Chapters 1 & 3: Investigating the Past Study Guide Read each
advertisement

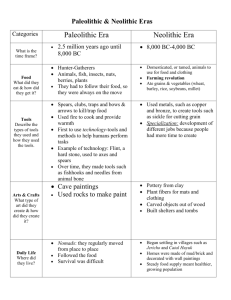
Chapters 1 & 3: Investigating the Past Study Guide Read each question carefully. Answer the question in the space(s) provided. 1. Why are social scientists who study the past compared to detectives? ~Social scientists have to collect clues (artifacts) and then make a guess about how ancient people lived based on these clues 2. How would an archaeologist study the past? ~Archaeologists would use artifacts (actual objects) left behind to determine how ancient people lived 3. What is one example of a humanmade feature that a geographer might study? ~roads ~houses 4. What types of evidence would an historian study? ~ Historians – study written items from the past (documents, pieces of writing, cave paintings or writing on the wall, hieroglyphics, cryptographs, pictographs) 5. What assumptions have social scientists been able to make from studying cave paintings? ~Some documented important events ~Some were for decoration/fun ~Handprints were use to sign the paintings by artists ~Some times cave paintings told about people’s way of life ~Some were stories ~Some were tributes ~Some told history ~Some were used for rituals 6. If a social scientist found artifacts and paintings in a cave, what question would be the hardest to answer? ~Why did people paint in caves? 7. What did people in Paleolithic times spend most of their time doing? ~hunting and gathering food 8. Describe the communities in the Paleolithic Age. ~People hunted and gathered food ~There were only those two jobs ~They depended on food they could find ~Stayed in caves that they found ~Usually the clans consisted of 20-60 (smaller than Neolithic) ~They didn’t stay in one place…they moved 9. The Neolithic Age, also called the New Stone Age, began with what discovery? ~agriculture (farming) 10.What are some changes that occurred when people began farming? ~Because they didn’t have to constantly move, they had more time to trade ~Allowed them to have bigger communities –better defense because of bigger numbers ~Didn’t use as many supplies because they didn’t have to set up over and over ~Kept them safe from the weather ~Could have more tools because they didn’t have to move everything ~Have better cooking tools (pit with hot rocks) ~More time meant better food, tools, ideas ~Houses were more insulated ~More stable food supply (domesticated animals, grew crops) ~Could support larger permanent communities (up to 600 people) ~People could have different types of jobs ~ Could trade because they had free time 11. Describe the communities in the Neolithic Age. ~They were larger and permanent ~More different types of jobs ~ Developed metal tools ~ Built houses instead of living in caves ~Homes gave more shelter because they were stronger ~ Homes kept warm in winter/cool in summer ~ Could trade because they had free time 12. If you were building a place to live during the Neolithic Age, how could you protect yourself from animal attacks? ~placing the door/entrance high on a wall with access from a ladder 13. Why did people live in larger communities during the Neolithic Age? ~They could grow enough food for larger groups ~Larger groups could provide better protection 14. If you were a Neolithic trader, what benefit could you gain from your travels? ~resources that were not available where you lived ~ideas that other groups had developed 15. What were the results of people developing specialized skills? ~items could be higher quality ~items could be decorated to show individuality, wealth, or ritual meaning ~trade with other groups could be established 16. Look around your home. What sorts of items would archaeologists, historians and geographers study to find out about you? Answers will vary based on your house, but basic guidelines for the types of items each social scientist would study are listed… Archaeologists – dig up items from the past (bones, plates, metal tools, cave paintings…) Geographers – study places from the past (human made features – houses, Great Wall, dams on rivers; natural features – rivers, mountains, mesas, forests) Historians – study written items from the past (The Constitution, pieces of writing, cave paintings or writing on the wall, hieroglyphics, cryptographs, pictographs) 17. How did building permanent shelters change people’s lives? ~Led to larger communities ~Led to better protection from weather, enemies, and animals ~Led to population growth ~Started new jobs ~Trade began ~Greater comfort 18. How would you compare (show similarities) and contrast (show differences) life in Neolithic times to life today? ~Answers will vary *don’t live in mud houses *don’t have doors high on buildings with access via ladder *most of us don’t raise our own food, we buy it in a grocery store *we still live in large communities *large population growth *specialized jobs still exist *trade with other groups/countries is common