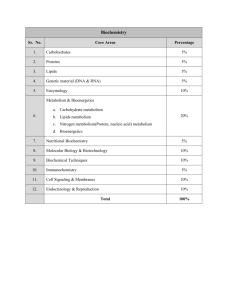
10. lipids metabolism ii
advertisement

6-YEAR MD PROGRAM TOPICS OF SEMINARS 6Y course BIOCHEMISTRY 2010/2011 http://biochemia.wum.edu.pl 1. PROTEINS 1. Amino acids structure and properties 2. Proteins classification and functions 3. Structure of proteins a) primary (peptide bonds) b) secondary (hydrogen bonds, - helix, - pleated sheet) c) tertiary (non-covalent and covalent bonds) d) quaternary 4. Structure of hemoglobin and myoglobin 5. Structure of insulin 6. Methods of proteins separation 7. Methods of molecular mass determination 8. Denaturation and coagulation processes (isoelectric point) 2 2. ENZYMES 1. General characteristic of enzymes 2. Exergonic and endergonic reactions 3. Coenzymes and prosthetic groups 4. Classification of enzymes 5. Mechanism of enzyme action a) energy changes b) enzyme specificity c) active site d) enzyme-substrate interactions (lock-and-key and induced fit mechanisms) 6. Factors affecting reaction velocity a) enzyme and substrate concentrations b) enzyme affinity for substrate (V max, Km) c) temperature d) pH e) modulators 7. Types of inhibition 8. Regulation of enzyme activity 9. Isoenzymes 3 3. ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN, OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, KREBS CYCLE 1. Localization of electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation and Krebs cycle 2. Organization of electron transport chain a) NADH - coenzyme Q reductase complex b) succinate - Q reductase complex c) QH2 - cytochrome reductase complex d) cytochrome c oxidase complex 3. Inhibitors of electron transport 4. Mechanisms of oxidative phosphorylation a) chemical hypothesis b) conformational hypothesis c) chemiosmotic hypothesis 5. Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate a) pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex b) regulation of the PDH complex 6. Krebs cycle, role (anabolic and catabolic), reactions and regulation 7. Generation of ATP from glucose 4 4. NUCLEIC ACIDS. CHROMATIN STRUCTURE. DNA REPLICATION, MUTATIONS, DNA REPAIR. 1. DNA and RNA primary structure 2. Cellular organization of DNA molecule a) higher order chromatin structure and the role of histones b) nucleosome core particle. The role of non-histone proteins 3. DNA replication a) substrates: dATP, dGTP, dCTP, dTTP - high energy bonds necessary for biosynthetic reactions b) mechanism and enzymes engaged in DNA replication bacterial and eukaryotic DNA polymerases, topoisomerases, helicases, single strand binding proteins, primase c) the leading versus the lagging strand. Okazaki fragments correction of mistakes by proofreading capability of DNA polymerases 4. Mutations - definition, types of mutations 5 5. TRANSCRIPTION. TRANSLATION. 1. Enzymatic synthesis of RNA upon DNA templates (Transcription) a) prokaryotic and Eukaryotic RNA polymerases b) initiation, elongation, termination c) poly- and monocistronic mRNA d) operons 2. Structure of RNA molecules (mRNA, rRNA, tRNA) 3. Post-transcriptional modifications a) splicing (introns and exons) b) modification of 5' and 3' end 4. Protein synthesis (Translation) a) genetic code b) structure of ribosomes, tRNA and mRNA c) initiation, elongation and termination of translation in Pro- and Eukaryotes d) post-translational modification of proteins. e) synthesis of membrane-bound and secretory proteins - signal peptides 5. Antibiotics affecting prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation. 6 6. REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION. VIRUSES. 1. Control of gene expression in Prokaryotes (lactose operon) 2. Control of gene expression in Eukaryotes a) chromosomal activation (hetero- and euchromatine) b) regulation of transcription initiation - DNA regulatory sequences (promoter, enhancer) - transcription factors (zink-finger structure) - small molecular weight effectors, e.g. steroid hormones - other effectors (e.g. differential splicing, mRNA degradation) 3. Viruses a) replication of viral genome – comparison of DNA and RNA viruses. b) interferon as a defense against viral infection – application in medicine MCQ TEST I: PROTEINS, ENZYMES, ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN, KREBS CYCLE, NUCLEIC ACIDS, PROTEIN BIOSYNTHESIS, VIRUSES 7 7. CARBOHYDRATES I 1. Chemical structure of carbohydrates 2. Phosphorylation of carbohydrates 3. Biosynthesis of "active glucose" (UDPG) 4. Glucose metabolism - glycolysis - fermentation - gluconeogenesis - pentose phosphate pathway 5. Cori cycle and glucose/alanine cycle 6. Galactose metabolism and its genetic disorders 7. Fructose metabolism and its disorders 8. Central role of glucose-6-phosphate in metabolism of carbohydrates 8 8. CARBOHYDRATES I I 1. Glycogen structure and storage 2. Glycogen metabolism - glycogenesis - glycogenolysis - regulation - glycogen storage defects (van Gierke and Pompe’s diseases) 3. Biosynthesis and metabolic importance of glucuronic acid 4. Glycosaminoglycans (mucopolisaccharidoses) 5. Proteoglycans 6. Glycoproteins (blood group substances) 7. Glycolipids 8. Hormonal regulation of blood glucose level and its disorders (diabetes mellitus) ASSESSMENT TEST II (written): CARBOHYDRATES 9 9. METABOLISM OF LIPIDS I 1. Lipid structure and classification - fatty acids - triacylglyceroles - glycerophospholipids - sphingolipids - steroids 2 . Digestion of lipids and absorption from gastrointestinal tract 3. Degradation of saturated, unsaturated and essential fatty acids (ß-oxidation) 4. Fatty acids biosynthesis 5. Ketogenesis 6. Central role of acetyl-CoA in metabolism 8. Generation of ATP from fatty acids 10 10. LIPIDS METABOLISM II 1. Biosynthesis of triacylglyceroles: - in liver and in adipose tissue 2. Phospholipids and sphingolipids – structure and biosynthesis 3. Prostaglandins and related compounds 4. Steroid metabolism: - synthesis of cholesterol and its regulation - cholesterol catabolism: bile acids, coprostanol - synthesis of steroid hormones - synthesis and function of vitamin D 5. Blood lipoproteins - classification and structure - synthesis and circulation between tissues ASSESSMENT TEST III (written): LIPIDS 11 11. UREOGENESIS, AMINO ACIDS METABOLISM 1. Protein turnover 2. Nitrogen balance 3. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids 4. Transamination: aminotransferases, role of pyridoxal phosphate 5. Oxidative deamination: glutamate dehydrogenase, amino acid oxidase 6. Decarboxylation, role of pyridoxal phosphate (physiologically active products) 7. Ammonia detoxification in liver (ureogenesis) and in brain (glutamine synthesis) 12 12. CATABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS 1. Metabolism of Gly (one-carbon units), Ala, Cys (PAPS, GSH, -glutamyl cycle), Met (SAM, polyamines), Arg, Pro, His, Phe & Tyr (catecholamines, melanine, thyroxine), Try, branched-chain AAs 2. Biosynthesis of creatine phosphate 3. Defects in amino acid metabolism 13 13. BLOOD 1. Functions of blood 2. Blood chemical constituents 3. Plasma proteins: albumin and globulins 4. Diagnostic proteins 5. Hemoglobin: different forms, their structure and properties 6. Heme biosynthesis 7. Genetic disorders of heme biosynthesis (porphyries) 8. Catabolism of heme 9. Biological function of hemoglobin: oxygen and carbon dioxide transport: - oxygen-binding curve - effects of pH, CO2, 2,3-DPG and temperature on hemoglobin oxygenation 10. Transport of CO2 (bicarbonate, carbamino compounds, CO2) 11. Maintenance of acid-base balance 12. Acidosis and alkalosis 14 14. VITAMINS 1. Definition, classification, sources, deficiency 2. Structure and functions of water-soluble vitamins - vitamins B-complex: Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, Biotin, Pantothenic acid, Folic acid, Vit12, Pyridoxine - - vitamin non-B-complex: vitamin C 3. Structure and function of fat-soluble vitamins - retinol (vit. A) - provitamins, role in vision - cholecalciferol (vit.D3) - sources, role in calcium metabolism - vitamin K (phylloquinones, memaquinones) - role in blood coagulation - -tocopherol (vit.E) - role in protection against peroxidases 15 15. RECEPTORS AND HORMONES 1. Types of receptors and role in hormonal signals transduction 2. Mechanism of action and metabolic effects of: a) peptide hormones: insulin, glucagon, calcitonin, PTH b) amino acid derived hormones: T4, T3, epinephrine c) steroid hormones: - glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, estrogens. - vitamin D3 (calcitriol) d) vit. A (retinoic acid) 16 16. LIVER METABOLISM AND BIOTRANSFORMATION 1. Metabolic pathways in the liver - metabolism of carbohydrates (glycogen storage) and lipids - lipoproteins synthesis, cholesterol (bile acids), proteins (plasma protein synthesis, urea cycle) - ketogenesis - catabolism of hemoglobin (bilirubin uptake, iron) - vitamins: A (storage), D3 (activation) 2. Detoxification in liver (ammonia, bilirubin, xenobiotics) 3. Enzymatic biotransformation: - phase I reactions (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) - phase II reactions (conjugation: sulfation, methylation, glucuronidation, acetylation, conjugation with glutathione and conjugation with amino acids) 4. Ethanol catabolism and effects on cell metabolism M C Q T E S T I V: A A S , N UC L E O T I DE S , B L O O D, H O R MO NE S , VI T A MI N S , M E T AB O L I S M O F L I VE R A N D K I DN E Y , B I O T RA NS F O RM A T I O N 17 Basic textbooks: 1. R.K. Murray, D.K. Granner, P.A. Mayers, V.W. Rodwell, Harpers’ Biochemistry, last edition, 1996, Appleton & Lange. 2. L. Stryer, Biochemistry, last edition, W.H. Freeman & Company, New York. 3. G. Meisenberg, W.H. Simmons, Principles of Medical Biochemistry, Elsevier, 2nd Edition 2006, (online access + interactive extras, studentconsult.com). 4. J.W. Baynes, M.H. Dominiczak, Medical Biochemistry, Elsevier, 3rd Edition 2009, (online access + interactive extras, studentconsult.com). 5. P.C. Champe, R.A. Harvey, Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry, I.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia. Complementary textbooks: T.M. Devlin, Textbook of Biochemistry with clinical correlations, WilleyLiss, Inc. last edition. 18