Soils and weathering
advertisement

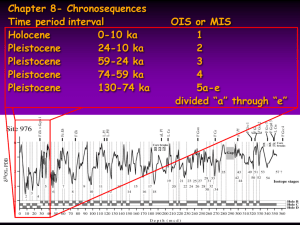
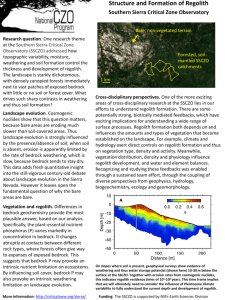
Soils and weathering • Soil: important resource, food, wood, etc. • Origin: weathering of regolith (fragmented bedrock) • 2 types weathering: physical and chemical • 4 ingredients: water, organic matter (humus), air (pores), minerals • 2 types: transported and no transport Factors controlling soil formation • Climate (humid or dry)- most important • Organic activity- e.g. worms • Relief of land • Parent rock (ign, met, sed) • Time (reaction rate) Weathering • Physical and chemical processes breakdown parent rock; operate together • Erosion: transportation of weathering products (ice, water, wind) • Residual soil: no transportation • Transported soils: water, ice Physical weathering • Important in dry climates • Breakdown of parent rock • Frost wedging (high latitudes) • Plant roots • Animals (worms): process 10 tons/acre/year) Chemical weathering • Important in humid climates (tropics) • 3 types of important chemical reaction (Table 6.1) • Solution: i) acid forms; ii) mineral dissolves • e.g. Limestone caves • Hydration and oxidation: addition of O and water. “rust” • Hydrolysis: breakdown of feldspar to clays Importance of clays in soils • Small size- large surface area • Adsorb water for plant roots • Attract nutrient ions: K+, Ca++, Mg++ etc • Too much clay: poor drainage • Too sandy: few nutrients, good drainage Rate of weathering • • • • • • • Temperature (climate) Grain size- smaller faster rates Environment (humid or dry) Mineral stability: Quartz (very stable), Feldspars (breakdown to clays) amphibole, pyroxene (Fe-Mg silicates) • Geologic features Spheroidal weathering: rectangular blocks become spherical (chemical weathering) • Exfoliation domes: uplift, erosion (physical weathering) Soils • Residual soils: develop from fragments of bedrock in place (regolith) • Transported soils: water, ice, wind • Glacial soils: glacial drift (water) • Loess (glacial origin; wind transport) • Mid-west breadbasket: Loess Soil profile • • • • • • Soil horizons: O, A, B, C O- organic rich (humus) A- leached zone B- accumulation zone C- weathered bedrock (regolith) Horizon thickness may vary (e.g. desert, no A zone, thick B zone)