Ionic Compounds
advertisement
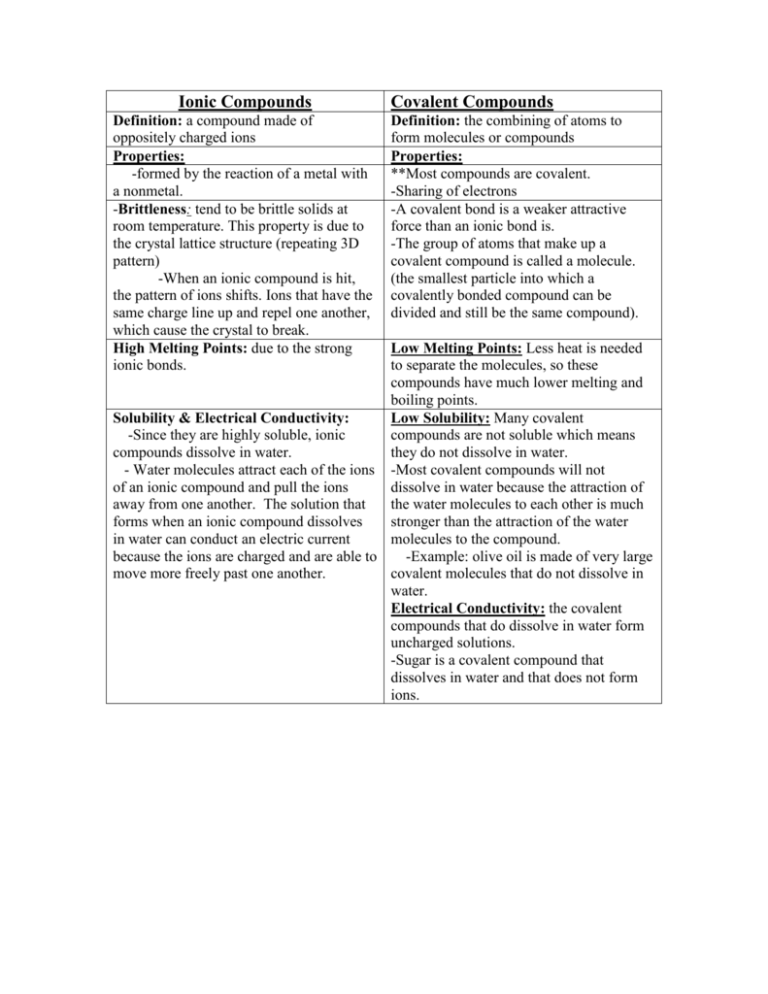
Ionic Compounds Definition: a compound made of oppositely charged ions Properties: -formed by the reaction of a metal with a nonmetal. -Brittleness: tend to be brittle solids at room temperature. This property is due to the crystal lattice structure (repeating 3D pattern) -When an ionic compound is hit, the pattern of ions shifts. Ions that have the same charge line up and repel one another, which cause the crystal to break. High Melting Points: due to the strong ionic bonds. Covalent Compounds Definition: the combining of atoms to form molecules or compounds Properties: **Most compounds are covalent. -Sharing of electrons -A covalent bond is a weaker attractive force than an ionic bond is. -The group of atoms that make up a covalent compound is called a molecule. (the smallest particle into which a covalently bonded compound can be divided and still be the same compound). Low Melting Points: Less heat is needed to separate the molecules, so these compounds have much lower melting and boiling points. Low Solubility: Many covalent Solubility & Electrical Conductivity: -Since they are highly soluble, ionic compounds are not soluble which means compounds dissolve in water. they do not dissolve in water. - Water molecules attract each of the ions -Most covalent compounds will not of an ionic compound and pull the ions dissolve in water because the attraction of away from one another. The solution that the water molecules to each other is much forms when an ionic compound dissolves stronger than the attraction of the water in water can conduct an electric current molecules to the compound. because the ions are charged and are able to -Example: olive oil is made of very large move more freely past one another. covalent molecules that do not dissolve in water. Electrical Conductivity: the covalent compounds that do dissolve in water form uncharged solutions. -Sugar is a covalent compound that dissolves in water and that does not form ions.