Minerals
advertisement

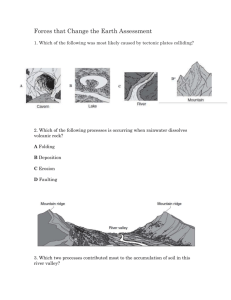
Mrs. Giorgianni/Physical Setting Earth Science UNIT #III: SURFACE PROCESSES AND LANDSCAPES Main Concepts/Ideas: Weathering is the physical and/or chemical breakdown of rocks. Erosion is the transport of weathered materials. The main agents of erosion are: Streams/running water, glaciers, wind, waves and mass movement. Deposition is the dropping off of weathered particles carried by erosion. Sediments are either sorted (water, wind, waves) or unsorted (glaciers, mass movement). Sorting is determined by the size, shape and density of the particles. Porosity and permeability determine how water passes through the soil. Landscape features result from the interaction of surface processes (weathering, erosion and deposition) and tectonic forces. Key Questions: What are the types of weathering? How do each of the main agents of erosion transport sediment? Explain how type of sorting can provide evidence of erosion and deposition. Describe the processes involved in the formation of landscape features. Integrate the processes of porosity and permeability into groundwater movement. Vocabulary: ~ Due Friday, November 15, 2013 Abrasion Deposition Discharge Erosion Erratic Infiltration Landscape Outwash Permeability Porosity Stream Drainage Pattern Striations U-Shaped Valley V-Shaped Valley Velocity Weathering Lab Activities: Chemical Weathering Deposition of Sediments Landscapes of NYS Porosity and Permeability Stream Abrasion Castle Learning Homework Assignments: ** ALL CASTLE LEARNING ASSIGNMENTS ARE DUE ON MONDAY OF THE FOLLOWING WEEK!!! ** Castle Learning Week #10: Castle Learning Week #11: Castle Learning Week #12: Castle Learning Week #13: Weathering/Erosion/Deposition ~ Due Monday, November 11 Surface Processes ~ Due Monday, November 18 Porosity/Permeability ~ Due Monday, November 25 NYS Landscapes ~ Due Monday, December 2 Quizzes/Unit Test: Topic Quizzes may be given after each sub-unit: Landscapes Types of weathering Erosion Deposition Water in the Ground Porosity and Permeability Surface Processes Unit Test ~ On or about Tuesday, December 3 o 25 Multiple choice questions – BRING A PENCIL o 5 Short answer questions Always bear in mind that your own resolution to succeed is more important than any other. Abraham Lincoln Giorgianni ~ Surface Processes Unit Outline 2013/2014 SURFACE PROCESSES Main Concept Review Weathering and Erosion 1. WEATHERING is BREAKDOWN of earth materials, and is either chemical or physical. 2. EROSION is when materials MOVE, by gravity, wind, water, or ice. 3. Abrasion and frost action are examples of physical weathering. Chemical weathering is more dominant in warm, humid climates. 4. Glaciers leave a U-shaped valley, rivers a v-shaped valley. 5. Glaciers also leave unsorted sediments, striations, erratic boulders, and drumlins. 6. Stream deposition occurs because of water velocity differences, with the slowest water depositing the smallest sediments. Deposition may be vertical or horizontal. 7. Most of NYS is made up of Sedimentary rock, with the Adirondacks being metamorphic and Long Island being glacially deposited mixtures of loose sediments. 8. NYS landscapes are either high, mid (plateau) or low elevation. 9. Erosion is dominant on the outer curve of stream, deposition, inner. Meanders develop over time. Flood plains are wide, flat areas in which streams flow. 10. Wind erosion leaves surfaces frosted and pitted. Water in the Ground 11. Water flows through soils down into the zone of saturation. Wells must be drilled into this zone. 12. Capillary action draws water UP, against gravity. 13. ALL SOIL PARTICLE SIZES HAVE THE SAME POROSITY. 14. Smaller sized sediments have greater capillarity. 15. Porosity is the amount of water the soil can hold and is determined by sorting of particles, NOT the size. 16. Permeability is the rate water passes through the soil and is determined by size, shape and sorting. 17. When rainfall exceeds permeability, the ground is saturated and runoff occurs. 18. Infiltration is water flowing into the soil. Giorgianni ~ Surface Processes Unit Outline 2013/2014