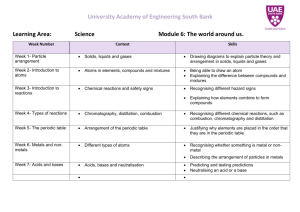
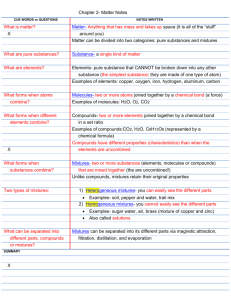
Year 8 Science Chemistry Program General
advertisement

Irene McCormack Catholic College YEAR 8 SCIENCE CHEMISTRY 2015 Chemical sciences The properties of the different states of matter can be explained in terms of the motion and arrangement of particles (ACSSU151) Elaborations explaining why a model for the structure of matter is needed modelling the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids and gases using the particle model to explain observed phenomena linking the energy of particles to temperature changes Differences between elements, compounds and mixtures can be described at a particle level (ACSSU152) Elaborations modelling the arrangement of particles in elements and compounds recognising that elements and simple compounds can be represented by symbols and formulas locating elements on the periodic table Chemical change involves substances reacting to form new substances (ACSSU225) Elaborations identifying the differences between chemical and physical changes identifying evidence that a chemical change has taken place investigating simple reactions such as combining elements to make a compound recognising that the chemical properties of a substance, for example its flammability and ability to corrode, will affect its use Year 7 8 9 10 Science Understandings Chemical Sciences Mixtures, including solutions, contain a combination of pure substances that can be separated using a range of techniques. The properties of different states of matter can be explained in terms of the motion and arrangement of particles. Differences between elements compounds and mixtures can be described at a particle level. All matter is made of atoms, which are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons; natural radioactivity arises from the decay of nuclei in atoms. The atomic structure and properties of elements are used to organise them in the Periodic table. Chemical change involves substances reacting to form new substances. Chemical reactions involve rearranging atoms to form new substances; during a chemical reaction mass is not created or destroyed. Different types of chemical reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates. Chemical reactions, including combustion and the reactions of acids, are important in both nonliving and living systems and involve energy transfer Science Inquiry Skills Questioning and predicting Students identify questions that can be investigated scientifically. Students identify and construct questions and problems that they can investigate scientifically. Planning and conducting They plan fair experimental methods, identifying variables to be changed and measured. They consider safety and ethics when planning investigations, including designing field or experimental methods. Processing and analysing data and information They select equipment that improves fairness and accuracy and describe how they considered safety. Students draw on evidence to support their conclusions. They summarise data from different sources, describe They identify variables to be changed, measured and controlled. Students design questions that can be investigated using a range of inquiry skills. They design methods that include the control and accurate measurement of variables and systematic collection of data and describe how they considered ethics and safety. They analyse trends in data, identify relationships between variables and reveal inconsistencies in results. Students construct representations of their data to reveal and analyse patterns and trends, and use these when justifying their conclusions. They explain how modifications to methods could improve the quality of their data and apply their own They analyse their methods and the quality of their data, and explain specific actions to improve the Students develop questions and hypotheses and independently design and improve appropriate methods of investigation, including fieldwork and laboratory experimentation. They explain how they have considered reliability, safety, fairness and ethical actions in their methods and identify where digital technologies can be used to enhance the quality of data. When analysing data, selecting evidence and developing and justifying conclusions, they identify alternative explanations for findings and explain any sources of uncertainty. Students evaluate the validity and reliability of claims made in Evaluating Communicating trends and refer to the quality of their data when suggesting improvements to their methods. They communicate their ideas, methods and findings using scientific language and appropriate representations. scientific knowledge and investigation findings to evaluate claims made by others. They use appropriate language and representations to communicate science ideas, methods and findings in a range of text types. quality of their evidence. They evaluate others’ methods and explanations from a scientific perspective and use appropriate language and representations when communicating their findings and ideas to specific audiences. secondary sources with reference to currently held scientific views, the quality of the methodology and the evidence cited. They construct evidence-based arguments and select appropriate representations and text types to communicate science ideas for specific purposes. Science as a Human Endeavour Nature and development of Science Scientific knowledge changes as new evidence becomes available, and some scientific discoveries have significantly changed people’s understanding of the world Science knowledge can develop through collaboration and connecting ideas across the disciplines of science Use and influence of Science Science and technology contribute to finding solutions to a range of Contemporary issues; these solutions may impact on other areas of society and involve ethical considerations Science understanding influences the development of practices in areas of human activity such as industry, agriculture and marine and terrestrial resource management People use understanding and skills from across the disciplines of science in their occupations Refer to year 7 descriptors. Scientific understanding, including models and theories, are contestable and are refined over time through a process of review by the scientific community Advances in scientific understanding often rely on developments in technology and technological advances are often linked to scientific discoveries People can use scientific knowledge to evaluate whether they should accept claims, explanations or predictions Advances in science and emerging sciences and technologies can significantly affect people’s lives, including generating new career opportunities The values and needs of contemporary society can influence the focus of scientific research Refer to year 9 descriptors. Wk Topic Content Activities 1 Safety Rules Lab Equipment Changes of State (ACSSU151) The properties of the different states of matter can be explained in terms of the motion and arrangement of particles Explain why a model for the structure of matter is needed Model the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids and gases Changing shape of form Expansion and contraction Changes of state Identifying chemical change Experiments using: Practical 6.1 (1) Practical 6.1 (2) Physical Change (ACSSU225) Using the particle model explain observed phenomena linking the energy of particles to temperature changes Expansion/contraction Changes of state and the particle model Practical Activity 6.2 (1,2 &4) Ball and ring Heating Bimetallic strip Pearson Chapter 6.2 Salt and sand dissolving in water. Atomic theory All matter composed of atoms Electron shells Explain atomic and mass numbers, relating to protons, neutrons and electrons Chemical change involves Practical activities 7.3 Pearson Chapter 7.3 Act: Comparing Pearson Chapter 2 3 4 Atoms (ACSSU151) 5-6 Elements, Review rules of Science Lab Drawing and naming scientific equipment Resources and Equipment 2D diagrams of equipment. Using a Bunsen burner. Pearson Chapter 6.1 Clickview: Types of changes. Assessment and Homework Review Laboratory equipment Research assignment? Dissolving Sugar Investigation Practical Activity 6.2 (3) http://www.chemsoc. Compounds, Mixtures. (ACSSU225) substances reacting to form new substances Investigate simple reactions such as combining elements to make a compound Atoms, Elements, Compounds, Molecules, Mixtures. Chemical Formula. mixtures and compounds, SO1 pg 204. Discuss organisation of Periodic Table. 7.1 – 7.3 Periodic Table of the Elements. org/viselements/page s/periodic_table.html Learn elements 120. Practical test? 7 Chemical Reactions (ACSSU225) Identify evidence that a chemical change has taken place Identify the differences between chemical and physical changes Chemical reactions Chemical change and reactions Energy in chemical reactions Chemical equations 8 Physical and Chemical Changes (ACSSU152) Recognise that elements and simple compounds can be represented by symbols and formulas View additional details about Critical and creative thinking Physical reactions Chemical reactions Chemical equations Melting, freezing (solidification), condensation, evaporation (boiling), sublimation. Latent Heat of Fusion Latent Heat of Vaporisation Kinetic Theory Pearson 6.4 Practical activities 6.4; 1&2 Link to change of state New substance formed Chemical/word equations Activity: Observing physical and chemical changes. Pearson 6.4 Revision Sheet 9 REVISION Chemistry test. Assessment Outline ASSESSMENT TYPE TITLE WORTH Practical Assessment Thio Sulphate Reaction 6% Research Unit test Research/ poster Unit Test 6% 8%