n=61 employed - Reilly Associates
advertisement
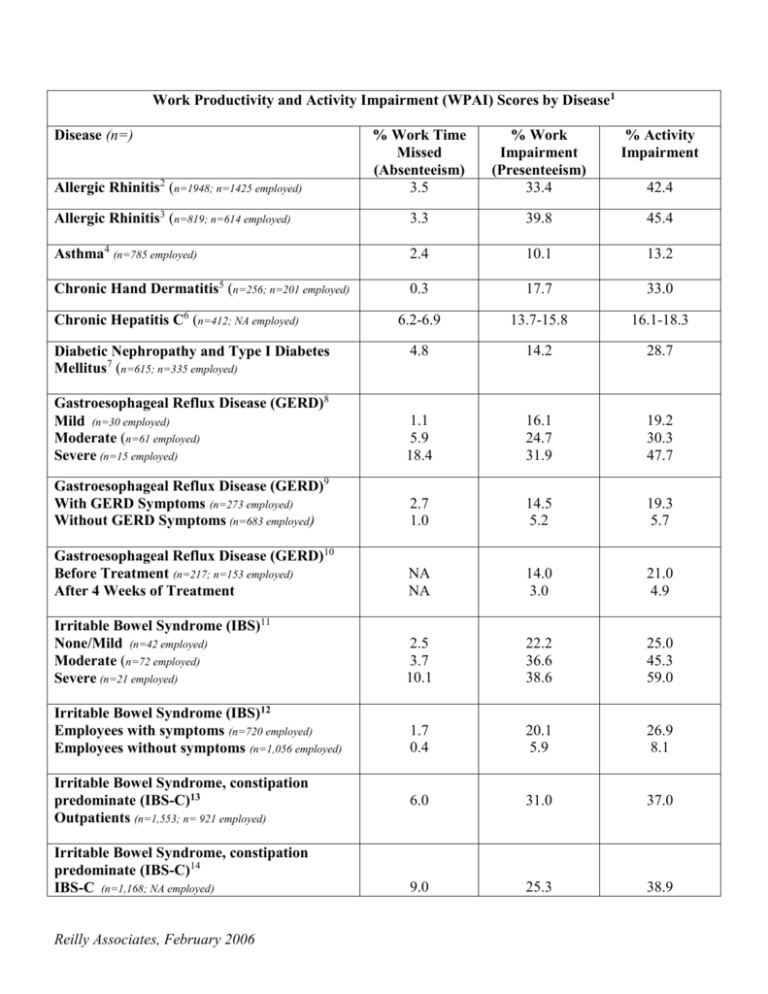
Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) Scores by Disease1 Disease (n=) % Work Time Missed (Absenteeism) 3.5 % Work Impairment (Presenteeism) 33.4 % Activity Impairment Allergic Rhinitis3 (n=819; n=614 employed) 3.3 39.8 45.4 Asthma4 (n=785 employed) 2.4 10.1 13.2 Chronic Hand Dermatitis5 (n=256; n=201 employed) 0.3 17.7 33.0 6.2-6.9 13.7-15.8 16.1-18.3 4.8 14.2 28.7 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)8 Mild (n=30 employed) Moderate (n=61 employed) Severe (n=15 employed) 1.1 5.9 18.4 16.1 24.7 31.9 19.2 30.3 47.7 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)9 With GERD Symptoms (n=273 employed) Without GERD Symptoms (n=683 employed) 2.7 1.0 14.5 5.2 19.3 5.7 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)10 Before Treatment (n=217; n=153 employed) After 4 Weeks of Treatment NA NA 14.0 3.0 21.0 4.9 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)11 None/Mild (n=42 employed) Moderate (n=72 employed) Severe (n=21 employed) 2.5 3.7 10.1 22.2 36.6 38.6 25.0 45.3 59.0 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)12 Employees with symptoms (n=720 employed) Employees without symptoms (n=1,056 employed) 1.7 0.4 20.1 5.9 26.9 8.1 6.0 31.0 37.0 9.0 25.3 38.9 Allergic Rhinitis2 (n=1948; n=1425 employed) Chronic Hepatitis C6 (n=412; NA employed) Diabetic Nephropathy and Type I Diabetes Mellitus7 (n=615; n=335 employed) Irritable Bowel Syndrome, constipation predominate (IBS-C)13 Outpatients (n=1,553; n= 921 employed) Irritable Bowel Syndrome, constipation predominate (IBS-C)14 IBS-C (n=1,168; NA employed) Reilly Associates, February 2006 42.4 Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) Scores by Disease1 Disease (n=) % Work Time Missed (Absenteeism) 4.6 % Work Impairment (Presenteeism) 12.7 % Activity Impairment Irritable Bowel Syndrome, constipation predominate (IBS-C)15 Tegaserod group-Baseline (n=1,363) Tegaserod group-Week 2 5.4 3.4 40.4 28.8 48.3 34.1 Placebo group- Baseline (n=312) Placebo group- Week 2 5.3 5.3 38.7 31.8 45.7 37.7 Nocturia Patients16 (n=203 employed) Nocturia Controls (n=80 employed) 1.5 4.4 12.3 3.5 18.1 5.2 Osteoarthritis17 (n=182; n=60 employed) 0.6 23.0 44.5 Social Phobia18 (n=65; n=48 employed) 8.3 23.3 27.7 Non IBS-C (n=11,694; NA employed) 21.3 1 References 7, 14 and 16 used the General Health version (WPAI-GH). All other studies used a disease-specific version. 2 Tanner LA, Reilly M, Meltzer EO, Bradford JE, Mason J. Effect of fexofenadine HCI on quality of life and work, classroom and daily activity impairment in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Am J Man Care 1999; 5 (suppl):S235-S247. 3 Meltzer EO, Casale TB, Nathan RA, Thompson AK. Once-daily fexofenadine HCI improves quality of life and reduces work and activity impairment in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy, Asthma, Immunol 1999; 83:311-317. 4 Andréasson E, Svensson K, Berggren F. The validity of the work productivity and activity impairment questionnaire for patients with asthma (WPAI-asthma): Results from a web-based study. Value in Health 2003;6(6):780 5 Reilly MC, Lavin PT, Kahler KH, Pariser DM. Validation of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment: Chronic Hand Dermatitis Questionnaire (WPAI-ChHD) in Chronic Hand Dermatitis (ChHD). J Am Academy Dermatol.2003;48:128-30. 6 Perrillo R, Rothstein KD, Rubin R, Alam I, Imperial J, Harb G, Hu S, Klaskala W. Comparison of quality of life, work productivity and medical resource utilization of peginterferon alpha 2a vs the combination of interferon alpha 2b plus ribavirin as initial treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2004 Mar;11(2):157-65. Reilly Associates, February 2006 7 Unpublished data. 8 Wahlqvist P, Carlsson J, Stalhammar NO, Wiklund I. Validity of a Work Productivity and Activity Impairment questionnaire for patients with symptoms of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (WPAI-GERD)- results from a cross-sectional study. Value in Health 2002; 5:106-113. 9 Dean BB, Crowley JA, Reeves JD, Aguilar D, Sullivan S. The cost of gastroesophageal reflux disease: it's what you don't see that counts. JMCM 2003; 7(2): 6-13. 10 Wahlqvist P, Guyatt G, Armstrong D, Austin P, Barkun A, Chiba N, degl'Innocenti A, El-Dika S, Fallone C, Heels-Ansdell D, Tanser L, Veldhuyzen van Zanten S, Wiklund I, Schünemann H. Responsiveness to change and English language validation of the WPAI-GERD questionnaire - results from a Canadian study. Value in Health 2004;7(3):A349. 11 Reilly MC, Bracco A, Ricci J-F, Santoro J, Stevens T. The validity and accuracy of the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire - Irritable Bowel Syndrome Version (WPAI:IBS). Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004; 20: 459-467. 12 Dean BB, Aguilar D, Barghout V, Kahler KH, Frech F, Groves D, Ofman JJ. Impairment in work productivity and health-related qulaity of life in patients with IBS. Amer J Man Care 2005 (11); S17-26. 13 Pare P, Lam S, Balshaw R, Keown P, Khorasheh S, Barbeau M, McBurney. Patient characteristics (irritable bowel syndrome with constipation [IBS-C]): baseline results from LOGIC (Longitudinal Outcomes study of GI symptoms in Canada). Presented American College of Gastroenterology October 30, 2005, Honolulu, Hawaii. 14 Bracco A, Reilly MC, McBurney C, Ambegaonkar B. Burden of Irritable Bowel Syndrome with constipation on health care resource utilization, work productivity and activity impairment and quality of life. Presented 13th World Congress of Gastroenterology, Montreal, Canada September 10-14, 2005. 15 Reilly MC, Barghout V, McBurney CR, Niecko TE. Effect of tegaserod on work and daily activity in IBS with constipation. Aliment Pharmacol & Ther 2005; 22:373-380. 16 Kobelt G, Borgstrom F, Mattiasson A. Productivity, vitality and utility in a group of healthy professionally active individuals with nocturia. Br Jurol Int 2003;9(3):190-5. 17 Unpublished data. 18 Wittchen HU, Beloch E. The impact of social phobia on quality of life. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1996; II(S3):15-23. Reilly Associates, February 2006






