Bachelor of Engineering with Honours
advertisement
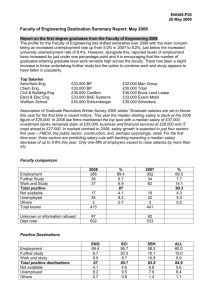
Faculty of Engineering Graduate Profile Bachelor of Engineering with Honours 2009 Introduction The Graduate Profile is a statement of the generic and specific attributes and skills of graduates of the programme including the body of knowledge attained (CUAP Functions and Procedures, 20132014). The framework for graduate outcomes in the Graduate Profile may vary depending on the award, however attention should be paid to the development in graduates of lifelong learning skills. A Graduate Profile may contain the personal attributes, interactive attributes and specific programme attributes which should ideally be displayed by graduates. Bachelor of Engineering with Honours This graduate profile is based on the information which IPENZ requires institutions must provide evidence that graduates have achieved the following attributes. Life-long Learning Skills and Attributes of Graduates Graduates can: understand and apply the mathematical and engineering sciences to one or more of the broad, general engineering disciplines; 2 formulate and solve models that predict the behaviour of part or all of complex engineering systems, using first principles of the fundamental engineering sciences and mathematics; synthesise and demonstrate the efficacy of solutions to part or all of complex engineering problems2 Complex engineering problems have some or all of the following characteristics: Involve wide-ranging or conflicting technical, engineering, and other issues; Have no obvious solution and require originality in analysis; Involve infrequently encountered issues; Are outside problems encompassed by standards and codes of practice for professional engineering; Involve diverse groups of stakeholders with widely varying needs; Have significant consequences in a range of contexts; Cannot be resolved without in-depth engineering knowledge. recognise when further information is needed and be able to find it by identifying, evaluating and drawing conclusions from all pertinent sources of information, and by designing and carrying out experiments; understand the accepted methods of dealing with uncertainty (such as safety factors) and the limitations of the applicability of methods of design and analysis and identify, evaluate and manage the physical risks in complex engineering problems; function effectively in a team by working co-operatively with the capacity to become a leader or manager; communicate effectively, comprehending and writing effective reports and design documentation, summarising information, making effective oral presentations and giving and receiving clear oral instructions; understand the role of engineers and their responsibility to society by demonstrating an understanding of the general responsibilities3 of a professional engineer; understand and apply project and business management, recognising and using the appropriate project and business management principles and tools for complex engineering problems; Demonstrate competence in the practical art of engineering in their area of specialisation by showing in design an understanding of the practical methods for the construction and maintenance of engineering products, and using modern calculation and design tools competently for complex engineering problems. This Graduate Profile is reviewed annually and was last reviewed in 2013. 3 General responsibilities of an engineer include: Social responsibilities including ethics, health and safety and other legislation Cultural responsibilities including, in New Zealand, the Treaty of Waitangi Environmental responsibilities including the need for sustainable development and design and legislative responsibilities Life long learning 2














![[Name of Graduate Degree] Notice of Intent [Date]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010441941_1-32bcab2438933ff9dca6fc65d3590ba9-300x300.png)