why? The circles around these stations intersect in two different locations. The circles around these stations intersect in only one location. The circle around Alabama is too small. New York is too far away from the epicenter. 24. A B C D Which measurement helps determine how far an earthquake’s epicenter is from a seismograph? the wavelength of the P wave the wavelength of the S wave the difference in the time between the arrival of the P wave and the S wave the sum of the time between the arrival of the P wave and the S wave 25. A B C D How can limestone be formed? by chemical processes only by organic activity only either by chemical processes or by organic activity either by fragmenting of other rock or by chemical processes 26. A B C D What is intrusive or plutonic igneous rock? magma that cooled slowly lava that cooled on the surface basalt rock and obsidian magma that formed and cooled underground 27. What process does the number “3” in the rock-cycle diagram show? A B C D weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition chemical change due to heat and pressure cooling and solidifying melting under extremely high temperature 28. What will happen to a sedimentary rock, such as sandstone, if it is buried and subjected to moderate heat and A B C D pressure? It will become a clay rock. It will become a metamorphic rock. It will become a plutonic rock. It will become a volcanic rock. 29. A B C D What forces acting on other rocks produce metamorphic rocks? heat only chemical action and pressure pressure and heat heat and chemical action 30. Sedimentary rocks can be sorted according to particle size. Which list below is correctly sorted from the smallest to A B C D the largest particle size? sandstone → breccia → shale breccia → shale → sandstone breccia → sandstone → shale shale → sandstone → breccia Use this diagram to answer the next 2 questions. 31. A B C D Which types of rock could change into a metamorphic rock? igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic igneous and sedimentary sedimentary only igneous only 32. A B C D If a rock has formed from molten material, such as magma or lava, what type of rock is it? clastic igneous sedimentary chemical ANSWER KEY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. D B D C A D A C B C C B C C A C D D B D D C A 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. C C D B B C D A B