Energy Transformations Study Guide Learning Target #1 Describe
advertisement

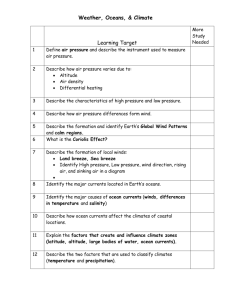
Energy Transformations Study Guide Learning Target #1 Describe how oceans affect climates a) Describe the salinity of ocean water b) Explain the cause and effect relationships between oceans and climate c) Identify what causes surface currents d) Explain how surface currents affect climate Why is water a slow conductor of heat? It needs to gain more energy for its temperature to increase Why are our oceans important as a source of heat energy? The oceans cover more than 2/3 of the Earth’s surface They absorb more sunlight and store more heat. Oceans retain heat longer Sun’s rays heat up the ocean to the depths of many meters Why can ocean water remain within a narrow range of temperatures as opposed to air temperatures? It has a high heat capacity Why do oceans have a major effect on climate? They hold a large amount of heat energy When you wake up before sunrise to go on a walk on the beach, what conditions would you expect? The air over the water is hotter than the air over the land What kind of temperatures would you look for if you expected to feel a sea breeze? The sea temperature would be lower than the land temperature (chart of temperatures will be used on test) After a hot, sunny day, the land cools faster than the sea. What is likely to happen after a hot, sunny day on the sea shore? Cool air from the shore will travel to the sea What is the relationship between heat absorption and heat loss in terms of ocean vs land? Land absorbs and loses heat faster than sea water What is a current? A large stream of moving water that flows through the oceans Some currents move water at the surface of the ocean, while other currents move water deep in the ocean The movement of water between the poles and the equator How do surface currents affect the ocean? They affect the water to a depth of several hundred meters driven MAINLY by winds What are some characteristics of surface currents? They move in circular patterns Most flow east or west, and then double back to complete the circle Why do surface currents move in circular patterns? As Earth rotates, the paths of the winds and currents curve, known as the Coriolis Effect. Northern Hemisphere – it causes currents to curve to the right Southern Hemisphere – it causes the currents to curve to the left What is the California current? The California current is an ocean current that moves cold water from the north along the west coast of the United States. What is the main effect of the California current? To make the climate of the west coast cooler How is the climate affected by the movement of cooler and warmer water from the poles and the equator? It moderates the global climate The movement of water between the poles and the equator is best described as???? Ocean Currents What is a climate? Pattern of temperature and precipitation typical of an area over a long period of time What is the main difference between weather and climate? Weather is short-term & Climate is long-term How do currents affect climate? Moving cold and warm water around the globe How does wind affect climate? It picks up moisture (rain) as it blows across warm-water currents bringing mild, rainy weather It picks up less moisture as it blows across cold-water currents bringing cool, dry weather What is the affect of the movement of air in coastal areas in relation to land versus sea? Cool air usually blows inland during the day Cool air usually blows out to sea at night What is an El Nino? An abnormal climate event that occurs every two to seven years in the Pacific Ocean Why is it helpful to be able to predict when El Nino will occur? It reduces its impact because scientists and public officials can plan emergency procedures and make changes to protect people and wildlife. Why is the ocean salty? The ocean used to cover much of the surface of the planet. Then, volcanoes erupted building more land. Rain washed chemicals from the barren rocks into the ocean. What is salinity? The total amount of dissolved salts in a sample of water What is the composition of ocean water? 96.5% water 3.5% dissolved salts What are the main kinds of dissolved salts found in the ocean? Sodium Chloride Magnesium Chloride What is the salinity of ocean water? In most parts of the ocean, the salinity is between 34 and 37 parts per thousand (One kilogram of ocean water contains about 35 grams of salts – that is, 35 parts per thousand) How does salinity affect ocean water? Ocean water does not freeze until it reaches 35.4 degrees. The salt acts as a kind of antifreeze that interferes. Ocean water has a higher density than fresh water. That means seawater has greater buoyancy. It lifts objects up less dense objects floating in it. Learning Target #2 Explain that the Sun is the major source of energy for Earth a) Explain and use models to demonstrate the water cycle b) Describe how the sun affects the water cycle, the wind, ocean currents, and growth of plants c) Explain how seasons are affected by the Sun’s energy What is the sun? It is a star located in the center of the solar system It is the largest object in our solar system It is an enormous ball of gas that produces energy by fusing hydrogen into helium in its core More than 99% of all matter in the solar system is contained in the sun The energy produced by the Sun comes from nuclear fusion reactions from the Sun’s core. It is so hot that the huge amount of hydrogen is undergoing a constant star-wide nuclear reaction, like in a hydrogen bomb. Even though it is constantly exploding in a nuclear reaction, the Sun and other stars are so large and have so much matter in them that it will take billions of years for the explosion to use all the "fuel" in the star. Earth’s major external source of energy What are the 2 sources of Earth’s energy overall? Sun Earth’s interior What is created by the Sun’s energy on Earth? Heat What is the major source of Earth’s external energy? Sun What form of energy comes from the sun? Solar How does the heating Earth’s surface and atmosphere by the Sun create energy? It drives convection within the oceans and atmosphere that create ocean currents and winds. It creates the climate variations across Earth Unequal heating of the Earth’s surface by the Sun causes winds What are trade winds? Tropical winds that blow toward the equator Why do trade winds blow toward the equator? The Equator receives the most heat energy Winds generally flow away from the equator and towards the poles. This is known as???? An energy transfer, with heat energy moving away from the equator How do green plants use energy from the Sun? They use energy from sunlight through photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates and oxygen from water and carbon dioxide How does sunlight affect photosynthesis? It provides solar energy, which plants use to drive reaction Why is the energy used by plants known as chemical energy? During photosynthesis, a chemical reaction occurs Why hasn’t solar energy replaced energy from other sources? It is only available when the sun is shining The energy Earth receives from the sun is very spread out What is renewable energy? Energy that comes from natural sources, such as the Sun How are seasons affected by the Sun’s energy? While the amount of heat coming from the sun stays the same, it is spread over a larger area during the winter than during the summer. This is due to the earth’s tilt. In the summer, the sun shines almost directly overhead when the Northern Hemisphere is pointed toward the sun. In the winter, the sun appears to be much lower in the sky, and the same amount of sunlight has to cover a larger area. Global climate and weather patterns are driven by differences in the amount of heat energy in different areas of the Earth. Why do different areas of Earth have different amounts of energy? Different regions of the Earth receive different amounts of solar energy Regions at different latitudes around the world receive different amounts of solar radiation. Polar regions receive the least amount of solar radiation, while the equator receives the most. How does this most likely affect the global climate? Polar regions experience colder climates How does the tilt of the earth affect the seasons? When the sun is overhead, the sun’s energy is more concentrated. When the sun shines on earth at an angle, the heat is less concentrated (spread over a much larger area). SUMMER in the Northern Hemisphere Notice how the top part of the earth is leaning toward the sun, which means it receives more of the sun’s energy. WINTER in the Northern Hemisphere Here, the top part of the earth is leaning away form the sun, meaning it receives less energy from the sunlight. What is the water cycle? It is the continuous process by which water moves from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back Within the closed system of Earth and its atmosphere, the amount of water is conserved What is the driving force behind the water cycle? The Sun Areas of Earth near the equator receive large amounts of solar energy. How does this lead to increased rainfall for these areas? The Sun provides the energy necessary for the water to evaporate and eventually return in the form of precipitation Why is the water cycle important to life on Earth? Every living thing needs water to survive What three processes make up the water cycle? Evaporation Condensation Precipitation What is evaporation? The process by which molecules of liquid water absorb energy and change to a gas What is water vapor? A gas in the atmosphere that forms from liquid water How do animals contribute water vapor back into the atmosphere? respiration What is an example of evaporation? Liquid water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and other surfaces and forms water vapor This stage of the water cycle depends on the Sun Where does the energy come from for evaporation to occur? Heat of the sun What are examples of evaporation from living things? Plants release water vapor from their leaves People release water vapor when you exhale What is transpiration? It is a process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves where it changes into water vapor (the evaporation of water from plant leaves) What is condensation? The process by which a gas changes to a liquid. How does the process of condensation work? As water vapor rises higher in the atmosphere, it cools down. The cooled vapor then turns back into tiny drops of liquid water. During condensation, if the water freezes, snow, hail, or sleet will fall in the form of precipitation What is precipitation? Drops of fresh water fall back to Earth in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail How does the process of precipitation work? As more water vapor condenses, the drops of water in the cloud grow larger. Eventually, the heavy drops formed will fall back to the ground – can cause flooding Where does most precipitation end up on Earth? Oceans or lakes What happens to the precipitation that falls on the land? It may soak into the soil and become groundwater or It may run off the land, eventually flowing back into a river or ocean Areas of the Earth near the equator receive large amounts of solar energy. How does this lead to increased rainfall? The solar energy provides the energy for water to evaporate The sun’s energy is critical to the Earth’s climate and weather patterns because it drives the water cycle. Which stage of the water cycle is the sun’s energy most critical to? Evaporation What order of water cycle changes would an ice cube most likely go through when it is put into a glass outside in the Sun? Melting, evaporation, condensation Learning Target: #3 Identify and explain three types of heat transfers: radiation, conduction, convection a) Explain how each heat transfer is related to temperature changes of an object/region What are 3 types of heat transfer? 1. Radiation 2. Conduction 3. Convection All heat transfer is the result of heat flowing from warmer objects to cooler objects What type of heat transfer is radiation? The transfer of energy through space (no direct contact between a heat source and an object) Transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves The flow of energy in the form of rays or waves which does not need a material medium What are examples of radiation? Sunlight that warms Earth’s surface and The heat you feel around a flame or open fire What type of heat transfer is conduction? The transfer of heat within a material or between materials that are touching Heat is transferred from one particle of matter to another without the movement of matter Transfer of heat through a solid What are examples of conduction? A spoon in a pot of soup heats up Burning your feet on hot sand at the beach What type of heat transfer is convection? The transfer of heat by the movement of fluids – liquids and gases, when a substance warms, expands, & rises It is caused by differences of temperature and density within a fluid What is an example of convection? Pot of hot water on the stove - - the water is moving (heat is transferred by the movement of currents within a fluid) How is heat transferred in Earth’s mantle? Large amounts of heat are transferred by convection currents because heat from the core and the mantle itself causes convection currents in the mantle What type of heat flow occurs if two object have different temperatures? Heat will flow from the warmer object to the colder one Heat will flow from one object to the other until the two objects have the same temperature What two forms of heat transfer most contribute to the creation of a land breeze? Convection and conduction What kind of example can be used to demonstrate all 3 types of heat transfer? Stone Chimney Fire in a home Convection – the air around the fire is heated, becoming less dense than the cooler air nearby; The warm air rises up the chimney, and cool air flow in to take its place Conduction – fast moving particles in the fire transfer head as they collide with slow moving particles in the stone hearth. Eventually the heat conducts through the stones to the metal tools. Radiation – The fire transforms chemical energy in the wood to electromagnetic energy, which radiates heat across the room