Natural Systems Unit Review

Natural Systems Unit Review
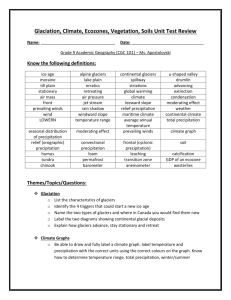
Unit Terminology: The following is a list of all the terminology from the unit.
Geographic region, continental drift, plate tectonics, crust, mantle, core, lithosphere, asthenosphere, weathering-erosion-deposition (WED), landform regions, cordillera, plains, highland, lowland, shield, precipitation, condensation (dew point), orographic (relief) precipitation, cyclonic (frontal) precipitation, convectional precipitation, average temperature, annual/total precipitation, temperature range, continental climate, maritime climate, southwesterlies, true soil, humus, leached soil, calcified soil, permafrost, vegetation regions (we have
7), coniferous trees, deciduous trees, boreal forest, treeline, tundra vegetation, ecozone, ecological characteristics, Point Pelee
Unit Topics: The following are the major topics of the unit with some practice questions. Your test will be a combination of multiple choice, fill in the blank and short answer on these topics.
You need to know the concepts to answer these questions but do not expect the exact same questions word for word on your test.
1.
Regions and Land Use a. Define the term region. b. Explain why they are used and an example. c. Why are the commercial zones in Paris moving out of down town?
2.
Composition of the Earth and Plate Tectonics a. Draw a diagram of the Composition of the Earth and explain what each of the layers is composed of. b. What is continental drift and what evidence did Alfred Wagner use to make this theory? What is plate tectonics? How is plate tectonics different from continental drift? d. Review the Haiti questions. What made it such a massive natural disaster?
3.
The Rock Cycle & Weathering a. Draw label and explain the rock cycle. Be sure you understand what causes the rocks to change from one form to another. b. What are the major forces of erosion?
4.
Canada’s Landform Regions a. What are the three distinct landforms that make up Canada? b. What are the landform regions of Canada? (there are 7) c. What types of rock are found in each of the major landform regions? Where are minerals found? Fossil fuels (oil and gas)? Precious metals (gold, nickle etc.)?
Remember try to make the links between rock type, how the region formed and what precious minerals are there.
5.
Climate Factors and Regions a. Name and explain the 6 factors that affect climate. Which areas (or ecozones) of
Canada are affected by the factors? b. Draw, label and explain the three ways precipitation forms.
6.
Analyzing Climographs a. Look at the climate graphs on page 142 and practice identifying where they are from. b. Be prepared to make a climograph and calculate average annual temperature, total precipitation, temperature range, and season of maximum precipitation and use these to determine the climate type (maritime or continental) and likely location of the climate station.
7.
Soil Components, Profiles, and Regions a. What are the 4 major components of soil? b. How does soil form? c. Describe the 4 major soil regions of Canada. d. Draw and explain a soil profile (leached, calcified, or normal). Be prepared to explain the difference between these.
8.
Vegetation Regions of Canada a. What are the 7 vegetation regions of Canada and what types of plants would you expect to grow there? b. Given a list of the 7 regions you should be able to link a region to its vegetation, soil, climate or a combination of the clues. ex. Where is Canada’s temperate rainforest? The
____________ region’s vegetation varies greatly due to the varying temperature and precipitation caused by the mountains. etc.
9.
Ecozones: definition, terminology a. Know the top two and bottom of the rankings for GDP, Population and Area. b. Know the Name, Population (high, medium or low is fine), Wildlife, Landforms,
Vegetation, and Climate of the Mixedwood Plains and at least one other ecozone off by heart. (probably the one you presented!) c. Explain how ecozones are defined and named. e. Practice using the names of ecozones to predict what they contain.
10.
National Parks: purpose, examples, and problems a. Define the purpose of having national parks in your own words. (Be sure to include the 4 major reasons in your definition.) b. Where is Point Pelee? Why was it preserved (give a minimum of 2 different things)?
What special habitats/vegetation are found in the park?
Paragraph Response.
You will be asked to write a compare and contrast paragraph on your test. Here is what is expected:
Your paragraph should begin with an introductory sentence. Then you should include at least 3 points with explanations. Your points must include at least one similarity and at least one difference Finally, you need a conclusion sentence. Here is an example of a proper paragraph answer.
The Boreal Shield and the Mixedwood Plains ecozones have many similarities and differences. First, they have similar vegetation growing within them. Both the Boreal Shield and
Mixedwood Plains support the growth of coniferous trees. However, there are few deciduous trees in the Boreal Shield and many in the Mixedwood plains. Second, the landscape is quite different. The Boreal Shield is made up of rolling hills and rocky outcrops of the Canadian
Shield, whereas, the Mixedwood plains is a flat to rolling area with lots of glacial deposits.
Finally, the climate is significantly different between the two. Although they both receive ample precipitation, the Boreal Shield has longer colder winters and shorter summers. Although, there are many similarities between these two ecozones they are still quite distinct.
Compare and contrast the following for practice (1 of 3 choice on test):
- Two types of precipitation (Frontal, orographic or convectional precipitation)
- Two soil types (ex. calcified, normal, or leached)
- Mixedwood Plains and an ecozone of your choice.