Chapter 15 Key Terms: Medieval Conflicts and Crusades
advertisement

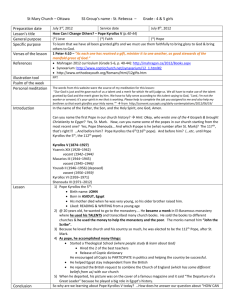
Chapter 15 Key Terms: Medieval Conflicts and Crusades 1. Clergy: group of people who give their lives to serve the Church as priests, monks, and high church officials 2. Pope Leo III: crowned Charlemagne as emperor, which gave much power to the church in the West 3. coronation: crowning ceremony of a king 4. Pope Gregory VII: declared supreme authority over the Church and nonchurch leaders 5. secular: not of the church 6. Henry IV: King who was involved in a bitter power struggle with the pope. He was excommunicated, but later removed the pope 7. excommunicate: to exclude a person from a church or a religious community 8. William the Conqueror: 1066, King who conquered England and introduced a strong feudal system 9. King John: 1199, king of England who claimed so much power that nobles forced him to sign the Magna Carta, limiting his power 10. Magna Carta: “Great Charter,” document that made the king obey the law and protected the rights of the people 11. Common Law: group of laws created by customs and judges’ decisions, instead of laws passed by a law-making group 12. Habeas corpus: a court order that brings an arrested person before a judge or court 13. parliament: an assembly of representatives who make laws 14. pilgrim: a religious person who travels to a holy place or shrine 15. crusade: a Christian religious war 16. expel: to force someone to leave a place 17. heresy: a belief that is rejected by official Church doctrine 18. Inquisition: a Church court designed to investigate and judge heretics 19. Reconquista: “reconquest,” the movement to drive Muslims from Spain 20. Ferdinand and Isabella: king and queen who united Spain under the Catholic church, drove out the Muslims and Jews, and sponsored Christopher Columbus Chapter 15 Key Terms: Medieval Conflicts and Crusades 1. Clergy: group of people who give their lives to serve the Church as priests, monks, and high church officials 2. Pope Leo III: crowned Charlemagne as emperor, which gave much power to the church in the West 3. coronation: crowning ceremony of a king 4. Pope Gregory VII: declared supreme authority over the Church and nonchurch leaders 5. secular: not of the church 6. Henry IV: King who was involved in a bitter power struggle with the pope. He was excommunicated, but later removed the pope 7. excommunicate: to exclude a person from a church or a religious community 8. William the Conqueror: 1066, King who conquered England and introduced a strong feudal system 9. King John: 1199, king of England who claimed so much power that nobles forced him to sign the Magna Carta, limiting his power 10.Magna Carta: “Great Charter,” document that made the king obey the law and protected the rights of the people 11.Common Law: group of laws created by customs and judges’ decisions, instead of laws passed by a lawmaking group 12.Habeas corpus: a court order that brings an arrested person before a judge or court 13.parliament: an assembly of representatives who make laws 14.pilgrim: a religious person who travels to a holy place or shrine 15.crusade: a Christian religious war 16.expel: to force someone to leave a place 17.heresy: a belief that is rejected by official Church doctrine 18.Inquisition: a Church court designed to investigate and judge heretics 19.Reconquista: “reconquest,” the movement to drive Muslims from Spain 20.Ferdinand and Isabella: king and queen who united Spain under the Catholic church, expelled the Muslims and Jews, and sponsored Christopher Columbus