Current Electricity
advertisement

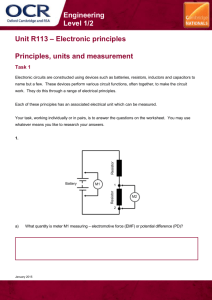
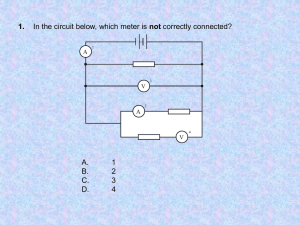
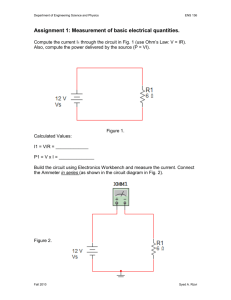
Current Electricity Test Review Key I. Matching: Match the terms and definitions _E__ 1. Ampere _H__ 2. Battery _K__ 3. Potential Difference _B__ 4. Capacitance (Pre-AP) _M__ 5. Electric Current _G__ 6. Capacitor _J__ 7. Electric Circuit _N__ 8. Schematic Diagram _A__ 9. Dielectric (Pre-AP) _D__ 10. Resistance _L__ 11. Voltmeter _F__ 12. Power _C__ 13. Ammeter _I__ 14. Ohmic Conductor A. An insulator separating two plates of a capacitor. B. The ratio of the charge on a body to its potential. C. A device that measures the current flowing through a point in the circuit. D. The opposition to current flow. E. A measure of the electric current in Coulombs per second F. The rate at which energy is transmitted. G. A device where electrical energy is stored. H. An example of a voltage source. I. A conductor which follows Ohm’s Law. J. A continuous path through which electric current flows. K. The difference in electric potential energy between two points in a circuit. L. A device that measures the potential difference across two points in a circuit. M. A flow of charged particles. N. This diagram represents the components of an electric circuit. 1. The direction of current flow in a circuit is said to be from the _positive_ terminal to the _negative_ terminal of a battery. Charges move because of a _potential__ difference. This flow of charges is called a __current__. 2. The charges that move in a circuit are those already found in the _atoms_ of the circuit. These charges move at a drift velocity of approximately _1 - 5__ mm/s (answers vary depending on textbook). 3. All capacitors are made of two __parallel or conducting__ plates separated by an insulator called a _dielectric_. The two conductors have (identical / opposite) charges. 4. What 3 things are necessary to make an electric circuit and what is their function in the circuit? Voltage source – provides the “push” or potential difference Conductor – provides the complete path Load – uses the electricity 5. Voltmeters are connected in _parallel_. Ammeters are connected in _series__. In the circuit below, add a voltmeter that will tell the potential difference across the resistor and an ammeter that will tell the current flowing through the resistor. V A 6. As a charge moves through resistors in a circuit, its potential energy is _reduced_. The energy used as the charge moves around the remainder of the circuit is _equal____ to the amount of work done to give the charge its initial energy. Therefore, the total voltage drop going around the circuit is __equal__ to the amount of potential difference supplied by the battery. 7. Resistance is the __opposition__ to the electric current. It is also the ratio of __voltage or potential difference__ across it to the ___current____ through it. 8. List four factors that affect the resistance of a wire and explain whether each is directly or inversely related to the resistance of the wire. Temperature - directly Resistivity (nature of the material) - directly Length - directly Cross Sectional Area - inversely 9. To create a wire with the least resistance would be made out of a material with a (high / low) resistivity, (long / short) length of the material, have a (large / small) diameter, and be at a (high / low) temperature. 10. To have the greatest current flow through a circuit, you want to have a (high / low) potential difference and a (high / low) resistance. Therefore, current and voltage are (directly / inversely) related whereas current and resistance are (directly / inversely) related. III. Identify the Parts of a Circuit: V _Battery__ __resistor__ lamp or light or bulb wire or conductor voltmeter_ A _ammeter_ V. Solve the following problems: 1. If you have a current flowing through a resistor of 5 Amps, how many Coulombs of charge pass through the resistor in 10 seconds? 5 = q / 10 q = 50 C 2. What is the capacitance of a capacitor with a charge of 50 microCoulombs when it is connected across a 220 V source? (Pre-AP) 50x10-6 = C(220) C = 2.27 x 10-7 F 3. How much energy is stored in a capacitor of 50 microFarads which has been connected to 120 V? (Pre-AP) W = 0.5 x (50x10-6)(1202) = 0.36 J 4. What is the resistance of a copper wire that is 1000 cm long and 0.81 mm in diameter at 20oC? (Resistivity is 1.724 x10-5 mm) (Pre-AP) A = (3.14)(0.81/2)2 R= (1.724 x10-5)(10000) / (0.515) R = 0.33 Ohms 5. A 15 Ohm resistor is connected to a 50 V battery. What is the current in the resistor? I = 50 / 15 I = 3.3A 6. A current of 5 A flows through a 50 Ohm resistor for 2 hours. How much energy is generated? 5 = V / 50 V = 250 P = 250(5) = 1250 W 1250 = W / (20 x 60 x 60) W = 9 x 106 J