MathsWeb Reception
advertisement
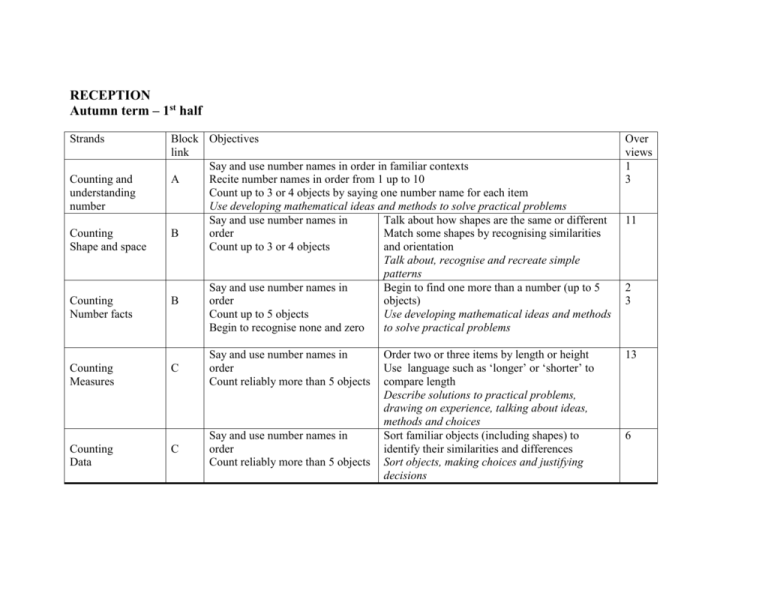
RECEPTION Autumn term – 1st half Strands Counting and understanding number Counting Shape and space Counting Number facts Block Objectives link Say and use number names in order in familiar contexts A Recite number names in order from 1 up to 10 Count up to 3 or 4 objects by saying one number name for each item Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Say and use number names in Talk about how shapes are the same or different B order Match some shapes by recognising similarities Count up to 3 or 4 objects and orientation Talk about, recognise and recreate simple patterns Say and use number names in Begin to find one more than a number (up to 5 B order objects) Count up to 5 objects Use developing mathematical ideas and methods Begin to recognise none and zero to solve practical problems Counting Measures C Say and use number names in order Count reliably more than 5 objects Counting Data C Say and use number names in order Count reliably more than 5 objects Order two or three items by length or height Use language such as ‘longer’ or ‘shorter’ to compare length Describe solutions to practical problems, drawing on experience, talking about ideas, methods and choices Sort familiar objects (including shapes) to identify their similarities and differences Sort objects, making choices and justifying decisions Over views 1 3 11 2 3 13 6 Autumn term – 2nd half Counting and understanding number A Counting Number facts Calculating D Counting Shape D Say and use number names in order in familiar contexts Begin to recite number names beyond 10 Begin to count backwards Begin to count up to 10 everyday objects Use language such as more or less to compare two numbers Match then compare the number of objects in two sets Recognise some numerals of personal significance Begin to represent numbers using fingers, marks on paper or pictures Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Say and use number names in order Find one more or one less than a number Use language such as more or less to from 1 to 5 compare two numbers Solve practical problems involving Begin to count up to 10 everyday objects counting in ‘real life’ or role play Count out up to 6 objects from a larger Describe solutions to practical problems, group drawing on experience, talking about Begin to represent numbers using fingers, ideas, methods and choices marks on paper or pictures Count up to 10 everyday objects Begin to use mathematical names for Estimate how many objects they can see ‘solid’ 3D shapes and flat 2D shapes and and check by counting mathematical terms to describe shapes Select a particular named shape Use familiar objects and common shapes to create and recreate patterns and build models Find items from positional or directional clues Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems 1 2 3 2 9 11 12 Counting measures D Use language such as more or less to compare two numbers Match then compare the number of objects in two sets Counting Number facts Calculation E Begin to recite number names to 20 Count reliably up to 10 everyday objects, including counting out objects from a larger group and counting irregular arrangements of objects Estimate how many objects they can see and check by counting Begin to represent numbers using fingers, marks on paper or pictures Order two items by weight or capacity Use language such as more or less, heavier or lighter to compare quantities Order and sequence familiar events Use everyday language related to time Sort objects, making decisions and justifying choices Find one more or one less than a number from 1 to 10 Solve practical problems involving counting in ‘real life’ or role play Find the total number of objects in two groups by counting all of them Recognise 1p coins Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Teachers would need to decide the number of days on each part depending on children in their class. 13 14 2 9 RECEPTION Spring term Strands Counting Calculating Block Objectives link Say and use number names in A order in familiar contexts (beyond 10) Recite number names in order forwards and backwards, starting from any small number Count reliably up to 10 everyday objects Estimate how many objects they can see and check by counting Counting Shape and space B Counting Number facts B Count reliably beyond 10 objects Count out objects from a larger group Count actions or objects that cannot be moved Use language such as 'more' or 'less' to compare two numbers Compare the number of objects in two sets, then put sets of objects in order Begin to relate addition to combining two groups of objects In practical activities and discussion begin to use the vocabulary involved in adding Select two groups of objects to make a given total of objects Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Use language such as 'circle' or 'bigger' to describe the shape and size of solids and flat shapes Use familiar objects and common shapes to create and recreate patterns and build models Talk about, recognise and recreate simple patterns Find one more or one less than a number from 1 to 10 In practical activities and discussion begin to use the vocabulary involved in adding and subtracting Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Over views 1 3 8 9 3 11 2 9 Counting Measures Counting Data Counting Calculating Counting Calculating C C A D Use ordinal numbers in different contexts Use language such as 'greater', 'smaller', 'heavier' or 'lighter' to compare quantities Order items by length, weight or capacity Sort objects, making choices and justifying decisions 1 13 Recognise some numerals of personal significance Know that numbers identify how many objects are in a set Represent numbers using fingers, marks on paper or pictures Count how many objects share a particular property (including shapes), presenting results using pictures, drawings or numerals Sort objects, making choices and justifying decisions 4 6 Recite number names in order forwards and backwards, starting from any small number Recognise numerals 1 to 5 Match sets of objects to numerals that represent the number of objects Begin to relate subtraction to 'taking away' In practical activities and discussion begin to use the vocabulary involved in subtracting Describe solutions to practical problems, drawing on experience, talking about their own ideas, methods and choices 1 7 9 Recite number names in order forwards and backwards, starting from any small number Find one more or one less than a given small number Begin to count in twos Begin to relate addition to combining two groups of objects and subtraction to 'taking away' In practical activities and discussion begin to use the vocabulary involved in adding and subtracting Select two groups of objects to make a given total of objects Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems 2 8 9 Recognise numerals 1 to 9 Match sets of objects to numerals that represent the number of objects Find items from positional or directional clues Use everyday words to describe position Talk about, recognise and recreate simple patterns 7 12 D Estimate how many objects they can see and check by counting Count an irregular arrangement of objects 3 14 E Recite number names in order forwards and backwards, starting from any small number Count in twos Recognise numerals 0 to 9 Use everyday language related to time; order and sequence familiar events and measure short periods of time Know days of the week Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Count repeated groups of the same size (twos/pairs) Share objects into equal groups (twos/pairs) and count how many in each group Describe solutions to practical problems, drawing on experience, talking about their own ideas, methods and choices Counting Shape D Counting Measures Counting Number facts Calculating Teachers would need to decide the number of days on each part depending on children in their class. 5 10