Alabama-Science-Assessment-Review-Notes
advertisement
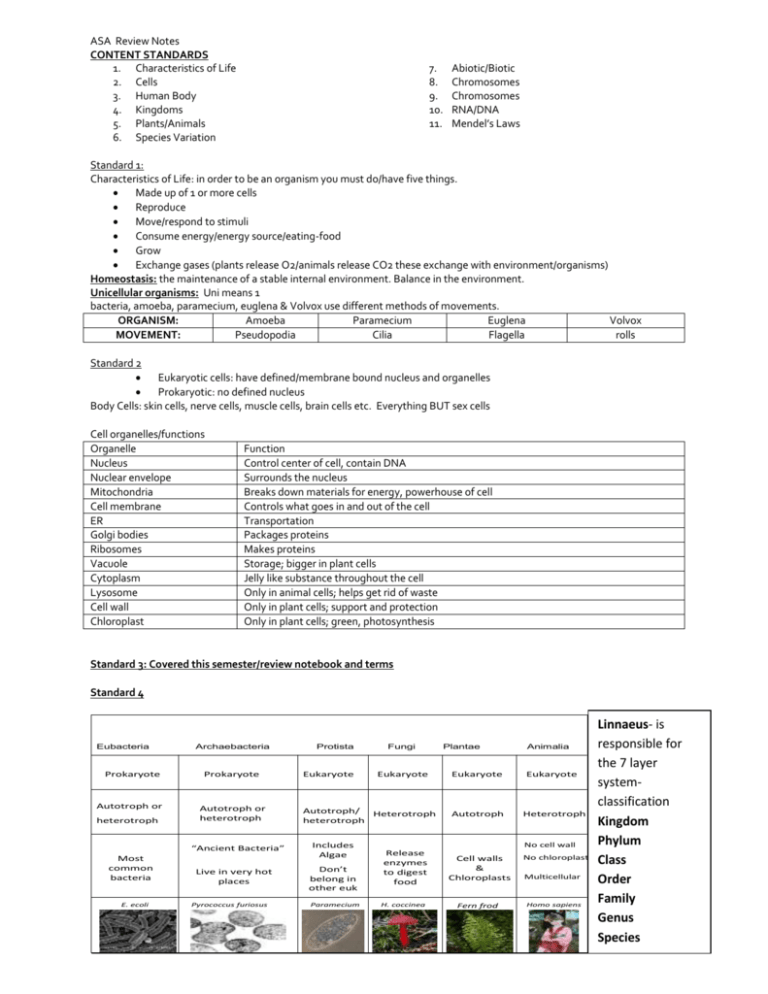
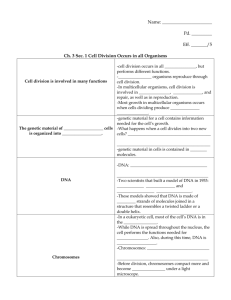
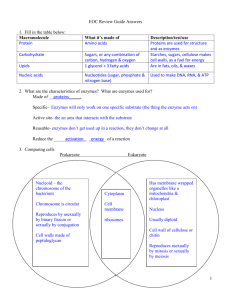
ASA Review Notes CONTENT STANDARDS 1. Characteristics of Life 2. Cells 3. Human Body 4. Kingdoms 5. Plants/Animals 6. Species Variation 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Abiotic/Biotic Chromosomes Chromosomes RNA/DNA Mendel’s Laws Standard 1: Characteristics of Life: in order to be an organism you must do/have five things. Made up of 1 or more cells Reproduce Move/respond to stimuli Consume energy/energy source/eating-food Grow Exchange gases (plants release O2/animals release CO2 these exchange with environment/organisms) Homeostasis: the maintenance of a stable internal environment. Balance in the environment. Unicellular organisms: Uni means 1 bacteria, amoeba, paramecium, euglena & Volvox use different methods of movements. ORGANISM: Amoeba Paramecium Euglena Volvox MOVEMENT: Pseudopodia Cilia Flagella rolls Standard 2 Eukaryotic cells: have defined/membrane bound nucleus and organelles Prokaryotic: no defined nucleus Body Cells: skin cells, nerve cells, muscle cells, brain cells etc. Everything BUT sex cells Cell organelles/functions Organelle Nucleus Nuclear envelope Mitochondria Cell membrane ER Golgi bodies Ribosomes Vacuole Cytoplasm Lysosome Cell wall Chloroplast Function Control center of cell, contain DNA Surrounds the nucleus Breaks down materials for energy, powerhouse of cell Controls what goes in and out of the cell Transportation Packages proteins Makes proteins Storage; bigger in plant cells Jelly like substance throughout the cell Only in animal cells; helps get rid of waste Only in plant cells; support and protection Only in plant cells; green, photosynthesis Standard 3: Covered this semester/review notebook and terms Standard 4 Eubacteria Prokaryote Autotroph or heterotroph Archaebacteria Prokaryote Autotroph or heterotroph “Ancient Bacteria” Most common bacteria E. ecoli Live in very hot places Pyrococcus furiosus Protista Eukaryote Autotroph/ heterotroph Includes Algae Don’t belong in other euk Paramecium Fungi Plantae Eukaryote Eukaryote Heterotroph Autotroph Release enzymes to digest food Cell walls & Chloroplasts Animalia Eukaryote Heterotroph No cell wall H. coccinea Fern frod No chloroplasts Multicellular Homo sapiens Linnaeus- is responsible for the 7 layer systemclassification Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Standard 5 Plants 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Autotrophs (make their own food) Cells: Square in shape, have chloroplasts, cell wall and large vacuole Producers (produce food for other organisms) In mitosis: cell plate forms Photosynthetic: process of using sun to Get energy from sun make their own food Parts of a plant: Stamen-this is the male part of the flower. It is made up of the filament and anther; it is the pollen producing part of the plant. The number of stamen is usually the same as the number of petals. Anther- This is the part of the stamen that produces and contains pollen. It is usually on top of a long stalk that looks like a fine hair. Filament- This is the fine hair-like stalk that the anther sits on top of. Sepal- The parts that look like little green leaves that cover the outside of a flower bud to protect the flower before it opens. Style- Another female part of the flower. This is the long stalk that the stigma sits on top of. Stigma-One of the female parts of the flower. It is the sticky bulb that you see in the center of the flowers, it is the part of the pistil of a flower which receives the pollen grains and on which they germinate. Pollen-sperm cells for a plant. Ovary- The part of the plant, usually at the bottom of the flower that has the seeds inside and turns into the fruit that we eat. The ovary contains ovules. Ovule- The part of the ovary that becomes the seeds. Pistil- This is the female part of the flower. It is made up of the stigma, style, and ovary. Each pistil is constructed of one to many rolled leaf-like structures. Petal- The colorful, often bright part of the flower. They attract pollinators and are usually the reason why we buy and enjoy flowers. Sperm-male sex cell Egg –female sex cell Endosperm- food storing tissue Fertilization-the joining of a egg and sperm Self pollination- gravity, insects, wind and rain and is when pollen is transferred to the stigma of a flower on the SAME plant. Cross-pollination -pollen is transferred from one plant to ANOTHER plant of the same species Animals: Heterotrophs: need outside source for food Consumers: eat producers and other organisms Cells: round, have Lysosomes Sexual reproduction only Get energy from plants Standard 6 Species Variation: Changes in species behaviors/relationships Adaptations are due to climate, camouflage, isolation, geography/location and species Interactions: Competition Mutualism: mutually beneficial for both organisms Parasitism: the relationship between two different kinds of organisms: 1 receives benefits from the other by causing damage to it Symbiotic Communities/populations; organisms living together Standard 7 Abiotic vs. Biotic Abiotic- non living (A = NO, BIO = Life)-water, soil, air/gases, metal, ect. Biotic – living Standard 8 and 9 Mitosis Meiosis Body Cells (Somatic) Sex Cells 2 diploid cells (2n, double # of chromosomes) 4 haploid cells( n, ½ the # of chromosomes) Goes through phases once Goes through phases twice Has Spindle fibers Has Spindle fibers Cells are identical Cells are different, more variation 23 chromosomes Crossing over occurs-Prophase I Standard 10 DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Deoxyribose sugar 2 strands ATCG Pairing A – T Chargaff’s Rule: A will always equal T and C will always equal G • • Job of DNA: Give instructions for building and maintaining cells Able to copy each time cells divide RNA: Ribonucleic Acid Ribose sugar 1 strand AUGC U-uracil A–T U-A • • DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides; consisting of a sugar, a phosphate, and a base All nucleotides are identical except for the base. There are four bases: • A-adenine • G-guanine • T-thymine • C-cytosine Heredity: the passing of traits from parents to offspring • Mutations: Changes in the number, type, or order of bases on a piece of DNA. Three mutations: 1. Deletion-base is removed 2. Insertion-base is added 3. Substitution-base is replaced • Chromosomes made of DNA. • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material that is located on a chromosome that determines the inherited characteristics. Standard 11 MENDELS LAWS: 1. Dominance: Dominance shows up if at least 1 allele 2. Segregation: separation 3. Independent Assortment: distributed Genetics info: HOMOZYGOUS: Same 2 alleles/DD, dd = Punnett square: same purebred show possible genotype for offspring HETEROZYGOUS: 2 different alleles/Dd different hybrid each square is worth 25% Dominant: Big letter/will always show anytime 2 heterozygous are crossed you get a 3:1 ratio Bb x Bb = BB, Bb,Bb, bb (3 will be Recessive: Little letter/ doesn’t show unless dominant to 1 recessive) rr if purebred: must be either homozygous and Ratio: 1 out of 4 or 1 out of 3 count boxes can be dominant homozygous (BB)or Probability: a percentage out of 100% homozygous recessive (bb) Allele’s individual letters if Hybrid : will always be heterozygous (1 big Genotype: 2 alleles coding for a trait letter/1 little letter) Phenotype: physical characteristics that genes code for/what it LOOKS LIKE