TWO MUSLIM EMPIRES: MALI AND DELHI
advertisement
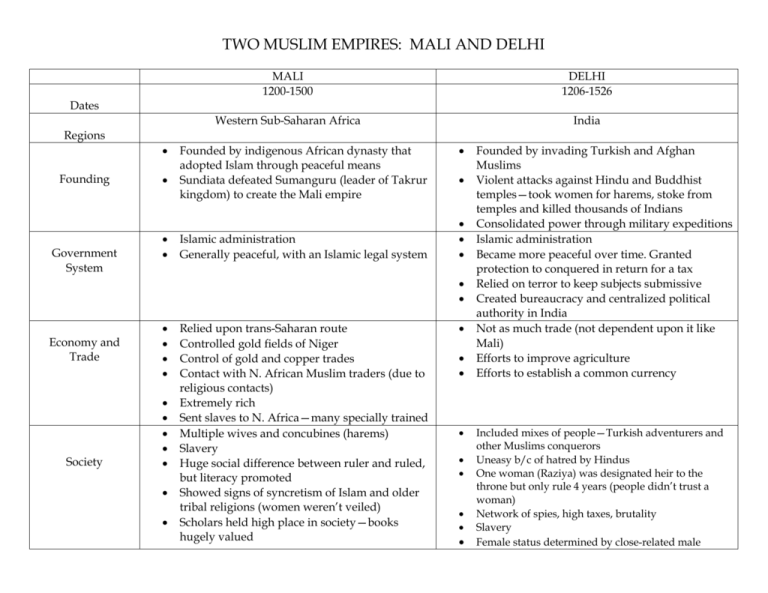
TWO MUSLIM EMPIRES: MALI AND DELHI MALI 1200-1500 DELHI 1206-1526 Western Sub-Saharan Africa India Dates Regions Founding Government System Founded by indigenous African dynasty that adopted Islam through peaceful means Sundiata defeated Sumanguru (leader of Takrur kingdom) to create the Mali empire Islamic administration Generally peaceful, with an Islamic legal system Economy and Trade Society Relied upon trans-Saharan route Controlled gold fields of Niger Control of gold and copper trades Contact with N. African Muslim traders (due to religious contacts) Extremely rich Sent slaves to N. Africa—many specially trained Multiple wives and concubines (harems) Slavery Huge social difference between ruler and ruled, but literacy promoted Showed signs of syncretism of Islam and older tribal religions (women weren’t veiled) Scholars held high place in society—books hugely valued Founded by invading Turkish and Afghan Muslims Violent attacks against Hindu and Buddhist temples—took women for harems, stoke from temples and killed thousands of Indians Consolidated power through military expeditions Islamic administration Became more peaceful over time. Granted protection to conquered in return for a tax Relied on terror to keep subjects submissive Created bureaucracy and centralized political authority in India Not as much trade (not dependent upon it like Mali) Efforts to improve agriculture Efforts to establish a common currency Included mixes of people—Turkish adventurers and other Muslims conquerors Uneasy b/c of hatred by Hindus One woman (Raziya) was designated heir to the throne but only rule 4 years (people didn’t trust a woman) Network of spies, high taxes, brutality Slavery Female status determined by close-related male MALI DELHI Technology Internal threats External threats Wealth attracted attackers Tuareg (Berber people) retook Timbuktu in 1433 By 1500, Mali had last much of its territory Spread through generally peaceful means— mostly trade contact Mansa Masu’s pilgrammage to Mecca in 1324— showed off Mali’s wealth and brought attention to the kingdom Masu built new mosques and opened Quranic schools Fostered trade contacts with other Islamic areas After decline of Mali, central Sudan city-states and empire adopted Islam and official religion Associated with the spread of literacy in region Role of Islam Decline Incompetent rulers (Mansa Suleiman’s successors) Rebellions amongst various groups within Cities along the upper Niger survived the collapse Trade and intellectual life moved to other African states in central Sudan Used crossbows and iron stirrups in conquest of India Introduces papermaking to India Harsh military reprisals to put down rebellions Personal and religious rivalries amongst Muslim elite Discontent of Hindus Bengal broke off to empire Mongol threats from NE 1398 Mongol leader Timur captured the city of Delhi—left the next year with thousands of captive and large amount of pillage—ruined the city Initial suppression of Hinduism Sometimes religiously tolerant, other time continued oppression (especially w/ high taxes) Acquired a permanent place in South Asia Buddhism virtually destroyed in India Muslim nobles created Bahmani Kingdom and Hindus created Vijayanagar Empire which split the Delhi Sultanate