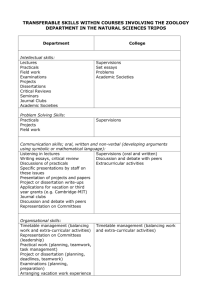
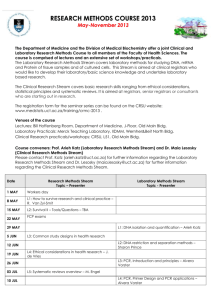
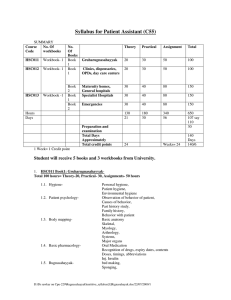
MGLO 7101Instrumentation and data analysis
advertisement

Makerere University Geology Department 1. Course Name: Instrumentaion and data analysis 2. Course Code: MGLO 7101 3. Course Description The course covers methods used in obtaining geoscience data write from desk study, to the field and the lab depending on the research problem. It also covers the methods that can be used to process and analyze the data into formats that are understandable and can be interpreted by end users. At first stage (desk study) the students learn about the various sources of data such as Geological Surveys, Universities, Research Centers, national and interntional information centers and networks as well as remote sensing techniques. In the field students are taught how to plan reconnaissance and detailed surveys as well as investigation strategies involving geological, geophysical and geochemical prospecting methods, sampling and use of GPS. In the lab the methods includes instrumentation, advantages and limitations of microscopic studies, microprobe analysis, AAS, ICP-AES, INAA, mass spectroscopy, XRF and XRD. The students learn how to plan their research by choosing methods that are easily available, easy to use, affordable, fast and answer as many questions as possible. Data quality is also emphasized by teaching about sources of error, types of errors and how they can be detected and eliminated. Students are also introduced to GIS especially in the production of maps and other types of modelling. . Students do practicals, assignments and tests. The course is divided into the following major topics: Data acquisition Data processing, analysis and presentation Data quality GIS 4. Course objectives To learn the systematic ways of selecting appropriate methods during geoscientific research. To identify the cheap and modern methods used at different stages in geoscientific research. To learn how to collect, analyze and present geoscientific data. 5. Teaching and Assessment Pattern Duration of course The content of the course will be covered in one 15 weeks academic semester with 4 hours of instruction per week. Assignments, tests and practicals. Mode of instructions Most of the instruction will be lecture oriented but usually the lectures start with a 10 minutes discussion to determine how the students understand the subject. The students are free to interrupt the instructor and ask questions whenever necessary. Students are encouraged to get more information from the reference list, other academic staff, fellow students and the internet. There will be assignments every two weeks, two tests, practicals. Assessment pattern The following instruments will be used to assess the extent of growth in skills, abilities and understanding acquired Requirements Tests Assignments Class discussions Practicals PA Exam Total Contribution 15% 10% 5% 10% 40% 60% 100% All scores will then be converted to letter grades using the system shown below: Marks 5 80-100 75-79.9 70-74.9 65-69.9 60-64.9 55-59.9 50-54.9 45-49.9 40-44.9 35-39.9 Below 35 Letter Grade A B+ B BC+ C CD+ D DE Grade Point 5 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 6. Reading List The reading list will include but not limited to the following: Hutchison, C. S., 1974. Laboratory handbook of petrographic techniques, 527p, John Willey and sons. Kearey,P., Brooks, M., 1984. An introduction to Geophysical Exploration. Lillesaand, T., Kiefer, R. W., 1979. Remote sensing and image interpretation,612p, Addison Wiley and sons, Canada. Gill, R., 1997. Modern analytical geochemistry> An introduction to quantitative chemical analysis techniques for earth, environment and material scientists. Rollinson, H. R., 1993. Using geochemical data evaluation, presentation, interpretation, Addison Wesley Longman, Harlow, 352p. Lecture notes. 7. Course Outline Data acquisition Desk study, field work, laboratory techniques Data processing, analysis and presentation Preparation and organization of a poster, how to write a dissertation, scientific report and paper, and oral presentation. Data quality Experimental errors, sources of error, detection and elimination of errors. GIS Definition, applications, types of models, types of boundaries, representations of geographic fields, data processing. 8. Suggested Teaching Program I. Data acquisition 4 weeks Assignment 1 Desk study Field work Laboratory techniques II. Data processing, analysis and presentation 3 weeks Preparation and organization of a poster How to write a dissertation, scientific report and paper Oral presentations Test Assignment 2 and 3 III. Data quality 3 weeks Experimental errors Sources of error Detection and elimination of errors. Assignment 4 IV. GIS 4 weeks Definition Applications Types of models, Types of boundaries of geographic phenomenon Representations of geographic fields and objects Data processing. Assignment 5 and 6 Test 9. Responsbility of students Regular attendance, do all assignments, practicals and tests 10. Responsibility of the Course Lecturer Regular and punctual teaching, accurate and prompt grading of assignments, tests, discussions, practicals and examinations. Should be available to students after formal lectures.