1.2 REVISION DOCUMENT Matters of Life and death
advertisement

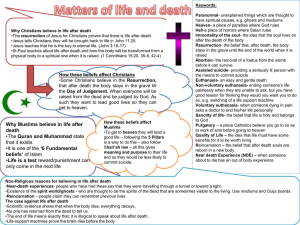
1.2 Matters of Life and Death. Christianity and Islam. Abortion Assisted suicide Euthanasia Immortality of the soul Near-Death experience Non-voluntary euthanasia Paranormal Quality of life Reincarnation Resurrection Sanctity of life Voluntary euthanasia the removal of a foetus from the womb before it can survive. providing a seriously ill person with the means to commit suicide. the painless killing of someone dying from a painful disease. the idea that the soul lives on after the death of the body. when someone about to die has an out of body experience. ending someone’s life painlessly when they are unable to ask, but you have good reason for thinking they would want you to do so. unexplained things which are thought to have spiritual causes e.g. ghosts, mediums. the idea that life must have some benefits for it to be worth living. the belief that after death, souls are reborn in a new body. the belief that, after death, the body stays in the grave until the end of the world when it is raised. the belief that life is holy and belongs to God. the situation where someone dying in pain asks a doctor to end her/his life painlessly. 2.1 Why Christians believe in Life after Death. Christians believe that this life is not all there is. They believe God will reward the good and punish the bad in some form of life after death. Although there are different views about what happens after death among Christians, all Christians believe in life after death because: The main Christian belief is that Jesus rose from the dead, as it is stated in the gospels. There are then accounts of several resurrection appearances. St Paul teaches that people will have a resurrection like that of Jesus and will have a spiritual resurrection body given to them by God. In revelations we are told that at the end of the world, the dead will be raised and brought before God for judgment. Jesus taught that he would come again at the end of the world for a final judgment. The major Church creeds teach that Jesus rose from the dead and that there will be life after death. All the Christian Churches teach life after death. Life after death gives life meaning and purpose. Some Christians believe because of the evidence of the paranormal. 1 How Christian beliefs about life after death affect their lives. Christians believe that what happens to them after they die will be determined by how they have lived this life. Living a good Christian life, loving God and loving your neighbor as yourself will determine their afterlife. The parable of the Sheep and Goats and the parable of the Good Samaritan clearly show how a good Christian life should be lived. Christians will avoid sin in order to get in heaven. Without belief in life after death they feel there is no purpose or meaning to life. 2.2 Why Muslims believe in Life after Death. Muslims believe in life after death because: The Qur’an teaches that there is life after death. Muhammad taught that there is life after death. He is the perfect example for Muslims. Life after death is one of the six fundamental Muslim beliefs. Muslims believe that life is a test. If you pass that test you get into heaven. Life after death gives meaning and purpose to life. How Muslims beliefs about life after death affect their lives. Those who have lived good Muslim lives will get a place in paradise; everyone else will fail and go to hell. This affects Muslims lives because they must try to be good Muslims in order to reach paradise. This includes observing the 5 pillars and following the Holy law of Islam, the Shari’ah. Muslims believe that nothing should be removed from the body after death, so they avoid post mortems and have concerns about transplant surgery. Living life with a purpose and meaning will affect how they live their lives. 2 2.3 Non-religious reasons for believing in Life after Death. All reasons are connected with evidence of the paranormal. This can refer to a wide range of things from ghosts to telekinesis (moving objects without touching them.) However there are three main parts of the paranormal that provide reasons for believing in life after death: 1. Near Death Experiences. A near death experience usually involves someone having an out- of- body experience when they are close to death. While apparently physically dead they may have glimpsed what they believe to be an after or ‘heaven’, feelings of peace and joy; feelings of floating above the body; seeing a bright light; meeting dead relatives. If near death experiences are true then some people may see this as evidence that there is life after death. 2. Evidence for a spirit world. Ghosts and Ouija boards appear to give evidence of the spirits or souls from the dead surviving death, but the clearest evidence seems to come from mediums. A medium is a person who claims to have the gift of communicating between the material world in which we live and the spirit world inhabited by those who have died. Mediums claim to provide evidence for life after death by contacting people’s dead relatives and telling them things only relatives could know. 3. The evidence of reincarnation. Hindus, Sikhs and Buddhists believe that life after death involves souls being reborn into another body. 2.4 Why some people do not believe in life after death. Many people who do not believe in God believe this life is all there is, and just like animals and plants, humans cease to exist when they die. They believe this because: If there is no God there is no life after death. There are so many different religious ideas about life after death. There is not enough actual evidence. Medical science says that the mind cannot exist without the brain. There is nowhere for life after death to take place. We can only recognize people by their bodies, so how would we recognize souls without bodies? 3 2.5 The nature of abortion. Abortion = the removal of a foetus from the womb before it can survive. The 1967 Act states that an abortion can be carried out if two doctors agree that; The mothers life is at risk There is a risk of injury to the mothers physical or mental health There is a risk that another child would put at risk the mental or physical health of existing children There is a substantial risk that the baby might be born seriously handicapped. Previously women had ‘backstreet abortions’. The 1990 Act states that there should be no abortions carried out after the 24th week of pregnancy unless the mother’s life is at great risk. Why abortion is a controversial issue. Many people believe that life begins at the moment of conception. Others would say it is not until the baby is capable of living outside the mother. Many non religious people believe that a woman should have the right to do what she wants with her own body. However many religious people believe that the unborn child’s rights are more important than that of the mother. Some people argue that because fetuses born at 22-24 weeks can now survive, the time limit for abortions should be reduced to 18 or 20 weeks. There are also arguments about whether medical staff should have to carry out abortions. 2.6 Christian attitudes to abortion. Roman Catholics and Evangelical = Not allowed in any circumstances, they support LIFE and SPUC which campaign for the rights of the foetus and support women with unwanted pregnancies. They believe this because: Life begins at the moment of conception, Life is holy, only God can decide, The foetus has a right to life, It is created in the image of God. The Bible forbids the murder of human beings. 4 Protestants. = Agree that abortion is evil but sometimes it is the lesser of two evils. Compassion should be shown and therefore they allow abortion if The woman has been raped. The foetus is severely handicapped. The mother’s life is in danger and sometimes for social reasons. They believe this because: Jesus said ‘love your neighbour’ It is right to try and prevent suffering and disease. Justice – it should be allowed to both the poor and rich not just those who can afford a private abortion. It is O.K. to break the sanctity of life in war, why not in abortion? Life does not begin at conception. New medical technology enables handicapped foetus’s to be quickly identified and allow for swifter abortions with fewer side effects for the mother. 2.7 Muslim attitudes to abortion. Islam does not allow abortion ‘after the foetus is completely formed and has been given a soul, but as in Christianity there is no specific teaching in their scriptures. Muslims have three different ideas about when life begins and this is what makes them have different opinions about abortion, they are: At the moment of conception. When the foetus has recognizable human features. After 120 days. (When ensoulment is given according to some Muslim lawyers.) This therefore leads to differing opinions about when abortion is allowed. Muslims believe that at up to 4 months the mother’s rights are greater than those of the foetus. After that they have equal rights. Some Muslims say that the mother’s life is more important and that if it is at risk an abortion should be allowed because the Shar’iah states that the mother’s life should always take priority. The majority of Muslims say abortion is a great sin and is only allowed if the mother’s life is threatened. Some allow Abortion up to 120 days if a test shows that the foetus is abnormal. As Muslim lawyers have stated that this is allowed. Others say it should not be allowed at all because the soul is present from the moment of conception. All Muslims believe in the sanctity of life. 5 The Sanctity of Life. The word Sanctity means purity or holiness. When it is used to describe life itself it expresses the idea of a preciousness worthy of the highest respect. Christians believe that life is a gift from God and therefore it is sacred. This means it is to be treated as holy and therefore valued and preserved. This is because according to the Bible humans are made in the image of God himself and this gives humanity a special relationship with God. Muslims believe that Allah alone is the author/creator of life and therefore all life is sacred to God. Therefore any aggression against human life is an attack on God. These beliefs affect both Christian and Muslim views on many topics – abortion, euthanasia, suicide, abusing the body with alcohol, drugs etc. 2.8 The nature of euthanasia. Euthanasia is normally thought of as providing a gentle and easy death to someone suffering from a painful, terminal disease and who has little quality of life. This can be done by: assisted suicide, voluntary euthanasia, nonvoluntary euthanasia. British law says that all these methods of euthanasia can lead to a charge of murder. However the law now agrees that withdrawing artificial nutrition and hydration is not murder. In the same way withholding treatment from patients with little or no chance of survival and ensuring a peaceful death for them is not murder. These 2 types of euthanasia (the withdrawal or withholding of treatment) are often called passive euthanasia, in contrast to positive euthanasia which is actually bringing someone’s life to an end. Why euthanasia is a controversial issue. Reasons against Euthanasia. Mistakes can happen. It is unnecessary with good painkilling drugs. The dying patient might not be able to think properly when deciding that he/she wants to die. It might be misused, e.g. on insane people or the handicapped. Hospices are there to help with the dying. Euthanasia is no better than murder. It could make the elderly feel in the way. It could make the ill feel in the way. Reasons for Euthanasia. We should be able to choose when we die. We should not have to live if there is no chance of getting better. Euthanasia stops the suffering of relatives having to watch the patient die a slow and painful death. It is cheaper than giving expensive drugs. It takes away the fear of a painful death. Allows money to be spent on people who could get better. Makes death gentle, peaceful and easy. It lessens the pain for the patient. 6 2.9 Christianity and Euthanasia. All Christians agree that Euthanasia, as such, is wrong. This is because life is given by God, and only God can take life. Human life is a gift from God and it is the duty of Christians to preserve life and to improve life. It is the teaching of all the Churches that Euthanasia in the form of the deliberate killing of a person is a grave sin. However there are disagreements among Christians as to what to do about patients who are incurably ill and are only being kept alive by intrusive treatment, and patients who are in a persistent vegetative-state (PVS or brain dead). The Roman Catholic Church teaches that Christians can never hasten death. Any action, which is intended to cause death to relieve suffering (e.g. giving a dying person a drug overdose), is wrong. In the same way any omission of treatment in order to cause death is wrong (e.g. not giving insulin to a dying diabetic). Catholics and most other Christians would regard both of these as euthanasia and therefore wrong. Christians have these beliefs because of the Christian teaching about the sanctity of life, the belief that only God has the right to take life. 2.10 Islam and Euthanasia. Muslims do not allow Euthanasia in any form. This life is a test and to use euthanasia is like cheating. It is up to God to decide when the test will end. As Muslims believe they must pass the test to get into heaven, they cannot accept euthanasia. The following quote from the Hadith gives the prophets opinion, ‘In the time before you, a man was wounded. His wounds troubled him so much that he took a knife and cut his wrist to bleed himself to death. Thereupon Allah said ‘My slave hurried in the matter of his life therefore he is deprived of the garden.’ (Hadith) The suffering of a terminally ill person is preferable to euthanasia. However, Muslim lawyers have recently agreed to allow the switching off of life support machines if doctors agree that life has ended. The religious arguments against euthanasia listed below can be applied to both Islam and Christianity. ‘You shall not murder said God’ so euthanasia is against God. Life is given by God and should only be taken by him. God will be there to help no matter how bad the pain is. All should be kind and merciful in their care of the sick. God has a purpose for everything even suffering. Nobody is ever useless. Both the dying and their relatives may learn from the experience. The care of the dying gives us the chance to be totally unselfish. 7 2.11 The Media and matters of life and death. The media refers to newspapers, television, radio, films and the internet. Religions make many statements about such matters of life and death as abortion, euthanasia, transplants, genetic engineering, cloning and fertility treatments. Arguments that the media should not be free to criticize what religions say about matters of life and death. Criticizing what religions say about life and death issues could be seen as a way of stirring up religious hatred. Maybe there should be some restrictions on the freedom of the media because criticism of religious attitudes can cause serious offence to believers. Some religious believers would argue that criticizing what religious leaders such as the Pope or Archbishop of Canterbury say about matters of life and death is close to the crime of blasphemy. Essentially, if the media criticizes the Pope’s teachings on a topic like abortion or euthanasia, they are condemning the Catholic Church. Some religious believers might feel that because their attitude is because their attitude is based on what God says, it should not be criticized because god is beyond human criticism. Arguments that the media should not be free to criticize what religions say about matters of life and death. All societies with democratic forms of government say they believe in freedom of expression. This means there should be a free media who must be able to criticize religious attitudes to matters of life and death. Many religious leaders use the media to criticize government policies on matters of life and death. Therefore they must be prepared to have their attitudes criticized. In a multi-faith society there must be freedom of religious belief and expression. This means to have the right to question and even criticize not only religious beliefs, but also what religions believe about controversial issues such as abortion, euthanasia and genetic engineering. A free media gives religious people a chance to put forward their ideas whilst at the same time allowing non-religious people (or people from a different religion) the chance to put forward their ideas. Societies who have freedom of expression make more progress. 8 9