contents 2002 MAY
advertisement
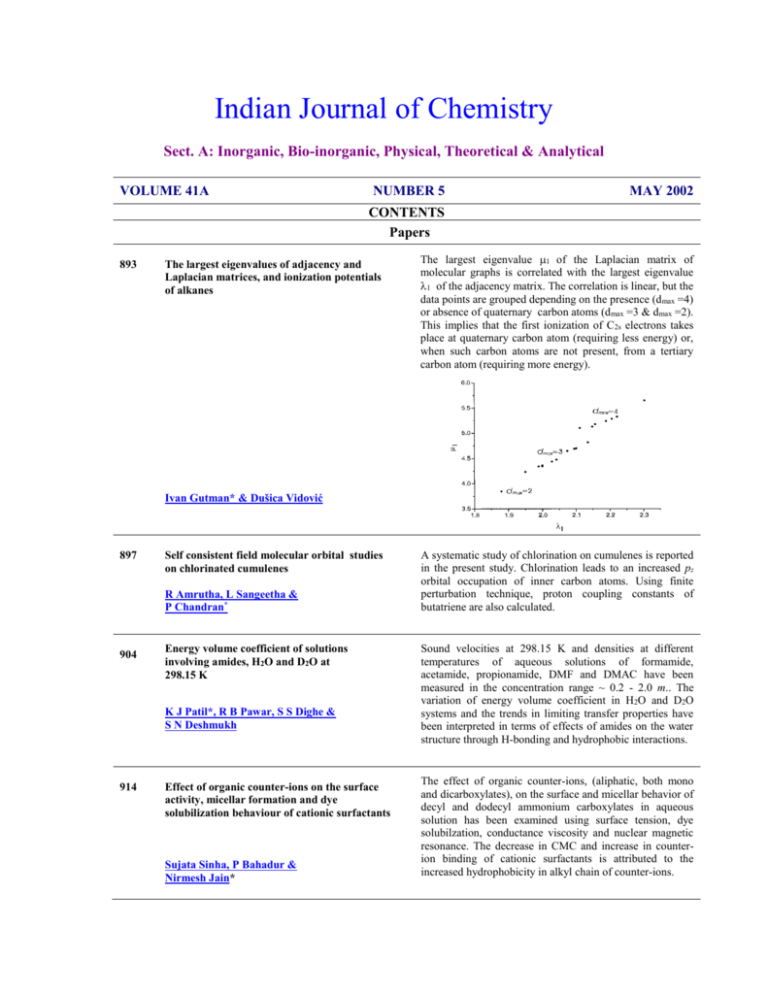
Indian Journal of Chemistry Sect. A: Inorganic, Bio-inorganic, Physical, Theoretical & Analytical VOLUME 41A NUMBER 5 MAY 2002 CONTENTS Papers 893 The largest eigenvalues of adjacency and Laplacian matrices, and ionization potentials of alkanes The largest eigenvalue 1 of the Laplacian matrix of molecular graphs is correlated with the largest eigenvalue 1 of the adjacency matrix. The correlation is linear, but the data points are grouped depending on the presence (d max =4) or absence of quaternary carbon atoms (d max =3 & dmax =2). This implies that the first ionization of C2s electrons takes place at quaternary carbon atom (requiring less energy) or, when such carbon atoms are not present, from a tertiary carbon atom (requiring more energy). Ivan Gutman* & Dušica Vidović 897 Self consistent field molecular orbital studies on chlorinated cumulenes R Amrutha, L Sangeetha & P Chandran* 904 Energy volume coefficient of solutions involving amides, H2O and D2O at 298.15 K K J Patil*, R B Pawar, S S Dighe & S N Deshmukh 914 Effect of organic counter-ions on the surface activity, micellar formation and dye solubilization behaviour of cationic surfactants Sujata Sinha, P Bahadur & Nirmesh Jain* A systematic study of chlorination on cumulenes is reported in the present study. Chlorination leads to an increased pz orbital occupation of inner carbon atoms. Using finite perturbation technique, proton coupling constants of butatriene are also calculated. Sound velocities at 298.15 K and densities at different temperatures of aqueous solutions of formamide, acetamide, propionamide, DMF and DMAC have been measured in the concentration range ~ 0.2 - 2.0 m.. The variation of energy volume coefficient in H2O and D2O systems and the trends in limiting transfer properties have been interpreted in terms of effects of amides on the water structure through H-bonding and hydrophobic interactions. The effect of organic counter-ions, (aliphatic, both mono and dicarboxylates), on the surface and micellar behavior of decyl and dodecyl ammonium carboxylates in aqueous solution has been examined using surface tension, dye solubilzation, conductance viscosity and nuclear magnetic resonance. The decrease in CMC and increase in counterion binding of cationic surfactants is attributed to the increased hydrophobicity in alkyl chain of counter-ions. 921 Electrochemical characterization of a Dowex-50 membrane has been described on the basis of mixed membrane potential and conductance measurements. It is shown that thermodynamic considerations can be used with advantage to derive permselective behaviour of the membrane even when electrolyte mixtures are used. Observed variation in permselectivity with composition of NaCl and KCl mixture is explained in terms of alteration in co-ion exclusion as a result of accompanying swelling/deswelling of the membrane matrix Mixed membrane potentials and electrochemical characterization of membranes Kehar Singh*, A K Tiwari & Chandra Shekhar Dwivedi 928 Liquid-phase Friedel-Crafts acylation using NixMn(1-x)Fe2O4 spinel catalysts S Sugunan*& K Nishamol 934 Heavy metal ion uptake by homo and copolymers – A comparative study K Hussain Reddy* & A Ravikumar Reddy 942 Synthesis, spectral, redox and biological studies of some Schiff base copper(II), nickel(II), cobalt(II), manganese(II), zinc(II) and oxovanadium(II) complexes derived from 1-phenyl-2,3-dimethyl-4(4-iminopentan-2-one) pyrazol-5-one and 2-aminophenol/2-aminothiophenol N Raman*, A Kulandaisamy & K Jeyasubramanian Notes 950 Stereochemical and compositional assignments of acrylonitrile/butylacrylate copolymers by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy Acrylonitrile/butylacrylate copolymers have been prepared by bulk polymerization using benzoyl peroxide as initiator. 2D-heteronuclear single quantum correlation (HSQC) and total correlated spectroscopy (TOCSY) spectra have been used to resolve the complex 1H NMR spectrum and to determine the compositional and configurational sequences of the copolymers A S Brar & D R Pradhan 955 Hydrogen production by water electrolysis using solid polymer electrolyte Sang-Do Han, K C Singh*, R K Rana & Kee-Bae Park Electro- catalysts platinum and iridium are deposited on Nafion-117 membrane by chemical deposition method. The minimum loading of Pt and Ir required on SPE for efficient working of electrolysis cell are found to be between 1.15mg/cm2 and 2.8mg/cm2 respectively. The cell voltage has been found to decrease with increase in temperature. 960 Potentiometric studies on the protonation constants and solvation of some -amino acid methyl- and ethyl esters in ethanol-water mixtures Alev Doğan , Fitnat Köseoğlu & Esma Kılıç 963 Preparation of phthalimide by ammoxidation of o-xylene and characterization of V-CrO/SiO2 catalyst Xie Guangyong, Zheng Qiong*, Huang Chi &Chen Yuanyin 967 Kinetics of reduction of triaminotolyl diphenylmethane chloride (rosaniline hydrochloride) by hydroxide ions in aqueous medium J F Iyun, A O Peters & O A Babutunde* 970 Novel synthesis of allyl and cyclopropylcarbinyl thiocyanates by the reaction of organocobaloximes with thiocyanogen B D Gupta*, Debprasad Mandal & Vandana Dixit The stoichiometric protonation constants of methyl- and ethyl esters of glycine, L-alanine, L-valine, L leucine, L-phenylalanine, L-serine, L-methionine and methyl ester of L -isoleucine in 20-80 % (v/v) ethanol-water mixtures and the effect of solvent on -amino acid methyl- and ethyl esters have been determined at 25C under nitrogen atmosphere. The variation of the protonation constants is discussed on the basis of specific solute-solvent interactions. O V-Cr-O/SiO2 CH3 + NH3 + 3O2 CH3 NH + 4H2O O 973 Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical properties of Fe(III) binuclear complexes C A Sureshan & P K Bhattacharya* 976 Synthesis and characterization of nicotinic acid coordinated metal carbonyl complexes Reflux,Ar M(CO)6 + CH3CN excess 8h, M=Mo 48 h, M= W D Jesudurai & S Vancheesan* fac-[M(CO)3(CH3CN)3] in situ NIC/EtOH (3 equiv.) RT,1h fac-[M(CO)3(NIC)3] 981 Adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of nickel (II) using N-2-pyridylbenzamidine as a complexing reagent An adsorptive stripping voltammetric method for the trace measurement of nickel(II) based on the use of N-2pyridylbenzamidine as the complexing agent at hanging mercury drop electrode in 0.8 M NH4Cl / NH3 buffer of pH 9.6 is described. R K Mahajan* & P Dhawan 985 Extractive determination of cobalt (II) using tri-iso-octylamine H K Mondal, B Sarkar & S Basu* 988 Rapid spectrophotometric determination of platinum(IV) using piperonal thiosemicarbazone Prakash Shetty, A Nityananda Shetty & R V Gadag 991 Preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of heavy metals in natural water samples using a C18 cartridge and atomic absorption spectrometry Y Yamini*, H Ebrahimzadeh & M Chaloosi 996 Liquid-liquid extraction of tin (IV) with Cyanex 302 Sunil G Sarkar Purushottam M Dhadke* A selective and quantitative exraction method for the determination of cobalt(II) using tri-iso-octylamine (TIOA), a high molecular weight tertiary amine, into cyclohexane from aqueous hydrochloric acid medium has been developed A simple, rapid, selective and sensitive spectrophotometric method for the determination of platinum has been proposed based on the colour reaction between platinum(IV) and piperonal thiosemicarbazone (PATS) in 0.008 - 0. 032 M sulphuric acid medium. A rapid and reliable sample preconcentration method has been developed to separate Ni2+, Bi3+, Cd2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+and Co2+ (heavy metal ions) from natural water samples. The chelating agent sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (SDDTC) and a C18 cartridge have been used for preconcentration. A method for liquid-liquid extraction of Sn(IV) has been proposed. The optimum extraction conditions have been evaluated by studying parameters like acidity, extractant concentration, period of equilibrium, effect of diluents and effect of diverse ions. 999 Fluoride estimations in water using ion selective electrode: Choice of appropriate TISAB Meetu Agarwal, Kavita Rai, Rohit Shrivastav & Sahab Dass* The efficacy of ten different TISABs for fluoride estimation in water samples in presence of F- binding cations, viz., Al3+ and Fe3+, has been investigated. The study suggests that the TISAB, containing tris - hydroxymethyl aminomethane hydrochloride buffer is probably best suited for F- estimation in samples, especially, in presence of high concentrations (1-2 g dm-3) of Al3+. Authors for correspondence are indicated by (*) Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 893-896 The largest eigenvalues of adjacency and Laplacian matrices, and ionization potentials of alkanes Ivan Gutman & Dušica Vidović If G is a molecular graph and A(G) its adjacency matrix, then the Laplacian matrix is defined as L(G)=D(G)-A(G) where D(G) is the diagonal matrix of vertex degrees. We establish a relation between the largest eigenvalues of A(G) and L(G) in case of the molecular graphs of alkanes. This relation is linear, but differs for alkanes with and without a quaternary carbon atom, revealing the main features of the structure-dependence of their (first) ionization potential. An analogous, yet more general, relation holds for all trees. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 897-903 Self consistent field molecular orbital studies on chlorinated cumulenes R Amrutha , L Sangeetha & P Chandran* Cumulenes are compounds containing a unit of ‘n’ carbon atoms with (n-1) double bonds between them (n>3).The members are propadiene(allene), butatriene, pentatetraene etc. A systematic study of chlorination on cumulenes is done in the present study. Geometrical optimisation is carried out on the cumulenes using RHF wave functions with 31-G basis set using Gaussian –94. Semi-empirical calculations(CNDO/2) are performed to elicit the trend of chlorination. Chlorination of cumulenes brings out some interesting properties such as lowering of energy, redistribution of charge density, stability of odd number of double-bonded cumulenes, etc. The ionisation potential of odd number of double bonded cumulenes are high compared to that of even number of double bonded cumulenes. To study the trend of redistribution of charge densities due to chlorination it is sufficient to substitute a single chlorine atom . The inner carbon atoms distribute their electronic charges in the direction of chlorinated carbon atoms. Chlorination leads to an increased pz orbital occupation of inner carbon atoms. Using finite perturbation technique , proton coupling constants of butatriene are also calculated. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, 904-913 Energy volume coefficient of solutions involving amides, H2O and D2O at 298.15 K K J Patil*, R B Pawar, S S Dighe & S N Deshmukh Sound velocities at 298.15 K and densities at different temperatures of aqueous solutions of amides (formamide, acetamide, propionamide, DMF and DMAC) have been measured in the concentration range ~ 0.2 to 2.0 m. The experimental data have been used to calculate the thermodynamic parameters like apparent molar volume (v), apparent molar isothermal compressibility (T) of solutes at various concentrations and energy volume coefficient (dU/dV)T of solutions at different amide concentrations in H2O as well as in D2O solutions. From the infinite dilution properties (v0 and T0), the transfer volumes and transfer compressibilities for the transfer of amides from H 2O to D2O solvent system have been calculated. The variation of energy volume coefficient in H2O and D2O systems and the trends in limiting transfer properties are examined and have been interpreted in terms of effects of amides on the water structure through H-bonding and hydrophobic interactions. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 914-920 Effect of organic counter-ions on the surface activity, micellar formation and dye solubilization behaviour of cationic surfactants Sujata Sinha, Nirmesh Jain* & P Bahadur The effect of eight organic counter-ions (aliphatic, both mono and dicarboxylates) on the surface and micellar behavior of decyl and dodecyl ammonium carboxylates in aqueous solution has been examined by different physico-chemical techniques such as surface tension, dye solubilzation, conductance viscosity and nuclear magnetic resonance. The effect of these counterions as observed from surface activity, and critical micelle concentration (CMC) is explained in terms of their condensation /penetration onto/into the micelles. The decrease in CMC and increase in counter-ion binding of cationic surfactants is attributed to the increased hydrophobicity in alkyl chain of counter-ions. In the case of monocarboxylate counter-ions, CMC decreases significantly in the order : n-butyrate < propionate < acetate <formate, while for dicarboxylates decrease in CMC with increase in number of carbon atoms in the counter-ion is very less substantial. Compared to monocarboxylates, dicarboxylate counter-ions condense strongly onto the micelle surface and thus are capable of being easily incorporated into the micelles and consequently show greater surface activity, and lower CMC of cationic surfactant. The effect of temperature on surface activity and micellar behavior of decyl ammonium succinate is also reported. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 921-927 Mixed membrane potentials and electrochemical characterization of membranes Kehar Singh*, A K Tiwari & Chandra Shekhar Dwivedi Mixed membrane potential and membrane conductance measurements have been carried out using Dowex-50 membrane and sodium chloride and potassium chloride solutions of variable composition with the object of electrochemical characterization of the membrane system. The data were examined in the light of thermodynamic considerations to obtain transport numbers of the ions in the membrane phase for the estimation of permselectivity. Variation of these electrochemical parameters with composition of the electrolyte mixtures has also been examined. The results show that the presence of additional electrolyte even if its concentration is same on both sides of the membrane, significantly influences electrochemical character of the membrane. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 928-933 Liquid-phase Friedel-Crafts acylation using NixMn(1-x)Fe2O4 spinel catalysts S Sugunan*& K Nishamol The liquid-phase Friedel-Crafts acylation of toluene using benzoyl chloride as benzoylating agent has been carried out over Nix Mn(1-x) Fe2 O4(x=0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0) type systems under different reaction conditions. It is observed that the systems with high ‘x’ values are effective for the conversion of BOC and the selective formation of 4MBP. Selectivity for 4-MBP over MnFe2O4 is more than 90% under the optimized reaction conditions. Sites of moderate acidity is effective in catalyzing the benzoylation reaction. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 934-941 Heavy metal ion uptake by homo and copolymers – A comparative study K Hussain Reddy* & A Ravikumar Reddy Homo and copolymers of 2-hydroxy ethyl methacrylate and chloromethylated styrene-anthranilic acid have been prepared by free radical polymerization technique. The chelating polymers have been characterized by IR and solid state 13C NMR spectroscopic techniques. Thermal stabilities of these polymers are investigated using thermogravimetric and differential thermal analyses. Heavy metal ions viz., Pb(II), Hg(II), Cd(II) and Cr(VI) have been removed by employing the present chelating polymers. Metal ion uptake efficiency, effect of pH and time on the metal removal have also been studied. The metal removal properties are also tested under competitive conditions and found to depend strongly on pH. The polymers possess appreciable selectivity for Pb(II) and Hg(II) over Cd(II) and Cr(VI). The amount of metal uptake by the polymer has been determined using atomic absorption spectrophotometer. The polymers have been reused after desorbing the metal ion from the polymer metal complex by HCl. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 942-949 Synthesis, spectral, redox and biological studies of some Schiff base copper(II),nickel(II), cobalt(II), manganese(II), zinc(II) and oxovanadium(II) complexes derived from 1-phenyl-2,3-dimethyl-4 (4-iminopentan-2-one) pyrazol-5-one and 2-aminophenol/ 2-aminothiophenol N Raman*, A Kulandaisamy & K Jeyasubramanian Neutral tetradentate complexes of Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II), Mn(II), Zn(II) and VO(II) have been synthesised using new Schiff bases derived from 2-aminophenol/2-aminothiophenol and 1-phenyl-2,3dimethyl-4(4-iminopentan-2-one)-pyrazol-5-one in ethanol and characterized by microanalytical data, IR, UV-Vis., 1H NMR and ESR spectra. Non-electrolytic behaviour and monomeric type of the chelates have been assessed from their low conductance and magnetic susceptibility values respectively. The IR and UV-Vis. spectra suggest that all the complexes have square planar geometry except vanadyl and manganese complexes which show square pyramidal and octahedral geometry respectively. The redox behaviour of copper and vanadyl complexes has been studied by cyclic voltammetry and the ESR spectra of copper and vanadyl complexes are recorded and discussed. Antimicrobial activity of the Schiff bases and their complexes have been extensively studied on some microorganisms like Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonous aeruginosa, Shigella flexneri, Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma viridi. Most of the complexes have higher activity than the free ligand. Notes Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 950-954 Stereochemical and compositional assignments of acrylonitrile/butylacrylate copolymers by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy A S Brar & D R Pradhan Acrylonitrile/butylacrylate (A/B) copolymers have been prepared by bulk polymerization using benzoyl peroxide as initiator. 2D-heteronuclear single quantum correlation (HSQC) and total correlated spectroscopy (TOCSY) spectra have been used to resolve the complex 1H NMR spectrum and to determine the compositional and configurational sequences of A/B copolymers. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 955-959 Hydrogen production by water electrolysis using solid polymer electrolyte Sang-Do Han, K C Singh*, R K Rana & Kee-Bae Park Electro- catalysts platinum and iridium are deposited on solid polymer electrolyte [(SPE) i.e. Nafion117] membrane by chemical deposition method. The minimum loading of Pt and Ir required on SPE for efficient working of electrolysis cell are found to be between 1.15mg/cm 2 and 2.8mg/cm2 respectively. The best hydrothermal treatment temperature is found to be between 110C and 120C. The effect of the operating temperature on the cell performance is also studied. The cell voltage has been found to decrease with increase in temperature. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 960-962 Potentiometric studies on the protonation constants and solvation of some -amino acid methyl- and ethyl esters in ethanol-water mixtures Alev Doğan, Fitnat Köseoğlu & Esma Kılıç The stoichiometric protonation constants of 15 esters (methyl- and ethyl esters of glycine, L- alanine, L-valine, L-leucine, L - phenylalanine, L -serine, L -methionine and methyl ester of L -isoleucine) in 2080 % (v/v) ethanol-water mixtures and the effect of solvent on -amino acid methyl- and ethyl esters have been determined at ionic strength of 0.1 M NaCl and at 25C under nitrogen atmosphere. A potentiometric method is used and the calculation of constants has been carried out using PKAS computer programme. The logarithm of the protonation constants of -amino acid esters decreases linearly with increase in ethanol contents. The variation of these constants is discussed on the basis of specific solute-solvent interactions. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 963-966 Preparation of phthalimide by ammoxidation of o-xylene and characterization of V-Cr-O/SiO2 catalyst Xie Guangyong, Zheng Qiong*, Huang Chi & Chen Yuanyin Phthalimide, as an important intermediate of organic synthesis, has been prepared with high yield by ammoxidation of o-xylene over silica-supported vanadium-chromium oxide catalysts. Under suitable conditions, the molar yield of phthalimide can reach 89% with purity of 98.6%. The catalysts, prepared via wet-impregnation method, have been characterized by BET, XPS and XRD. Results show that vanadia and chromia form composite oxides, which exist mostly in the pores of silica. Their concerted catalytic function is the main reason for high activity. Vanadium exists mainly as pentavalent and chromium mainly as trivalent in the V-Cr-O/SiO2 catalysts, with their oxidation states changing in the redox cycles. The additive chromium can interact with the surface vanadium oxide phase and alter the structure of vanadia, which delays the formation of crystalline V2O5 and increases the catalytic activity and selectivity. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 967-969 Kinetics of reduction of triaminotolyl -diphenylmethane chloride (rosaniline hydrochloride) by hydroxide ions in aqueous medium J F Iyun, A O Peters & O A Babutunde* Kinetics and mechanism of reduction of rosaniline hydrochloride (RH) by hydroxide ions have been studied in aqueous medium at 30C at ionic strength of 1.0 mol dm-3 (NaCl). The reduction follows a second order kinetics and it conforms to the rate law: d [RH] = k2 [RH][OH-] and k2 is dt found to be 1.84 0.04 102 mol dm-3 min-1. The rate of reaction is not sensitive to changes in dielectric constant of the medium and free radicals have not been detected in the reaction. The rate of reaction decreased with increase in ionic strength. The results from our spectroscopic investigations and Michaelis-Menten analysis do not show any evidence for an intermediate of significant stability. The outersphere mechanism is, therefore, postulated for this reaction. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 970-972 Novel synthesis of allyl and cyclopropylcarbinyl thiocyanates by the reaction of organocobaloximes with thiocyanogen B D Gupta*, Debprasad Mandal & Vandana Dixit Thiocyanogen reacts in aprotic solvents with allyl and but-3-enyl cobaloximes to give moderate yields of allyl and cyclopropylcarbinyl thiocyanates. Using this method highly unstable allyl thiocyanates may be prepared in situ at low temperature. Their rearrangement to isothiocyanates is observed at sub-zero temperatures. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 973-975 Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical properties of Fe(III) binuclear complexes C A Sureshan & P K Bhattacharya* Ternary binuclear complexes (AFeL'FeA) Cl4 where L1 is the binucleating ligand 5,5-methylene-bissalicylaldehyde and ligand A is 2,2-bipyridyl or 1,10-phenanthroline, and binary binuclear complexes of the binucleating schiff base with two tridentate coordination sites, obtained by the condensation of 5,5methylene-bis-salicylaldehyde with aminoethyl pyridine, have been synthesized and characterized by spectral, magnetic, mass spectral and electrochemical studies. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 976-980 Synthesis and characterization of nicotinic acid coordinated metal carbonyl complexes D Jesudurai & S Vancheesan* Two zero-valent metal carbonyl complexes fac-[M(CO)3(NIC)3] (where M = Mo, W; 3, 4; NIC = 3HO2CC5H4N) have been synthesized and characterized by elemental and thermal analysis ( TGA, EGA ), IR and powder X-ray diffraction ( XRD ) spectroscopic techniques. The IR spectrum of complex 3 exhibits three CO stretching bands and 4 shows two CO stretching bands in addition to a carboxyliccarbonyl stretching band. The possibility of fac / mer isomerization in complex 3 has been studied by IR spectroscopy in various solvents. Elemental and mass spectrometric data are consistent with the formation of the title complexes. The powder X-ray diffractogram of complexes 3 and 4 exhibit similar pattern suggesting the same geometry. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 981-984 Adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of nickel (II) using N-2-pyridylbenzamidine as a complexing reagent R K Mahajan* & P Dhawan An adsorptive stripping voltammetric method for the trace measurement of nickel(II) based on the use of N-2-pyridylbenzamidine as the complexing agent at hanging mercury drop electrode in 0.8 M NH4Cl / NH3 buffer of pH 9.6 is described. Variable factors affecting the response, i.e., the concentration of ligand, pH, adsorption potential and adsorption time are assessed and optimized. The calibration curve for nickel(II) is linear over the range 5.0 x10 – 9 – 5.0 x 10 –8 M with accumulation time of 180 s at –0.4 V vs Ag/AgCl. The method has been applied for the determination of nickel(II) in urine samples of exposed workers of nickel plating industries. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 985-987 Extractive determination of cobalt (II) using tri-iso-octylamine H K Mondal, B Sarkar & S Basu* A selective and quantitative exraction method for the determination of cobalt(II) using tri-isooctylamine (TIOA), a high molecular weight tertiary amine, into cyclohexane from aqueous hydrochloric acid medium has been developed. The effects of concentration of HCl, extractant, metal ions, role of various diluents and diverse ions on the extraction of cobalt have been studied. The method has been successfully applied to the estimation of cobalt in several ores and pharmaceutical drug samples. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 988-990 Rapid spectrophotometric determination of platinum(IV) using piperonal thiosemicarbazone Prakash Shettya, A Nityananda Shetty & R V Gadag A simple, rapid, selective and sensitive spectrophotometric method for the determination of platinum has been proposed based on the colour reaction between platinum(IV) and piperonal thiosemicarbazone (PATS) in 0.008 - 0. 032 M sulphuric acid medium. The greenish yellow complex has an absorption maximum at 360 nm. Beer’s law is obeyed upto 6.5 ppm of Pt and the optimum concentration range is 1 - 5.1 ppm of Pt. The molar absorptivity and Sandell’s sensitivity are 3. 239 104 l mol-1 cm-1 and 0.006 g cm-2, respectively. The optimum conditions for complete colour development have been investigated by studying parameters like effect of medium, acidity, reagent concentration, time period and effect of diverse ions. The method is used for the determination of platinum in hydrogenation catalysts and platinum complexes. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 991-995 Preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of heavy metals in natural water samples using a C18 cartridge and atomic absorption spectrometry Y Yamini*, H Ebrahimzadeh & M Chaloosi A rapid and reliable sample preconcentration method has been developed to separate Ni 2+, Bi3+, Cd2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+and Co2+ (heavy metal ions) from natural water samples. The chelating agent sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (SDDTC) and a C18 cartridge have been used for preconcentration. Extraction efficiency, influence of sample and eluent flow rates, pH, amount of SDDTC, nature and amount of eluent for elution of metal ions from cartridge, break through volume and the limit of detection have been evaluated. The effects of alkali and alkaline earth metal ions on percent recovery of heavy metal ions have also been studied. The limit of detection of the proposed method for Ni 2+, Bi2+, Cd2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+and Co2+ are found to be 1.5, 5, 0.4, 3, 2.5, 0.6, 0.5 and 1 ppb, respectively. The method is applied to the recovery and determination of heavy metal ions in different water samples. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 996-998 Liquid-liquid extraction of tin (IV) with Cyanex 302 Sunil G Sarkar Purushottam M Dhadke* A method for liquid-liquid extraction of Sn(IV) has been proposed. Tin (IV) is extracted from hydrochloric acid solution of 0.25 mol dm3 with 5102 mol dm3 Cyanex-302 in toluene, followed by spectrophotometric determination of Sn(IV) after stripping the non-aqueous phase with 4.0 mol dm3 perchloric acid by Morin method. The optimum extraction conditions have been evaluated by studying parameters like acidity, extractant concentration, period of equilibrium, effect of diluents and effect of diverse ions. The method has been applied for the determination of Sn (IV) in real samples. Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 41A May 2002, pp 999-1002 Fluoride estimations in water using ion selective electrode: Choice of appropriate TISAB Meetu Agarwal, Kavita Rai, Rohit Shrivastav & Sahab Dass* Choice of appropriate TISAB (total ionic strength adjusting buffer) plays a crucial role in fluoride (F-) analysis in water samples by ion selective electrode. Despite this no guideline is, yet, available on the choice of appropriate TISAB for F- analysis in samples, particularly in presence of other ionic and nonionic species. In this study, the efficacy of ten different TISABs for fluoride estimation in water samples in presence of F- binding cations, viz. Al3+ and Fe3+ has been investigated. The study suggests that the TISAB, containing tris - hydroxymethyl aminomethane hydrochloride buffer is probably best suited for F estimation in samples, especially, in presence of high concentrations (1-2 g dm-3) of Al3+.