GLY 110-101: GENERAL GEOLOGY EXTRA CREDIT
advertisement

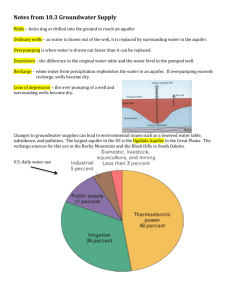
GLY 110-101: GENERAL GEOLOGY EXTRA CREDIT ASSIGNMENT: GROUNDWATER AVAILABILITY The questions for this assignment pertain to the United States Geological Survey (USGS) publication, Groundwater Availability in the United States (2008). The link below provides access to the document: http://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/1323/ 1. Groundwater exists almost everywhere across the U.S. a. true b. false 2. Groundwater is usually available even where surface water is not. a. true b. false 3. The availability of groundwater varies widely across the U.S. a. true b. false 4. Determining the availability of groundwater in any given area can usually be done reliably and quickly. a. true b. false 5. What is the potential effect of groundwater withdrawal on streams connected to the aquifer that is being pumped? a. b. c. d. decreased flow from the aquifer to the stream increased flow from the stream to the aquifer streamflow capture all of the above 6. What type of aquifer systems are most extensive in the western U.S. (first part of Figure 2)? a. b. c. d. sand and gravel sandstone sandstone / carbonate carbonate 7. What type of aquifer systems are most extensive in the eastern U.S. (second part of Figure 2)? a. b. c. d. sand and gravel sandstone sandstone / carbonate carbonate 8. Which of the following is true about groundwater withdrawals for irrigation in the U.S.? a. Western states pump more water than eastern states but the volume pumped in the western states has been decreasing. b. Eastern states pump more water than western states but the volume pumped in the eastern states has been decreasing. c. Western states pump more water than eastern states and the volume pumped in the western states has been increasing. d. Eastern states pump more water than western states and the volume pumped in the eastern states has been increasing. 9. Figure 5 shows that, at 17 million gallons of water per day, the High Plains aquifer is far and away the biggest source of water for irrigation in the U.S. According to Figure 2, where is this aquifer system located? a. b. c. d. California Michigan and Wisconsin Texas and Louisiana Texas, Oklahoma, Nebraska, and Kansas 10. The eastern seaboard, from Florida to the Carolinas to the Mid-Atlantic states, is located in a wet climate with abundant renewable freshwater resources. Why, then, is significant decline in groundwater levels occurring in some of the principal aquifers in this area? a. b. c. d. increased pumping for agricultural use increased pumping to support growing population wasteful use of water for nonessential needs like water parks and golf courses increased evaporation due to global warming 11. Which one of the following statements is true about groundwater recharge? a. Recharge generally exceeds the amount of evapotranspiration (evaporation plus transpiration from plants). b. Potential evapotranspiration cannot exceed the amount of precipitation. c. In extremely wet areas recharge can exceed the amount of precipitation. d. Recharge is generally highest in areas where precipitation is highest. 12. What are some of the consequences of groundwater pumping? a. b. c. d. e. less base flow less water for native plants less water for other wells lowered aquifer levels all of the above 13. Starting on page 39 are examples of regional aquifer assessments. The Central Valley Aquifer System is of note because 8% of the nation’s agricultural output is produced on only 1% of its land area, thanks in large part to irrigation of crops with groundwater. How can so much water be pumped from this aquifer when the climate is arid to semiarid? a. More marijuana is being grown, which uses less water than fruits and vegetables. b. The aquifer system gets additional recharge in the form of snowmelt from the mountains. c. Ocean water from coastal areas is pumped over the mountains to supplement the water pumped from the ground. d. Decreasing population in the Central Valley means people don’t need as much water, so agriculture can use more. 14. The assessment of the Coastal Plain Aquifer System mentions the transition zone between salt and fresh water in aquifers along the coastline. After, looking at Figure 20 and reading the accompanying text, select the best answer of the following: a. A normal transition zone consists of a wedge of fresh water sitting on top of salt water and angled seaward. b. A normal transition zone consists of a wedge of salt water sitting on top of fresh water and angled seaward. c. A normal transition zone consists of a wedge of fresh water sitting on top of salt water and angled landward. d. A normal transition zone consists of a wedge of salt water sitting on top of fresh water and angled landward. 15. The assessment of the Coastal Plain Aquifer System also mentions that “saltwater encroachment” can be a problem. How can this problem develop? a. b. c. d. Fresh water invades salt water-pumping wells due to over-pumping. Fresh water invades salt water-pumping wells due to under-pumping. Salt water invades fresh water-pumping wells due to over-pumping. Salt water invades fresh water-pumping wells due to under-pumping.