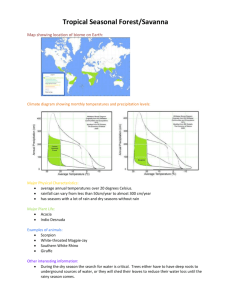
Asian Brown Cloud notes
advertisement
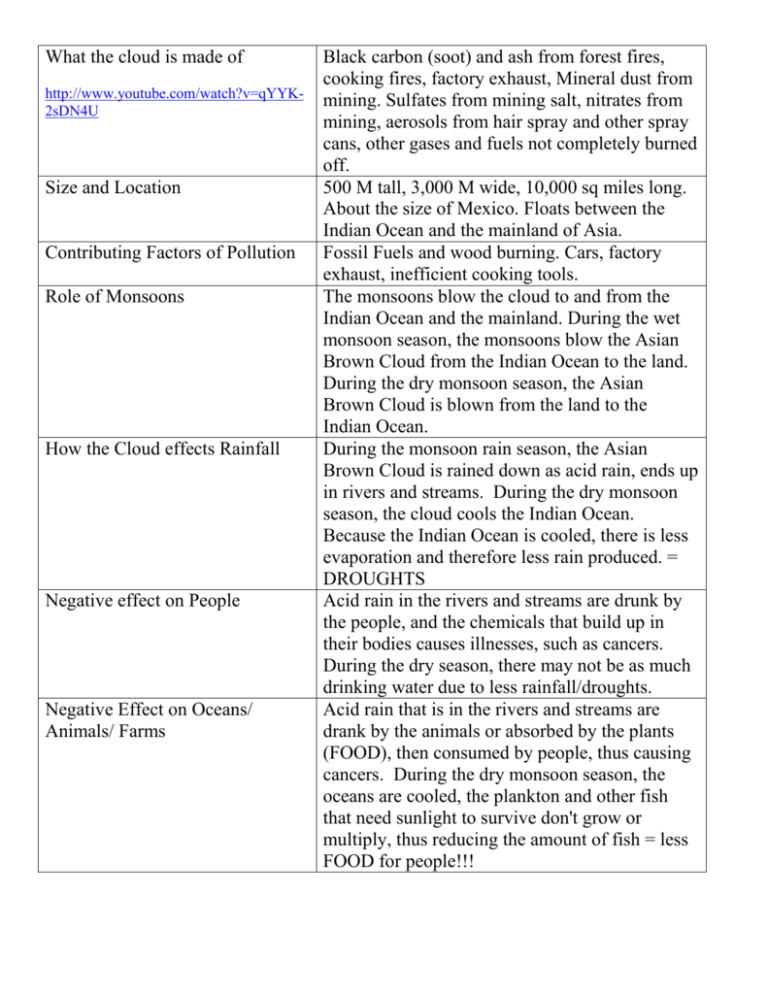
What the cloud is made of http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qYYK2sDN4U Size and Location Contributing Factors of Pollution Role of Monsoons How the Cloud effects Rainfall Negative effect on People Negative Effect on Oceans/ Animals/ Farms Black carbon (soot) and ash from forest fires, cooking fires, factory exhaust, Mineral dust from mining. Sulfates from mining salt, nitrates from mining, aerosols from hair spray and other spray cans, other gases and fuels not completely burned off. 500 M tall, 3,000 M wide, 10,000 sq miles long. About the size of Mexico. Floats between the Indian Ocean and the mainland of Asia. Fossil Fuels and wood burning. Cars, factory exhaust, inefficient cooking tools. The monsoons blow the cloud to and from the Indian Ocean and the mainland. During the wet monsoon season, the monsoons blow the Asian Brown Cloud from the Indian Ocean to the land. During the dry monsoon season, the Asian Brown Cloud is blown from the land to the Indian Ocean. During the monsoon rain season, the Asian Brown Cloud is rained down as acid rain, ends up in rivers and streams. During the dry monsoon season, the cloud cools the Indian Ocean. Because the Indian Ocean is cooled, there is less evaporation and therefore less rain produced. = DROUGHTS Acid rain in the rivers and streams are drunk by the people, and the chemicals that build up in their bodies causes illnesses, such as cancers. During the dry season, there may not be as much drinking water due to less rainfall/droughts. Acid rain that is in the rivers and streams are drank by the animals or absorbed by the plants (FOOD), then consumed by people, thus causing cancers. During the dry monsoon season, the oceans are cooled, the plankton and other fish that need sunlight to survive don't grow or multiply, thus reducing the amount of fish = less FOOD for people!!!