Internal vs. External Fertilization
advertisement

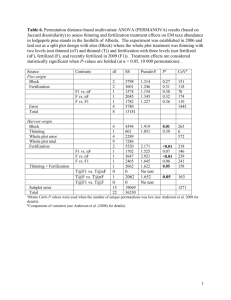
Name _______________________ Lakeland High School Date ________________________ Biology/Mrs. Cropsey - Packet # 44 Internal vs. External Fertilization What is fertilization? The union of sperm and egg cells to form a zygote How are sperm cells different from egg cells? Sperm cells are smaller Sperm cells can move – they swim with a flagellum There are two types of fertilization – internal and external Internal = inside the body External = outside the body Both types require a fluid environment-why? So sperm can swim External Fertilization Definition: Fertilization which occurs outside the body What types of organisms use external fertilization? Water animals (such as fish) What are some disadvantages of external fertilization? Eggs may wash away Eggs can die / get eaten Sperm may get lost Sperm \ eggs may get swept away 1 What can these organisms do to make sure that at lease some eggs are fertilized? Produce lots of eggs and lots of sperm, so at least some are fertilized. Internal Fertilization Definition: Fertilization inside the body What types of organisms use internal fertilization? Land animals – birds, reptiles, mammals The fluid environment needed for the sperm to swim is provided for by the female What is the advantage of this type of fertilization? More protection Note: There are fewer eggs produced by the female of a species that has internal fertilization as compared to external fertilization, but both types require a large amount of sperm to be produced by the male Why? The eggs are protected so less chance of something happening to them, but sperm can still get lost or die before they make their way to the egg. 2 Development after fertilization External Development Definition: Development outside the body – usually in an egg Examples: fish, birds, reptiles What problem does this create for the developing organism? It is unprotected – open to effects of the weather, predators, etc. Internal Development The zygote remains in the female’s body and develops (no shell is formed) Examples: us, dogs, cats Care of young There are different degrees of parental care provided to the developing offspring Examples: Fish - no parental care Birds- a little bit of parental care Mammals- a lot of parental care What do you think is the relationship between the amount of parental care and the number of eggs produced? The more care provided, the less eggs produced 3 Summary Questions 1. Why do organisms in which external fertilization and external development occurs produce large numbers of eggs? 2. Why wouldn’t external fertilization work on land? 3. In organisms that use internal fertilization, what are the 2 ways in which the zygote can develop? 4. Describe the relationship between the amount of parental care and the survival of the organism? 4