Normalcy and the Jazz Age, The 1920s
advertisement

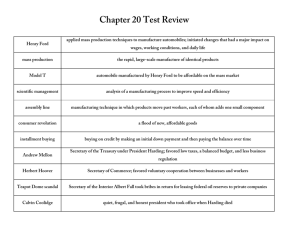
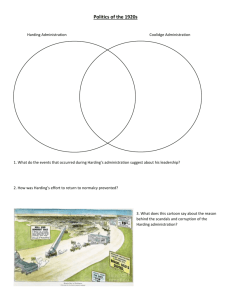
Normalcy and the Jazz Age, The 1920s Clash of Values Red Scare in 1919 brought on by the Russian Revolution Lenin-Marxism is contrary to American values. A. Mitchell Palmer targeted groups that posed a “clear danger.” Nativism Resurges Fear of losing our historic political, ethnic, cultural and religious identity. Sacco-Vanzetti Their conviction may have been influenced by being Italian immigrants who held radical (anarchist) ideas. Pseudo-Scientific Racism Eugenics Return of the Ku Klux Klan Targeting Blacks, Catholics, Jews, and immigrants, it actively recruited in Churches across America with an impressive advertising campaign. Scandals involving the leaders led to its decline. Controlling Immigration Emergency Quota Act Admission based on ethnicity and country of origin. National Origins Act, 1924 Exempted Canadians and Mexicans Hispanic Immigration The New Morality emphasized personal freedom. ` Women in the 1920s Now have the right to vote, but will they exercise it? Their status at the workplace does not improve. Women are freer to experiment with bolder styles and manners. Flappers are unconventional and actively seek to break from the past. The Fundamentalist Movement Fundamentalism: involves the literal interpretation of the Bible. The Scopes Trial: John Scopes was prosecuted for violating the Butler Act. He was defended by Clarence Darrow while William Jennings Bryan represented the state of Tennessee. Prohibition: The 18th Amendment will increase federal police power with the rise of organized crime. Volstead Act: To enforce prohibition and stop racketeering. Speak easies: Illegal bars Cultural Innovations Art and Literature Greenwich Village and the South Side Modern American Art Poets and Writers Sinclair Lewis: Babbitt dealt with themes of hypocrisy, dishonesty, and corruption in small town America. Carl Sandburg Eugene O’Neil Ernest Hemingway: Farewell to Arms * F. Scott Fitzgerald: The Great Gatsby * * Writers identified with the “Lost Generation.” Popular Culture Heroes symbolize traditional American values of honesty, courage, Baseball, Boxing and Other Sports Rise of Hollywood “The Golden Age” began in 1927 with the Jazz Singer, first movie with sound. Movie Stars become important to Americans Popular Radio Shows and Music Mass Media promoted the creation of a national culture. African American Culture The Great Migration The result of an industrial boom The Harlem Renaissance Harlem became the cultural center of African Americans. The Writers James Weldon Johnson Claude McKay Langston Hughes Zora Neale Hurston Jazz, Blues and Theater Jazz Cotton Club: Harlem night spot where Black artists got their start and frequented by White patrons. Blues African American Politics Race Riots The race riot in Chicago was due to housing overcrowding neighborhoods. The Black Vote in the North NAACP Battles Lynching NAACP lobbies the House of Representatives in 1922 to pass legislation to make this practice illegal. Black Nationalism and Marcus Garvey Self respect, economic power, return to Africa Presidential Politics The Harding Administration A Self-Doubter in the White House Normalcy: Harding expressed Americans desire to return to normal life after the war. The Ohio Gang: Harding brought his friends from Ohio. They would play poker in the White House. Harry Daugherty resigned in disgrace for taking bribes in exchange for the drilling of public land, and will narrowly escape conviction. Teapot Dome Scandal Albert Fall, Secretary of the Interior, went to jail for leasing government oil reserves, one in Teapot Dome, Wyoming to oil men for a $400,000 bribe. The Coolidge Administration “Silent Cal” believed in not interfering with business. The policies of Secretary of the Treasury Mellon The Election of 1924 Progressive Party A Growing Economy The Rise of New Industries Mass Production The Assembly Line simple tasks divided among the workforce; increased efficiency; workers wages were doubled but his sociological department could place demands on employees private life. Model T Ford makes his car more affordable through vertical consolidation. The Social Impact of the Automobile Tourist industry grows; new roads built; motels; service stations The Consumer Goods Industry Installment plans and easy credit The Airline Industry Charles Lindbergh was the first to fly solo across the Atlantic. Commercial flight gains popularity. The Radio Industry takes off with the reporting of Harding winning the election of 1920. NBC CBS The Consumer Society is built on consumer spending. Easy Credit Installment plans fueled the growth of the consumer economy. Mass Advertising Emphasis shifted from product quality to consumer image. Managerial Revolution Welfare Capitalism National Harvester offered two week annual paid vacation. Ford offered pensions. Open shop The Farm Crisis Returns Changing Market Conditions Buying on margin; speculation Rise in stock market benefitted the wealthy. Helping Farmers McNary Haugen Bill: government to buy crop surpluses and sell abroad. Farmers were hit hard in the 1920s. The Policies of Prosperity Promoting Prosperity (Republican Party Plan) Isolationism and laissez fair business policy Mellon Program Supply Side Economics Cut corporate taxes to lower prices and individual tax burden to increase consumer spending Hoover’s Cooperative Individualism Reduce corporate costs if trade organizations share information with the government Isolationism After WWI Americans wanted to avoid involvement in world affairs The Dawes Plan The US funds German debt; European debt deepens. The Washington Conference International agreement to reduce the size of the Naval forces. Abolishing War Kellogg-Briand Pact 15 nations agreed not to use war in resolving conflict with one another. Signs of Economic Trouble Uneven prosperity: farmers and laborers did not enjoy the prosperity. 60% had difficulty making ends meet. Personal debt Over production Stock Market Speculation