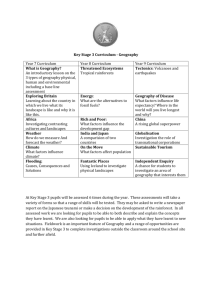
110-S09syllabus_1
advertisement
Fall 2009 Prof. R. Walker GSI: Katy Guimond Department of Geography Univ of California, Berkeley CCN 36490 COURSE SYLLABUS: Geography 110/C110/ISF101 Economic Geography of the Industrial World In this class, we look at the geographic side of economic life and modern industry in the advanced capitalist world. Geography is an indelible part of all economic processes, whether production, consumption, trade, finance or extraction (though sorely neglected in traditional economic theory). It rears its head in the siting of factories, multinational corporations, global trade, the design of malls, subcontracting networks, immigration, the shape of cities, international currency exchange, and much more. It comes into play at all scales, from the location of an office park and build-up of Silicon Valley to the European Union and trans-Pacific manufacturing systems. While probing the geographic dimension, we will also engage such fundamental economic questions as: what causes growth? is the consumer sovereign? is technology the key? what are the wages of labor? when are resources obsolete? what is the value of a dollar? Nor will we forget to spice things up with classic problems of political economy: inequality, national rivalry, warfare, imperialism, class conflict, and the like. Lectures Tuesday-Thursday 2:00 - 3:30 in141 McCone Hall. Attendance is required: lectures are where the principal themes of the course are introduced. Powerpoints will NOT be available, so if you miss class you miss a lot. No reading, chatting, sleeping or web-surfing in class! Sections Sections offer a valuable supplement to the lectures; they are used to discuss readings closely, review lectures, and prep you for exams. Unfortunately, budget cuts have taken away our second GSI, so they will have to be voluntary this year. 101 102 103 T 11-12 W 9-10 W 2-3 135 McCone 135 McCone 135 McCone Sections begin Second Week. Examinations Midterm and final. Your choice of in-class or take-home exams -- a low-anxiety system where you can take the exam or walk out and do the take-home within 48 hours. Same exam, different curves. Exams cover lecture and reading material. Exams are open book, open note. Grading: Final 2/3, midterm 1/3. Students with Disabilities or Special Needs: Please bring these to our attention and we will do our best to accommodate you. 2 Office Hours and Access Prof. Walker, W 2-4, room 599 McCone. Sign-up ahead of time on the door. Email: walker@berkeley.edu. Katy Guimond Office hours: W 10:30-11:30, room 583 McCone Email: cguimond@berkeley.edu Webbing The course has its own webpage on bspace.berkeley.edu, where the syllabus, resources and announcements will be posted. The course will also be available on podcasts @webcast.berkeley.edu/courses Readings Readings are an essential complement to lectures and sections, going over the same ground but also amplifying ideas, filling out the picture and providing more empirical evidence. You are not expected to remember everything for exams, but you are expected to be able to answer exam questions that refer to the books. A reading schedule will be distributed in class & section, and posted on the webpage. You are expected to keep up with the readings. There is too much to try to do it at the last minute! So if you're not serious about doing the readings, please don't enroll in the course. Required Books: Kevin Phillips, 2009. Bad Money: Reckless Finance, Failed Politics, and the Global Crisis of American Capitalism. New York: Viking Press. (second edition) Amsden, Alice. 2007. Escape from Empire: The Developing World’s Journey Through Heaven and Hell. Cambridge: MIT Press. Harvey, David. 2005. A Brief History of Neo-Liberalism. New York: Oxford University Press. Fields, Gary. 2004. Territories of Profit: Communications, Capitalist Development and the Innovative Enterprises of G.F. Swift and Dell Computer. Stanford University Press. Schlosser, Eric. 2001. Fast Food Nation: The Dark Side of the All-American Meal. Boston: HoughtonMifflin. Prudham, Scott. 2005. Knock on Wood: Nature as Commodity in Douglas Fir Country. London & New York: Routledge. Books are available at ASUC bookstore, Ned’s, and on 2 hr reserve at McCone Library 3 Geography 110 Fall 2009 Part I. THE RESTLESS GLOBE 8/27 1. The Great Recession & Economic Geography 9/1 2. Global Industrialization 9/3 3. The Rise of the Rest Part II. TERRITORY AND POLITICAL ECONOMY 9/8 4. States & Political Economy 9/10 5. Comparative Capitalisms 9/15 6. Global Trade & Neoliberalism 9/17 7. Empire & Global Economy 9/22 & 24 -- Professor away. NO CLASS. Part III. WORLDS OF PRODUCTION 9/29 8. Localized Industry 10/1 9. Globalized Industry 10/6 10. Flow & Logistics 10/8 11. Cities & Regions 10/13 12. Competition & Technology MIDTERM EXAM 10/15 Midterm Part IV. RETAIL, FINANCE & BUSINESS GEOGRAPHY 10/20 13. Retailing 10/22 14. Banking & Finance Department of Geography Univ of California, Berkeley 4 10/27 15. Finance & Development xx. Financial Crisis (see opening lecture) 10/29 16. Business Organization Part V. WORKERS OF THE WORLD 11/3 17. Complex & Creative Labor 11/5 18. Class Struggle in the U.S.A. 11/10 19. Will Work for Fast Food 11/12 20. Fate of the Global Working Class Part VI. NATURAL RESOURCES 11/17 21. Nature & Industry 11/19 22. Resource Industries (campus strike day) 11/24 & 26 THANKSGIVING WEEK - NO CLASS 12/1 23. Energy Lifelines 12/3 24. Waste & Want FINAL EXAMINATION