pdf file
advertisement

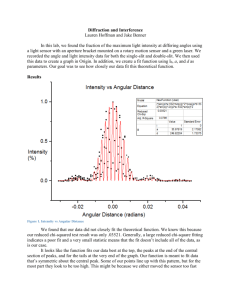
16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS University of Massachusetts Lowell The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Subject: Introduction to Biosensors Wireless Optical Sensor Network Project Report One Team members: Ravi G Bhatia Wenchan Tong Aiken Pang Report Submit Date: 21st March, 2007 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS CONTENTS Objectives ..........................................................3 Background.......................................................4 Methodology .....................................................7 Implementation ................................................8 Result .............................................................. 10 Challenges ...................................................... 12 Reference ........................................................ 13 2 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS Objectives In the market, optical fiber biosensor needs to use bulky equipments that include tunable laser and spectrum analyzer. The spectrum analyzer cans only analyzer one to two optical fiber biosensor. If we have a lot of sample need to be analyze at the same time. We need to use more equipment that is expensive. The target samples need to be connected physically to the equipments. These wired connection let the testing not flexible enough, when you testing the samples in a lab which use a central computer to log and analyze all the samples data at the same time. In this project, we would want to provide a low cost wireless network for the connection between optical fiber biosensor and central computer. It will include three parts. Wireless module: It include a microcontroller, Analog to Digital converter and RF transmitter Photo detector: It converts light intensity to electrical signal (Voltage) Optical biosensor: It will reflect the laser which the intensity will affect by number of biomaterials attachments. 3 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 1 Background Optical Fiber BioSensor System 1.1 Review of Optical Fiber biosensor Theory (Field of study) The biosensor Fabry-Pérot interferometer 1.2 Motivation of using wireless network in optical sensor system We want to find a low cost, ease of deployment, multi-source sensor and battery operation platform to transfer the data to central computer. Using wireless sensor network is one of good solution. 1.3 Problem description Using optical fiber as biosensor has grown popular over the past few years as makers continue to develop new technology. One of the problems of optical biosensor is that the sensor needs to wire with a massive machine. This limitation make the sensor cannot be portable. Although 4 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS the technology have fast testing using optical biosensor, the time for transport the sample and setup the testing is too long. Another problem is that we need use more machines (increase the cost), if we want to do more than one testing at the same time. However, the demand of the market is increasing. Portable device is a trend for sensor. Therefore, it is important to create a portable, multi-sources, ease of setup platform for optical biosensor 1.4 Optical sensor Sensor Head is an optical cavity such as a Fabry Perot cavity. Biomolecular interaction changes optical path length. Intensity change proportional to optical path length and as the path length changes photodetector will detect change in intensity and transmit that information through the wireless module. Assumption: Wavelength: 1550nm Peak Output: 0.04mW Valley: 0.004mW Intensity Change: 1µW 5 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 1.5 Photo detector The input of the photodetector is the laser reflected from the optical biosensor. The intensity of the laser is proportional to the wavelength and the “L”. The “L” is related to the number of biomaterials attached on the biosensor. From the about assumption, we need to use InGaAs Avalanche Photodetector (APD). 1.6 Wireless sensor network We select the wireless sensor network because the network itself is a mesh network. Mesh network mean that it can auto construct the network connection. Each node in the network can work as forwarder (help other node to forward their data to the PC). Therefore, the sensor can be far away from the computer. In the network, it can be more than one sensor and each node can also have more than one sensor. Network coordinator Full Function node Reduced Function node Communications flow 6 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 2 Methodology For designing a wireless optical sensor network (WOSN) , there were three predicaments. Optical Sensor 1. Transform the laser intensity to voltage from optical sensor 2. Digitize the voltage value to digital format 3. Transmit the digital data from the remote site to PC Photo Sensor ADC Microcontroler MCU Radio Frequency Transmitter Microcontroler MCU Radio Frequency Transmitter Analog data PC Digital data For design of WOSN, this project comprises four stages. First stage: “Selection of photo detector” Second stage: “Simulation of optical sensor response” Third stage: “Connect photo detector to the wireless network module” Fourth stage “Modify PC program for display Intensity and detect changing ” Fifth stage: “Testing the sensitivity of the ADC” 7 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 3 Implementation 3.1 Division of work 3.1.1 Ravi Ravi will work on optical biosensor and photo sensor. He will find a correct photo sensor depends on the need of the optical sensor. He will ready the laser for the input to the biosensor. 3.1.2 Wenchan Wenchan will modify the PC side software for display the correct value with the unity of light intensity and the Analog to Digital converter. 3.1.3 Aiken The wireless network will be ready by Aiken. He will programming the wireless sensor node for correctly send the data back to PC. 3.2 Timetable WEEK TASK PLAN March 21 - 25 Order InGaAs APD March 26 - 31 Modify Wireless Sensor Algorithm for Voltage Calibration April 2-7 Simulate Biosensor operation for obtaining intensity change April 9 - 21 Hardware Assembly & Testing 8 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 3.2 Budge Wireless sensor node: US$100 each (we need at least two) Photosensor: US$50 each Connector: US$10each (at least 4) Total cost will be $290 3.3 Optical sensor simulation We will use a connect optical fiber equipment to simulate the situation of attaching bio materials. 3.4 Software development 3.4. 1 Programming wireless sensor module Now the module can be send the photosensor (one of the ADC in the module) value back to PC. 9 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 5 Result The purpose of the project is to construct wireless optical sensor network, which is cost-effective and low power consumption. 5.1 Data from sensor node 10 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 5.2 Simulation of optical biosensor (OBS) The left hand side is the output of the OBS under the simulation of no biomaterials attached on the biosensor. The right hand side is the output of the OBS under thesimulation of some biomaterials attached on the biosensor. We found that the output of the OBS would increase where there is some biomaterials attached on the OBS. 11 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 6 Challenges 6.1 Difficulties encountered 1. 1550 nm wavelength Detection - InGaAs Avalanche Photodetector needed 2. Aligning sensor with photodetector – Need a photodetector with Fiber Pigtail connector 3. Calibration of wireless sensor to convert intensity difference into appropriate voltage for information processing 4. Cost and Compactness of our Design 12 16.541 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSENSORS 8 Reference 1) www.moteiv.com 2) www.zigBee.org 3) Fiber Optic Sensors, Francis Yu, Shizhuo Yin 4) www.sales.hamamatsu.com 13