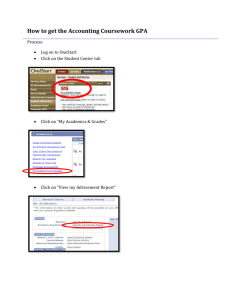
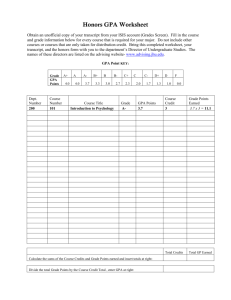
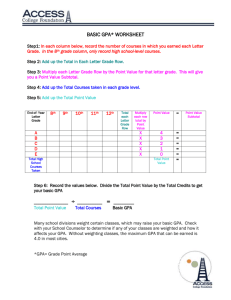
factors_for_admission - University of Washington

Case: Selection of Factors for UW Admission
The data for this case has been supplied by Professor Vandra Huber, Professor of
Management, University of Washington Business School. Variables 1 through 23 are potential predictors of school success, which is measured by Variable 24 College GPA.
Variable 24 is the criterion or outcome variable. Your goal is to use any or all of the predictor variables to predict College GPA and account for as much variance as possible.
Determine a best subset of predictors of College GPA, which could be used to select students for admission to the University of Washington.
In Professor Huber’s class, following statistical analyses are assigned.
1.
Calculate the following:
Calculate the means, standard deviations for all variables.
For the demographic variables (gender, ethnicity) and the biodata items (mother and father’s occupation, work, birth order), calculate percentages by each level of the variable (e.g. 55% female and 45% male)
Calculate the correlation coefficient and significance level for each predictor variable with college GPA.
You should prepare a summary table (Label it Table A, Mean, Standard Deviations,
Significance level and Correlation Coefficients).
2.
For each significant predictor, what type of selection test (i.e. cognitive ability, biodata, physical ability test) is it? Justify your answer.
3.
For each valid predictor, what type of validity does it represent (e.g. concurrent, predictive, face, content, etc.) ? Justify your answer.
4.
Look at all the significant personality variables. What kind of personality does well ( as measured by
GPA) in college? Write a summary paragraph describing the personality of the college student who does well (e.g. Students who earn high GPAs in college tend to be very calm. That is they have a low level of neuroticism. They also are low in Machiavelliansm such that they do not believe they will not use any means to influence others…etc)
5.
Graph (scatter diagram) the relationships (one graph per variable set) between college GPA and (1)
High school GPA, (2) Intelligence;(3) Conscientiousness, and (4) NEO-N, extraversion. Assume that the university uses a cutoff score between good and poor performance of 3.4 College GPA. Assume the cutoff scores for each predictors is the mean for that variable, determine base rates, predictor rates, true positive, false positive, true negative and false positive rates for each variable set.
Using the graphs and what you know the relationship between base rates and predictor rates and the criteria for a good predictor, indicate the extent to which each of three predictors would help improve your ability to identify successful performers prior to admission.
6.
How would your answer to the last question change if the cutoff scores on each predictor was raised by
20%?
7.
What is your final recommendation as to which predictors and cutoff scores should be used. You should consider each variable examined in this study (not just the three examined in response to the preceding question). Your recommendation should be clearly justified and include all relevant considerations including EEO (sex) ramification, costs, etc. You should develop a multiple regression equation including the variables. The higher R² the greater the amount of variance accounted for in
College GPA. Summarize your recommendations for selecting undergraduate business school students in a properly formatted, business memorandum to Associate Dean of Admission.
Appendix:
List of variables in HRMOB.XLS:
The survey data includes:
1.
V1 = age;
2.
V2 = sex (0 male 1 female);
3.
V3 = Ethnicity (1) Caucasian (2) Afro-American (3) Asian (4) Latino (5) Other;
4.
V4 = High School GPA cumulative;
5.
V5 = High School last 2 years;
6.
V6 = SAT Verbal;
7.
V7 = SAT Math;
8.
V8 = SAT Cumulative;
9.
V9 = Work in High School (0) No (1) Yes;
10.
V10 = Mother’s occupation. (0) Not employed (1) Employed
11.
V11 = Father’s occupation. Note: All fathers were employed
12.
V12 = Birth order (1) first born (2) second born (3) third born (4) fourth born (5) fifth born (6) sixth born
13.
V13 = Intelligence;
14.
V14 = Emotional IQ Overall. Emotional intelligence has often been associated with “street smarts.” EQ is a type of social intelligence that involves the ability to monitor one's own and others' emotions, to discriminate among them, and to use the information to guide one's thinking and actions. Self-awareness (intrapersonal intelligence), empathy and handling relationships
(interpersonal intelligence) are essentially dimensions of social intelligence.
15.
V15 = Survey A Neuroticism. Neuroticism is a measure of one’s predisposition to anxiety. Low scores indicate that the individual does not normally get anxious. Typically, low scores need external stimulation (instructions for the boss, goals) to get motivated. Moderate scores tend to be associated with high performance. Individuals who score very high on neuroticism tend to be extremely anxious. The higher the score, the greater the degree of neuroticism
16.
V16 = Survey B Locus of Control. Individuals who have an internal locus of control believe that the things that happen to them are under their control. Conversely, individuals who have an external locus of control believe that chance, luck, and external factors affect what happens to them. The higher the score the more external the locus of control.
17.
V17 = Survey C Self Monitoring. People who are high self monitors tend to pay attention to external cues and adjust their behavior to “fit the situation.” High Self monitors do well is sales jobs and boundary spanning positions.
18.
V18 = Survey D Tolerance of Ambiguity. In the U.S. Department of Education’s SCAN’s report, tolerance of ambiguity was cited as one of the most important skills needed for today and tomorrow’s workforce. Individuals who have a high tolerance for ambiguity tend to be able to adjust better to variations in work, culture and handle life’s ups and downs better. The higher the score on this measure, the greater the tolerance for ambiguity.
19.
V19 = NEO-N Emotional Stability (The” Big Five” dimensions of personality are assessed by the
NEO-Personality Inventory. The five factors are discussed in your textbook in the chapter entitled “Personality Assessment.” A high score indicates that the individual displays more of that attribute than an individual who scores lower.
20.
V20 = NEO-E Extraversion
21.
V21 = NEO-O Openness to new experiences
22.
V22 = NEO-A Agreeableness
23.
V23 = NEO-C Conscientiousness
24.
V24 = College GPA