Example - boutlis.com
advertisement
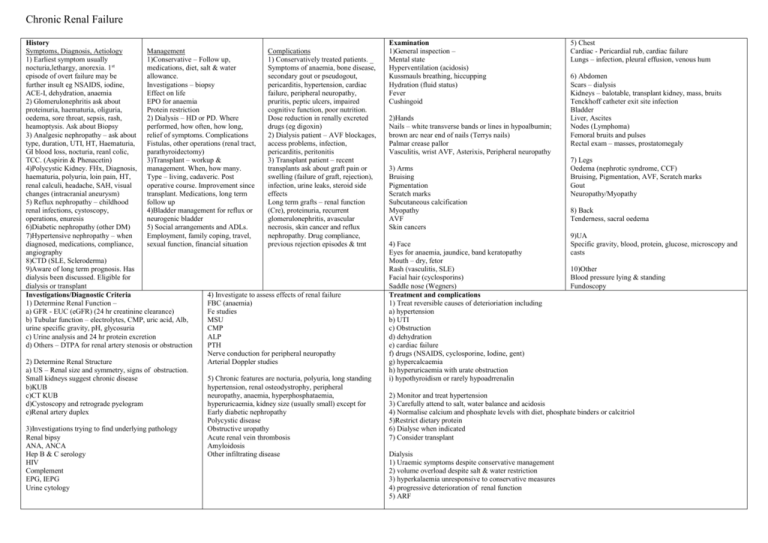
Chronic Renal Failure History Symptoms, Diagnosis, Aetiology Management Complications 1) Earliest symptom usually 1)Conservative – Follow up, 1) Conservatively treated patients. _ nocturia,lethargy, anorexia. 1st medications, diet, salt & water Symptoms of anaemia, bone disease, episode of overt failure may be allowance. secondary gout or pseudogout, further insult eg NSAIDS, iodine, Investigations – biopsy pericarditis, hypertension, cardiac ACE-I, dehydration, anaemia Effect on life failure, peripheral neuropathy, 2) Glomerulonephritis ask about EPO for anaemia pruritis, peptic ulcers, impaired proteinuria, haematuria, oliguria, Protein restriction cognitive function, poor nutrition. oedema, sore throat, sepsis, rash, 2) Dialysis – HD or PD. Where Dose reduction in renally excreted heamoptysis. Ask about Biopsy performed, how often, how long, drugs (eg digoxin) 3) Analgesic nephropathy – ask about relief of symptoms. Complications 2) Dialysis patient – AVF blockages, type, duration, UTI, HT, Haematuria, Fistulas, other operations (renal tract, access problems, infection, GI blood loss, nocturia, reanl colic, parathyroidectomy) pericarditis, peritonitis TCC. (Aspirin & Phenacetin) 3)Transplant – workup & 3) Transplant patient – recent 4)Polycystic Kidney. FHx, Diagnosis, management. When, how many. transplants ask about graft pain or haematuria, polyuria, loin pain, HT, Type – living, cadaveric. Post swelling (failure of graft, rejection), renal calculi, headache, SAH, visual operative course. Improvement since infection, urine leaks, steroid side changes (intracranial aneurysm) transplant. Medications, long term effects 5) Reflux nephropathy – childhood follow up Long term grafts – renal function renal infections, cystoscopy, 4)Bladder management for reflux or (Cre), proteinuria, recurrent operations, enuresis neurogenic bladder glomerulonephritis, avascular 6)Diabetic nephropathy (other DM) 5) Social arrangements and ADLs. necrosis, skin cancer and reflux 7)Hypertensive nephropathy – when Employment, family coping, travel, nephropathy. Drug compliance, diagnosed, medications, compliance, sexual function, financial situation previous rejection episodes & tmt angiography 8)CTD (SLE, Scleroderma) 9)Aware of long term prognosis. Has dialysis been discussed. Eligible for dialysis or transplant 4) Investigate to assess effects of renal failure Investigations/Diagnostic Criteria 1) Determine Renal Function – FBC (anaemia) a) GFR - EUC (eGFR) (24 hr creatinine clearance) Fe studies b) Tubular function – electrolytes, CMP, uric acid, Alb, MSU urine specific gravity, pH, glycosuria CMP c) Urine analysis and 24 hr protein excretion ALP d) Others – DTPA for renal artery stenosis or obstruction PTH Nerve conduction for peripheral neuropathy 2) Determine Renal Structure Arterial Doppler studies a) US – Renal size and symmetry, signs of obstruction. Small kidneys suggest chronic disease 5) Chronic features are nocturia, polyuria, long standing b)KUB hypertension, renal osteodystrophy, peripheral c)CT KUB neuropathy, anaemia, hyperphosphataemia, d)Cystoscopy and retrograde pyelogram hyperuricaemia, kidney size (usually small) except for e)Renal artery duplex Early diabetic nephropathy Polycystic disease 3)Investigations trying to find underlying pathology Obstructive uropathy Renal bipsy Acute renal vein thrombosis ANA, ANCA Amyloidosis Hep B & C serology Other infiltrating disease HIV Complement EPG, IEPG Urine cytology Examination 1)General inspection – Mental state Hyperventilation (acidosis) Kussmauls breathing, hiccupping Hydration (fluid status) Fever Cushingoid 2)Hands Nails – white transverse bands or lines in hypoalbumin; brown arc near end of nails (Terrys nails) Palmar crease pallor Vasculitis, wrist AVF, Asterixis, Peripheral neuropathy 3) Arms Bruising Pigmentation Scratch marks Subcutaneous calcification Myopathy AVF Skin cancers 4) Face Eyes for anaemia, jaundice, band keratopathy Mouth – dry, fetor Rash (vasculitis, SLE) Facial hair (cyclosporins) Saddle nose (Wegners) Treatment and complications 1) Treat reversible causes of deterioriation including a) hypertension b) UTI c) Obstruction d) dehydration e) cardiac failure f) drugs (NSAIDS, cyclosporine, Iodine, gent) g) hypercalcaemia h) hyperuricaemia with urate obstruction i) hypothyroidism or rarely hypoadrrenalin 5) Chest Cardiac - Pericardial rub, cardiac failure Lungs – infection, pleural effusion, venous hum 6) Abdomen Scars – dialysis Kidneys – balotable, transplant kidney, mass, bruits Tenckhoff catheter exit site infection Bladder Liver, Ascites Nodes (Lymphoma) Femoral bruits and pulses Rectal exam – masses, prostatomegaly 7) Legs Oedema (nephrotic syndrome, CCF) Bruising, Pigmentation, AVF, Scratch marks Gout Neuropathy/Myopathy 8) Back Tenderness, sacral oedema 9)UA Specific gravity, blood, protein, glucose, microscopy and casts 10)Other Blood pressure lying & standing Fundoscopy 2) Monitor and treat hypertension 3) Carefully attend to salt, water balance and acidosis 4) Normalise calcium and phosphate levels with diet, phosphate binders or calcitriol 5)Restrict dietary protein 6) Dialyse when indicated 7) Consider transplant Dialysis 1) Uraemic symptoms despite conservative management 2) volume overload despite salt & water restriction 3) hyperkalaemia unresponsive to conservative measures 4) progressive deterioration of renal function 5) ARF







